AP Psychology Motivation and Emotion: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide... Show more
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
301
•
Dec 22, 2025
•
AP Psychology Motivation and Emotion: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide... Show more









This page delves into various motivational theories for AP Psychology, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of different perspectives on what drives human behavior.
The section begins by defining needs as physiological necessities for survival, such as food, water, sleep, and air. It then introduces the concept of drives, which are aroused tension states when a need is not met.
Vocabulary: Primary drives are physiological, while secondary drives, like the desire for money, are learned to satisfy primary needs.
Several key theories are discussed:
Example: Survival instincts and maternal instincts are examples of behaviors explained by instinct theory.
Drive Reduction Theory: This theory suggests that physiological needs create aroused tension states (drives) that motivate organisms to satisfy those needs.
Incentive Theory of Motivation: This theory focuses on how positive or negative environmental stimuli can motivate behavior.
Homeostasis: The tendency to maintain a balanced internal state is introduced as a key concept in understanding motivation.
Definition: Homeostasis is the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry around a particular level.
Understanding these theories is crucial for success in the AP Psychology unit 7 motivation, emotion, and personality Practice Test.

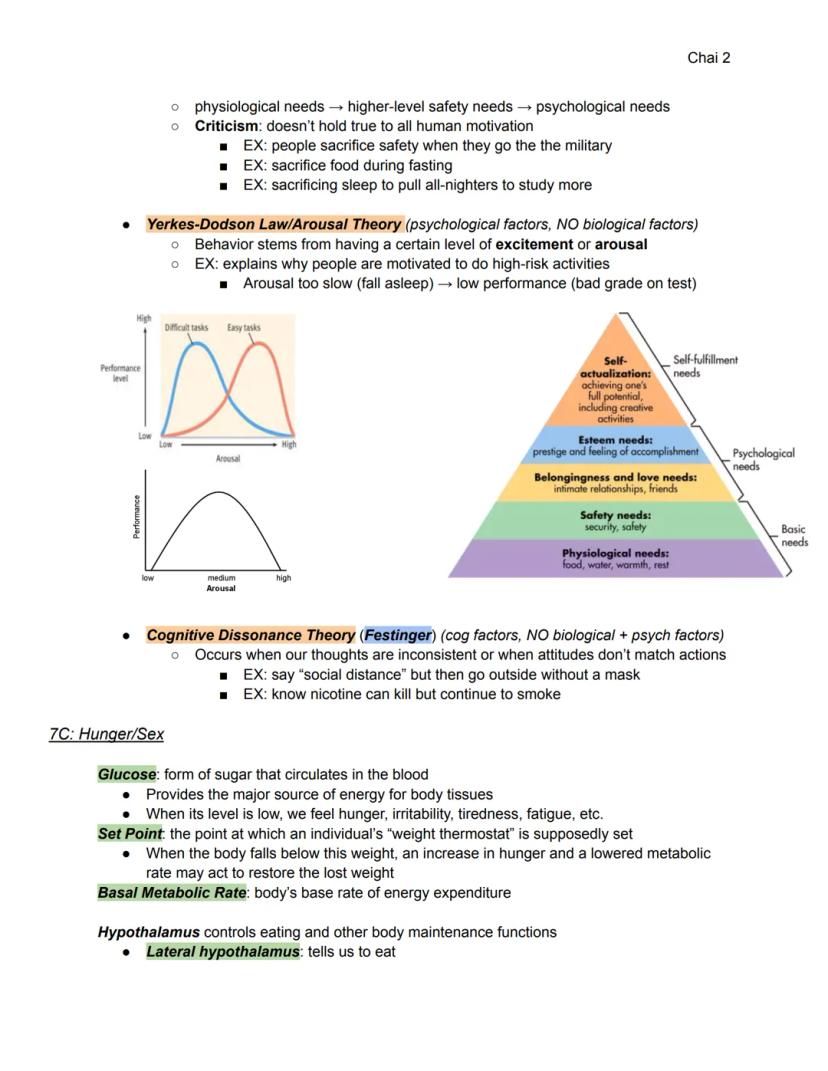
This page continues the discussion of motivational theories, focusing on the Yerkes-Dodson Law (Arousal Theory) and Cognitive Dissonance Theory.
