Auditing is the systematic process of examining financial statements to... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Knowunity AI
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
309
•
Updated Feb 25, 2026
•
studywithnessa
@studywithnessa
Auditing is the systematic process of examining financial statements to... Show more




![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_1.webp&w=2048&q=75)
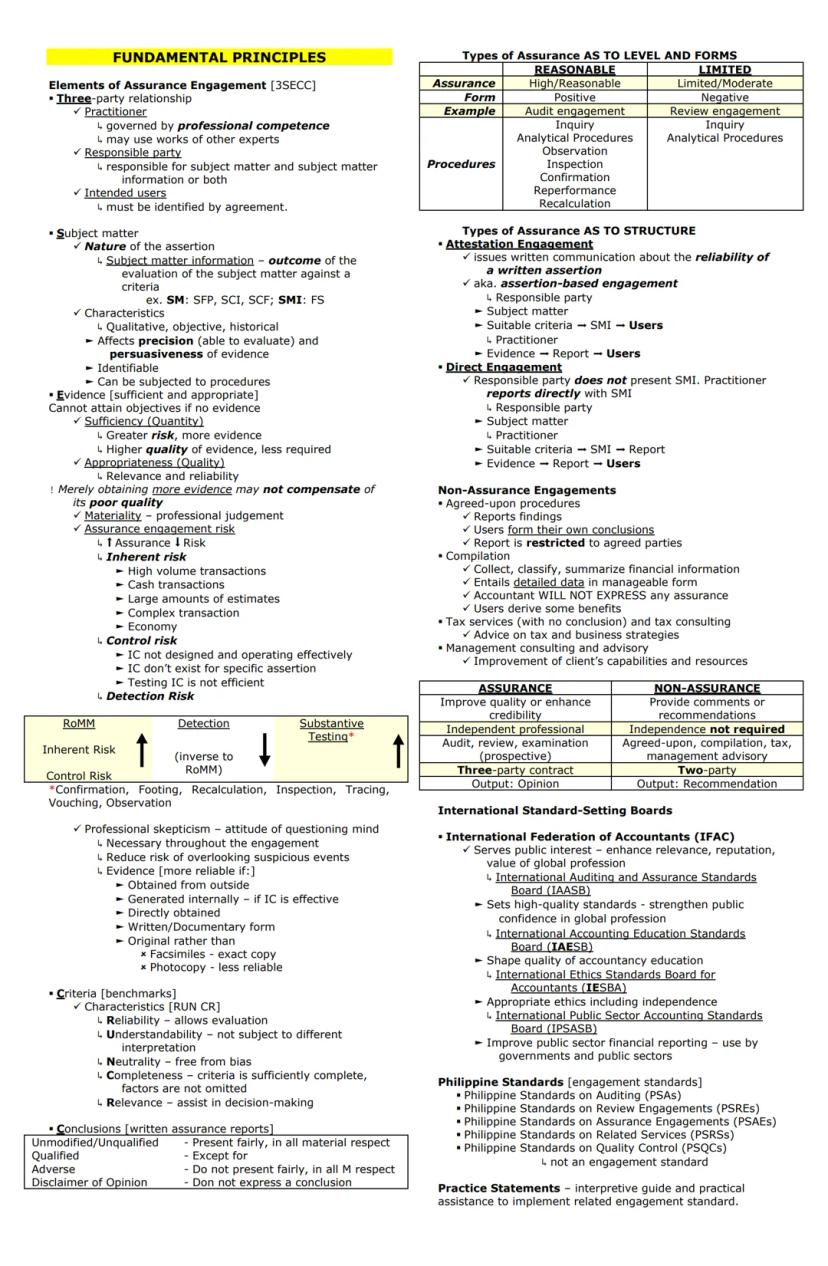
An assurance engagement involves three essential parties: the practitioner (governed by professional competence), the responsible party (accountable for the subject matter), and the intended users (identified by agreement).
The subject matter is what's being evaluated—like financial statements—while the subject matter information is the outcome of this evaluation against specific criteria. For example, in a financial audit, the financial statements themselves are the subject matter information.
When gathering evidence, auditors must consider both sufficiency (quantity) and appropriateness (quality). Remember that more evidence may be needed when risk is higher, but simply getting more low-quality evidence doesn't compensate for poor quality. Evidence is more reliable when:
Pro Tip: Professional skepticism is crucial throughout an engagement. Maintaining a questioning mindset helps you avoid overlooking suspicious circumstances and strengthens your ability to gather appropriate evidence.
