Active and passive immunity explainedin this comprehensive guide on... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
25
•
Dec 16, 2025
•
Active and passive immunity explainedin this comprehensive guide on... Show more



This page delves into the mechanics of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly the mRNA vaccines developed by Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech. It also introduces the concept of herd immunity.
The mRNA vaccines use lipid nanoparticles to deliver genetic instructions for producing the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. This triggers an immune response, preparing the body to fight off future infections.
Vocabulary: Herd immunity is a form of indirect protection from infectious diseases that occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population becomes immune, reducing the likelihood of infection for non-immune individuals.
Key features of a successful vaccination program include:
Highlight: Herd immunity helps protect vulnerable groups who cannot be vaccinated by reducing the overall spread of the virus in the population.

This page further explores herd immunity and addresses controversies surrounding vaccines, particularly the MMR vaccine.
Herd immunity against measles requires about 95% of a population to be vaccinated. The remaining 5% are protected by the reduced spread of the disease among vaccinated individuals.
Example: The MMR vaccine, which protects against measles, mumps, and rubella, is 97% effective.
Highlight: A controversial 1998 study suggested a link between the MMR vaccine and autism. However, the vast majority of scientists have since discredited this claim.
The page emphasizes the importance of widespread vaccination to achieve herd immunity and protect vulnerable populations who cannot be vaccinated.
Quote: "With herd immunity, the vast majority of a population are vaccinated, lowering the overall amount of virus able to spread in the whole population."
This comprehensive overview underscores the critical role of vaccines in public health and the ongoing importance of scientific research in addressing vaccine safety and efficacy.

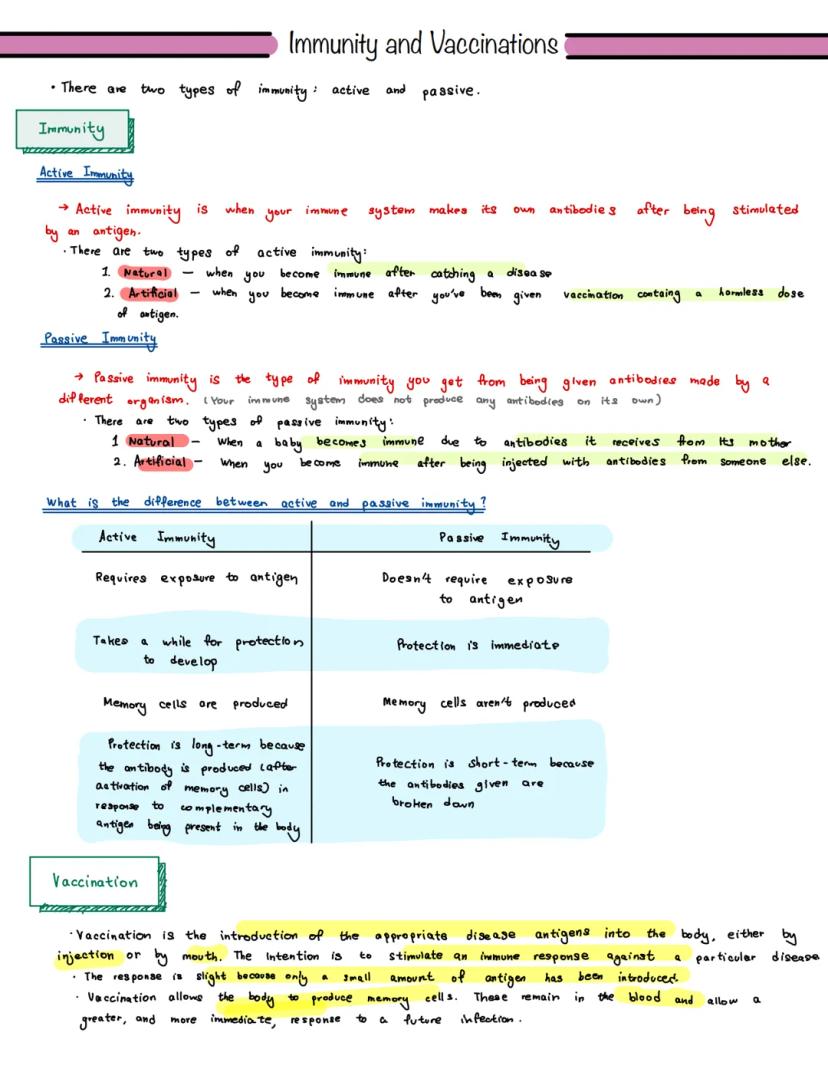
This page introduces the key concepts of active and passive immunity, highlighting their differences and mechanisms.
Active immunity occurs when the body's immune system produces antibodies in response to an antigen. There are two types:
Passive immunity involves receiving pre-made antibodies from another source. It can be:
Definition: Vaccination is the introduction of disease antigens into the body to stimulate an immune response against a particular disease.
Highlight: Active immunity produces memory cells, leading to long-term protection, while passive immunity offers immediate but short-term protection.
Example: The COVID-19 vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, stimulate active immunity by introducing harmless versions of the virus's spike protein.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Active and passive immunity explained in this comprehensive guide on immunity and vaccinations, covering how COVID-19 vaccines like Moderna and Pfizer work, as well as the benefits of vaccinations and herd immunity.
Key points:

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page delves into the mechanics of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly the mRNA vaccines developed by Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech. It also introduces the concept of herd immunity.
The mRNA vaccines use lipid nanoparticles to deliver genetic instructions for producing the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. This triggers an immune response, preparing the body to fight off future infections.
Vocabulary: Herd immunity is a form of indirect protection from infectious diseases that occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population becomes immune, reducing the likelihood of infection for non-immune individuals.
Key features of a successful vaccination program include:
Highlight: Herd immunity helps protect vulnerable groups who cannot be vaccinated by reducing the overall spread of the virus in the population.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page further explores herd immunity and addresses controversies surrounding vaccines, particularly the MMR vaccine.
Herd immunity against measles requires about 95% of a population to be vaccinated. The remaining 5% are protected by the reduced spread of the disease among vaccinated individuals.
Example: The MMR vaccine, which protects against measles, mumps, and rubella, is 97% effective.
Highlight: A controversial 1998 study suggested a link between the MMR vaccine and autism. However, the vast majority of scientists have since discredited this claim.
The page emphasizes the importance of widespread vaccination to achieve herd immunity and protect vulnerable populations who cannot be vaccinated.
Quote: "With herd immunity, the vast majority of a population are vaccinated, lowering the overall amount of virus able to spread in the whole population."
This comprehensive overview underscores the critical role of vaccines in public health and the ongoing importance of scientific research in addressing vaccine safety and efficacy.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page introduces the key concepts of active and passive immunity, highlighting their differences and mechanisms.
Active immunity occurs when the body's immune system produces antibodies in response to an antigen. There are two types:
Passive immunity involves receiving pre-made antibodies from another source. It can be:
Definition: Vaccination is the introduction of disease antigens into the body to stimulate an immune response against a particular disease.
Highlight: Active immunity produces memory cells, leading to long-term protection, while passive immunity offers immediate but short-term protection.
Example: The COVID-19 vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, stimulate active immunity by introducing harmless versions of the virus's spike protein.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
1
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Notes on blood and what it does for the body for anatomy and physiology.
DNA RNA and Proteins
for quiz
This study note will give an explanation of how protein Synthesis was used in our body and its steps.
DNA & Protein Synthesis is to help students to learn and understand what is DNA and how it is made.
Notes on bacteria- honors biology
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user