The Yerkes-Dodson Law, also known as Arousal Theory, is a psychological concept that relates performance to arousal levels:
Highlight: The Yerkes-Dodson Law suggests that there is an optimal level of arousal for performance, which varies depending on the difficulty of the task.
The theory is illustrated with a graph showing how performance changes with arousal levels for both easy and difficult tasks. This concept is crucial for understanding how motivation affects performance in various situations.
Example: Low arousal might lead to falling asleep during a test, resulting in poor performance.
The page then introduces Cognitive Dissonance Theory, developed by Festinger:
Definition: Cognitive dissonance occurs when our thoughts are inconsistent or when attitudes don't match actions.
Example: Knowing the importance of social distancing but going outside without a mask is an instance of cognitive dissonance.
The page also touches on hunger motivation, introducing key concepts such as glucose and its role in energy regulation:
Vocabulary: Glucose is a form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues.
Definition: Set point is the point at which an individual's "weight thermostat" is supposedly set.
Vocabulary: Basal Metabolic Rate refers to the body's base rate of energy expenditure.
These concepts are essential for the AP Psych motivation and emotion study guide and will likely appear in AP psychology motivation and emotion practice tests.

This page delves deeper into the physiological and psychological factors influencing hunger and introduces the concept of sexual motivation.
The role of the hypothalamus in controlling eating is explained:
Highlight: The lateral hypothalamus tells us to eat, while the ventromedial hypothalamus signals us to stop eating.
The page provides a comprehensive list of appetite hormones and their functions:
Psychological factors influencing eating behavior are also discussed:
Vocabulary: Externals are motivated by the attractiveness or availability of food, while internals are less affected by these factors and listen more to internal cues.
Definition: The Garcia Effect refers to a classically conditioned aversion to certain foods.
The page concludes with an introduction to sexual motivation:
Highlight: Sex is a physiologically based motive but is significantly affected by learning and values.
The work of Alfred Kinsey in sexology is mentioned, and the sexual response cycle is introduced as having four stages of sexual responding.
This information is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between physiological and psychological factors in motivation, a key topic in AP psychology motivation and emotion notes and quizlets.







This section introduces fundamental concepts in motivation, emotion, and personality, which comprise 11-15% of the AP Psychology exam.
Motivation is defined as a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior. The guide distinguishes between two types of motivation:
Definition: Extrinsic motivation refers to motivation from external rewards such as grades, salary, or applause.
Definition: Intrinsic motivation comes from internal rewards like enjoyment, personal satisfaction, or fulfillment.
The concept of achievement motivation is introduced as a desire for significant accomplishment, mastery, or attaining high standards.
Vocabulary: Self-efficacy, a term coined by Bandura, refers to one's belief in their ability to accomplish a task.
An important phenomenon discussed is overjustification, where external rewards can decrease intrinsic motivation for an activity one already enjoys.
Example: Athletes who initially play a sport for enjoyment may experience decreased intrinsic motivation once they start getting paid for it.
This section provides a solid foundation for understanding the complex factors that drive human behavior and emotions, essential knowledge for the AP Psychology motivation and emotion practice test.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
AP Psychology Motivation and Emotion: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide covers key concepts in motivation, emotion, and personality for AP Psychology students. It explores various motivational theories, including drive reduction, incentive, and arousal theories, as well as hunger and... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page delves into various motivational theories for AP Psychology, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of different perspectives on what drives human behavior.
The section begins by defining needs as physiological necessities for survival, such as food, water, sleep, and air. It then introduces the concept of drives, which are aroused tension states when a need is not met.