Assurance engagements vary by level and structure. Reasonable assurance engagements (like audits) provide high assurance with positive opinions, while limited assurance engagements (like reviews) offer moderate assurance with negative opinions. The procedures differ significantly—audits require more extensive procedures beyond inquiry and analytics.
The structure can be either attestation-based (practitioner evaluates assertions made by the responsible party) or direct (practitioner directly reports on the subject matter).
Non-assurance engagements include agreed-upon procedures (reporting findings without conclusions), compilations (organizing financial information without assurance), tax services, and management consulting. These services don't provide the same level of confidence as assurance engagements.
Professional standards are established by various boards under the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC), with corresponding Philippine Standards covering auditing (PSAs), review engagements (PSREs), assurance engagements (PSAEs), related services (PSRSs), and quality control (PSQCs).
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_2.webp&w=2048&q=75)
A financial statement audit is a systematic process where auditors obtain and evaluate evidence about management's assertions to determine if they match established criteria. This verification process forms the backbone of financial reporting credibility.
The theoretical framework for audits rests on several key principles. Auditors must maintain their independence to provide objective opinions, and the reliability of financial statements increases with effective internal controls and consistent application of accounting policies.
Businesses require audits due to several factors that create demand:
Important: Companies with gross annual sales of ₱3 million or more (vatable businesses) must undergo BIR-required audits, while SEC requirements vary based on entity type and asset/liability thresholds.
When examining financial statements, auditors focus on specific assertions made by management. These are organized into three categories:
All audits face inherent limitations. These include sampling risk (testing only a portion of transactions), judgment limitations, internal control weaknesses, and evidence that is persuasive rather than conclusive.
The audit process follows a structured approach: preliminary engagement activities, planning, internal control evaluation, substantive testing, completion, report issuance, and post-audit responsibilities. Preliminary activities focus on client acceptance considerations, including the auditor's competence and independence, client integrity, and establishing audit preconditions through an engagement letter.
For recurring audits, new engagement letters aren't required unless significant changes have occurred in circumstances, terms, or management. If a client requests changing the engagement's nature, auditors must carefully evaluate whether there's reasonable justification before proceeding.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_3.webp&w=2048&q=75)
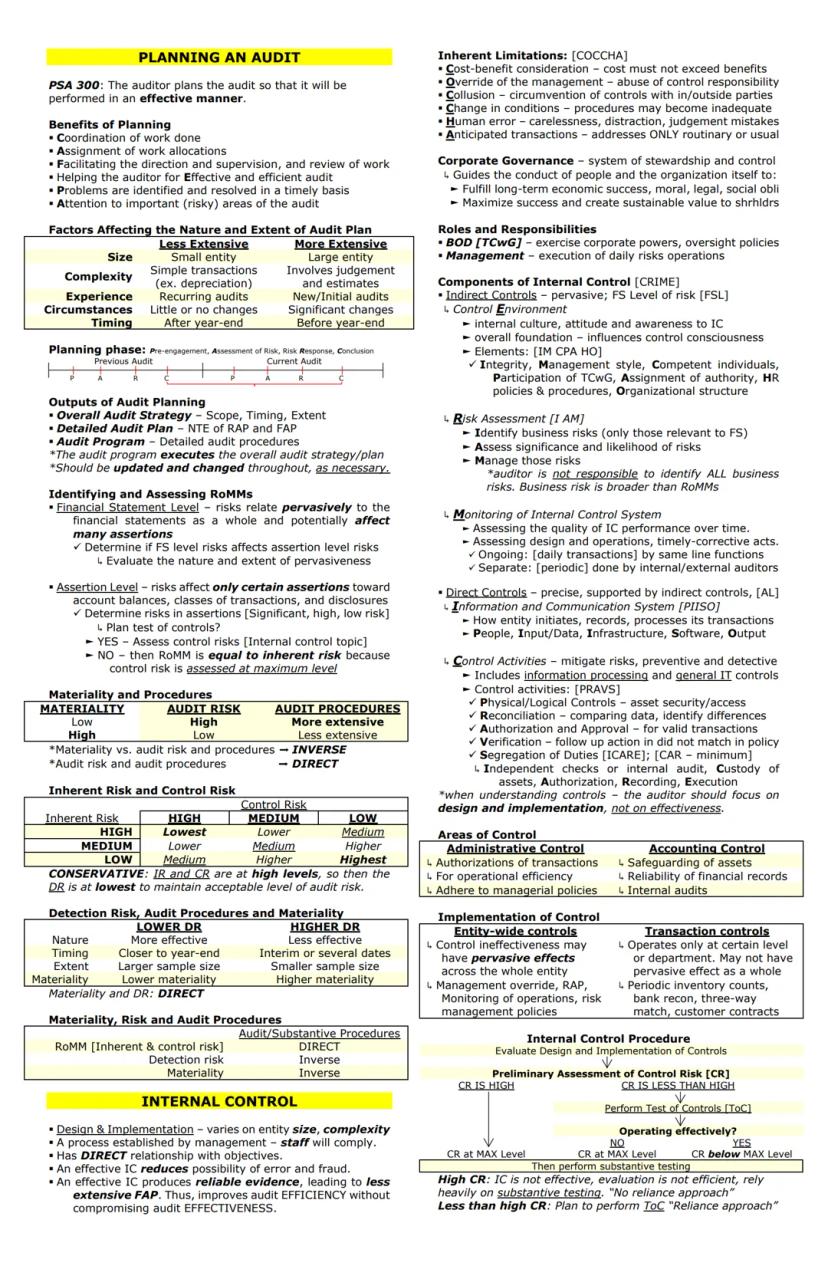
Planning is essential for an effective audit. According to PSA 300, proper planning helps coordinate work, assign responsibilities, facilitate supervision, and identify problems early. The nature and extent of planning varies based on the entity's size, complexity, prior experience with the entity, and circumstances.
The planning process produces three key outputs:
When identifying and assessing risks of material misstatements (RoMMs), auditors consider both:
Materiality directly impacts the extent of audit procedures. Lower materiality levels require more extensive procedures, while higher levels allow for less extensive testing. Remember this key relationship: materiality and audit risk have an inverse relationship, while audit risk and audit procedures have a direct relationship.
Remember: When control risk and inherent risk are both high, detection risk must be at its lowest level to maintain an acceptable overall audit risk. This means you'll need to perform more extensive substantive testing.
Internal control is a process established by management to provide reasonable assurance about operations, reporting, and compliance. Effective internal controls can significantly improve audit efficiency by allowing for reduced substantive testing.
Internal controls face inherent limitations (COCCHA):
The five components of internal control (CRIME) include:
After evaluating the design and implementation of controls, auditors make a preliminary assessment of control risk. If control risk is assessed at less than maximum, auditors perform tests of controls to confirm operating effectiveness. If controls aren't effective or it's inefficient to test them, the control risk is set at maximum, requiring more extensive substantive testing.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_4.webp&w=2048&q=75)
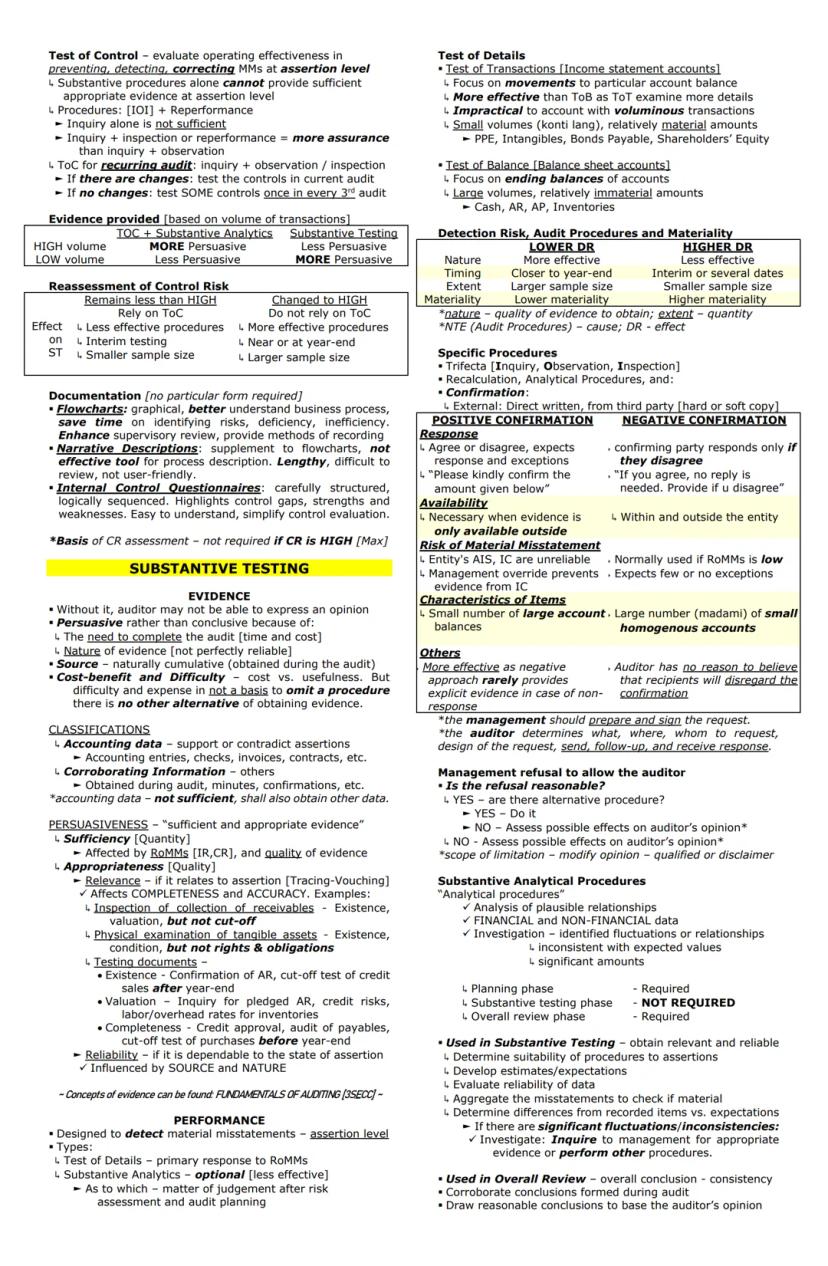
Tests of Controls evaluate whether internal controls operate effectively in preventing, detecting, or correcting material misstatements. These tests go beyond just understanding the design—they confirm that controls actually work in practice.
For high-volume transactions, tests of controls combined with substantive analytics provide more persuasive evidence than substantive testing alone. Key procedures include inquiry, observation, inspection, and reperformance, with inquiry alone never being sufficient.
When controls aren't operating effectively, auditors must rely more heavily on substantive procedures, testing closer to year-end with larger sample sizes.