Vocabulary: Primary drives are physiological, while secondary drives, like the desire for money, are learned to satisfy primary needs.
Several key theories are discussed:
Example: Survival instincts and maternal instincts are examples of behaviors explained by instinct theory.
Drive Reduction Theory: This theory suggests that physiological needs create aroused tension states (drives) that motivate organisms to satisfy those needs.
Incentive Theory of Motivation: This theory focuses on how positive or negative environmental stimuli can motivate behavior.
Homeostasis: The tendency to maintain a balanced internal state is introduced as a key concept in understanding motivation.
Definition: Homeostasis is the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry around a particular level.
Understanding these theories is crucial for success in the AP Psychology unit 7 motivation, emotion, and personality Practice Test.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page continues the discussion of motivational theories, focusing on the Yerkes-Dodson Law (Arousal Theory) and Cognitive Dissonance Theory.
The Yerkes-Dodson Law, also known as Arousal Theory, is a psychological concept that relates performance to arousal levels:
Highlight: The Yerkes-Dodson Law suggests that there is an optimal level of arousal for performance, which varies depending on the difficulty of the task.
The theory is illustrated with a graph showing how performance changes with arousal levels for both easy and difficult tasks. This concept is crucial for understanding how motivation affects performance in various situations.
Example: Low arousal might lead to falling asleep during a test, resulting in poor performance.
The page then introduces Cognitive Dissonance Theory, developed by Festinger:
Definition: Cognitive dissonance occurs when our thoughts are inconsistent or when attitudes don't match actions.
Example: Knowing the importance of social distancing but going outside without a mask is an instance of cognitive dissonance.
The page also touches on hunger motivation, introducing key concepts such as glucose and its role in energy regulation:
Vocabulary: Glucose is a form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues.
Definition: Set point is the point at which an individual's "weight thermostat" is supposedly set.
Vocabulary: Basal Metabolic Rate refers to the body's base rate of energy expenditure.
These concepts are essential for the AP Psych motivation and emotion study guide and will likely appear in AP psychology motivation and emotion practice tests.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This page delves deeper into the physiological and psychological factors influencing hunger and introduces the concept of sexual motivation.
The role of the hypothalamus in controlling eating is explained:
Highlight: The lateral hypothalamus tells us to eat, while the ventromedial hypothalamus signals us to stop eating.
The page provides a comprehensive list of appetite hormones and their functions:
Psychological factors influencing eating behavior are also discussed:
Vocabulary: Externals are motivated by the attractiveness or availability of food, while internals are less affected by these factors and listen more to internal cues.
Definition: The Garcia Effect refers to a classically conditioned aversion to certain foods.
The page concludes with an introduction to sexual motivation:
Highlight: Sex is a physiologically based motive but is significantly affected by learning and values.
The work of Alfred Kinsey in sexology is mentioned, and the sexual response cycle is introduced as having four stages of sexual responding.
This information is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between physiological and psychological factors in motivation, a key topic in AP psychology motivation and emotion notes and quizlets.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
This section introduces fundamental concepts in motivation, emotion, and personality, which comprise 11-15% of the AP Psychology exam.
Motivation is defined as a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior. The guide distinguishes between two types of motivation:
Definition: Extrinsic motivation refers to motivation from external rewards such as grades, salary, or applause.
Definition: Intrinsic motivation comes from internal rewards like enjoyment, personal satisfaction, or fulfillment.
The concept of achievement motivation is introduced as a desire for significant accomplishment, mastery, or attaining high standards.
Vocabulary: Self-efficacy, a term coined by Bandura, refers to one's belief in their ability to accomplish a task.
An important phenomenon discussed is overjustification, where external rewards can decrease intrinsic motivation for an activity one already enjoys.
Example: Athletes who initially play a sport for enjoyment may experience decreased intrinsic motivation once they start getting paid for it.
This section provides a solid foundation for understanding the complex factors that drive human behavior and emotions, essential knowledge for the AP Psychology motivation and emotion practice test.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
26
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user