Substantive testing focuses on gathering evidence about the accuracy of account balances and transactions. Without sufficient evidence, an auditor cannot express an opinion. This evidence must be both persuasive and relevant to the assertions being tested.
Audit Insight: Evidence quality matters more than quantity. Evidence obtained from independent external sources is generally more reliable than information generated internally, and original documents are more reliable than copies.
Substantive testing can be performed as:
The nature, timing, and extent of substantive procedures depend on the assessed risk levels. Lower detection risk requires more effective procedures, testing closer to year-end, and larger sample sizes.
Specific substantive procedures include the "trifecta" (inquiry, observation, inspection) plus recalculation, analytical procedures, and confirmations. External confirmations are particularly valuable as they provide evidence directly from third parties.
For positive confirmations:
For negative confirmations:
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_5.webp&w=2048&q=75)
As the audit nears completion, auditors perform crucial wrap-up procedures to ensure all material matters are properly addressed before issuing their opinion.
Searching for unrecorded liabilities is a critical step since companies tend to understate liabilities. Auditors review subsequent cash disbursements, examine unapproved invoices, and perform analytical procedures to detect missing obligations.
When evaluating litigation and claims, auditors:
Warning: If management refuses to allow communication with the entity's external legal counsel, this may result in a qualified opinion or disclaimer of opinion.
Related party disclosures require special attention. Auditors must identify relationships, evaluate unusual transactions, and assess whether disclosures comply with accounting standards. Failure to obtain sufficient evidence about related parties may lead to a qualified or adverse opinion.
Assessing going concern is another critical element. Management must evaluate the entity's ability to continue operating for at least 12 months from the financial statement date. If significant doubt exists, auditors must:
If going concern is appropriate but material uncertainty exists, an unqualified opinion with an Emphasis of Matter paragraph is required. If going concern is not appropriate and financial statements are prepared on a going concern basis, an adverse opinion is warranted.
For subsequent events, auditors must distinguish between:
If management amends financial statements to reflect subsequent events, the auditor must extend procedures to cover these changes and issue a new report. If management refuses to make necessary amendments, the auditor may need to modify their opinion or seek legal advice.
Before finalizing the audit, auditors perform analytical procedures to help form an overall conclusion about whether the financial statements are consistent with their understanding of the entity.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_6.webp&w=2048&q=75)
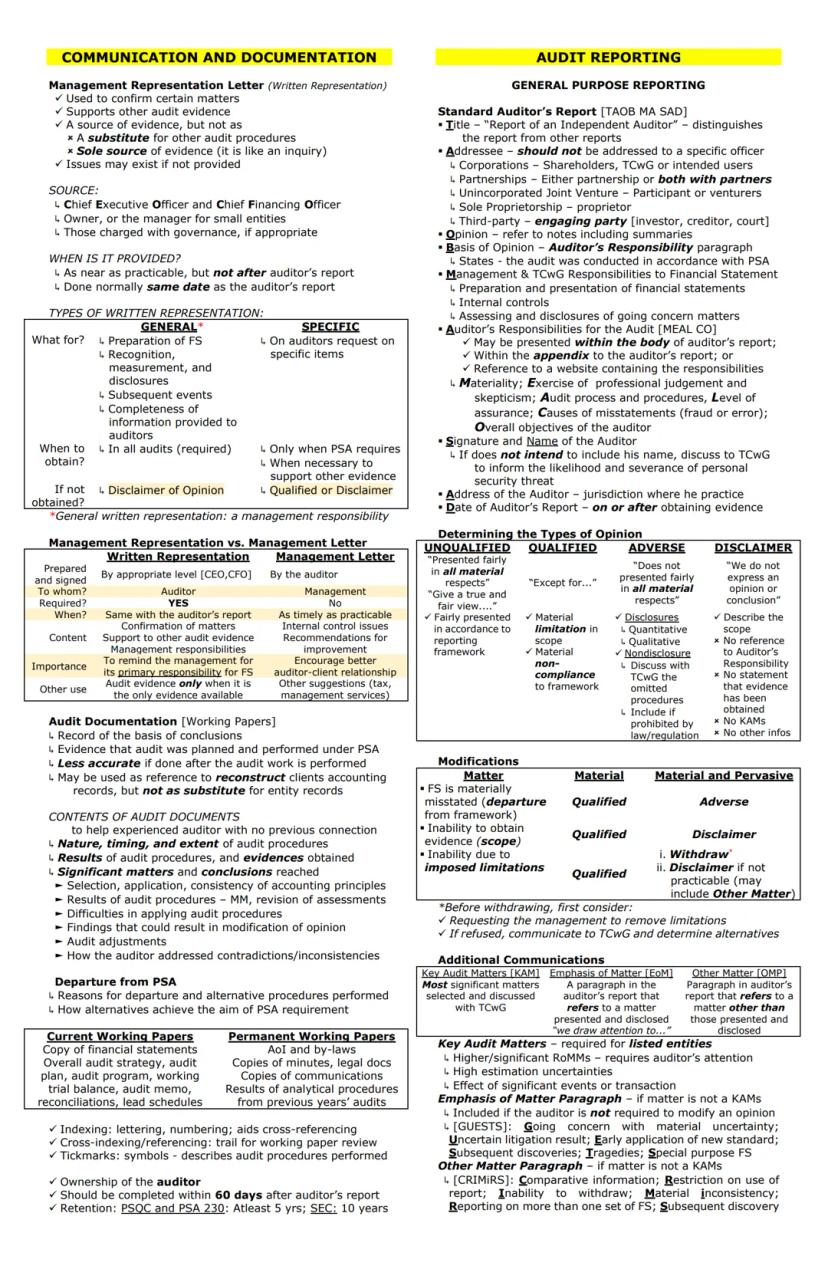
Effective communication and thorough documentation are essential components of a quality audit. A key communication tool is the Management Representation Letter, which:
However, remember that written representations aren't substitutes for other audit procedures—they're like inquiries and should be supported by additional evidence.
Important Distinction: Don't confuse a Management Representation Letter (from the client to the auditor) with a Management Letter (from the auditor to the client). The latter contains recommendations for improving internal controls and operations.
Audit documentation (working papers) provides a record of procedures performed and conclusions reached. It should be sufficient for an experienced auditor with no previous connection to understand the work performed, significant findings, and conclusions reached.
Documentation typically includes:
Working papers should be properly indexed, cross-referenced, and marked with tick marks to show procedures performed. They remain the property of the auditor and must be completed within 60 days after the audit report date.
Audit reporting communicates the results to users. The standard auditor's report follows a structured format (TAOB MA SAD):
The type of opinion depends on the circumstances:
Additional paragraphs may include Key Audit Matters (most significant matters for listed entities), Emphasis of Matter (drawing attention to disclosed issues), and Other Matter paragraphs (addressing matters not presented in the financial statements).
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_7.webp&w=2048&q=75)
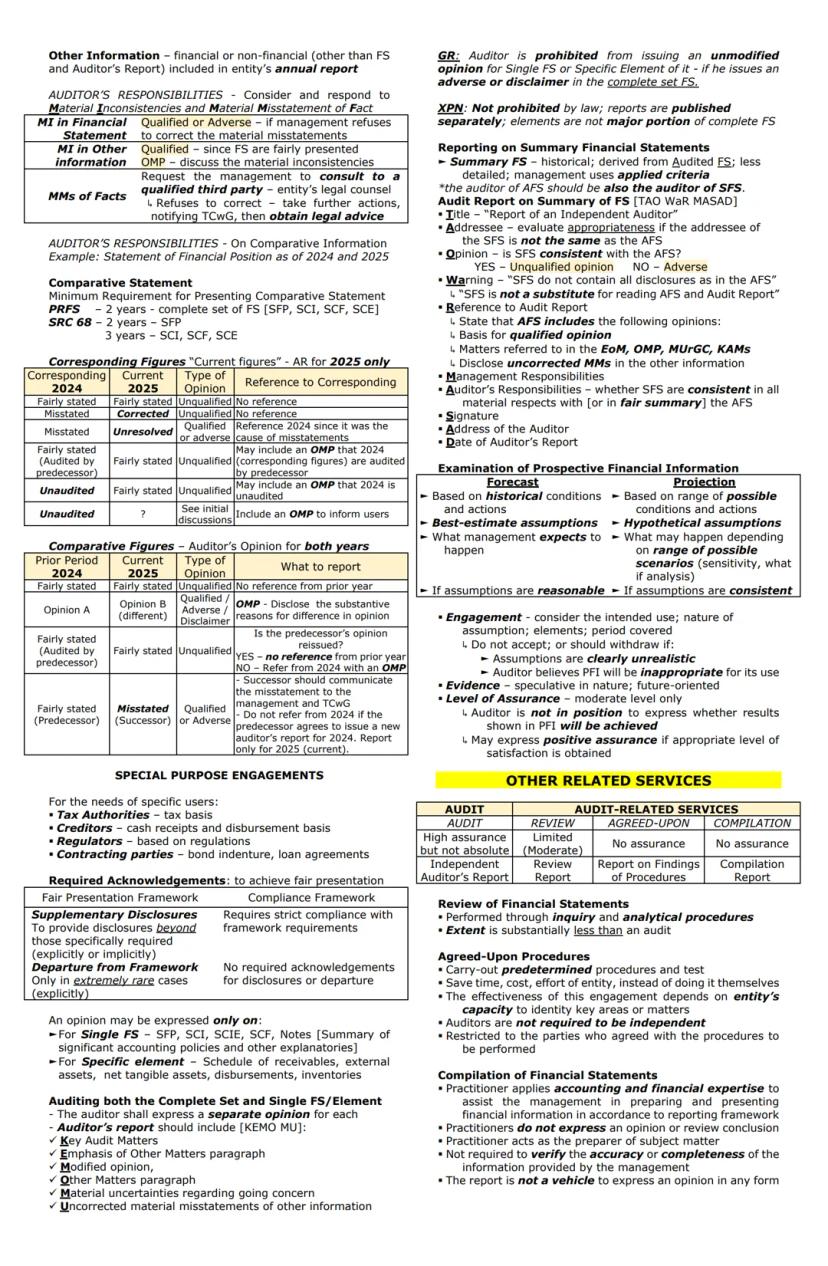
When auditors encounter other information , they must consider whether it's consistent with the audited financial statements. If material inconsistencies or misstatements exist, auditors must request management to make corrections or, if management refuses, modify their report accordingly.
Comparative information presents special considerations. Two approaches exist:
The approach determines how the auditor addresses prior period matters and whether separate opinions are expressed on each period.
Special purpose engagements address the specific needs of certain users:
For single financial statements or specific elements, auditors may express separate opinions, but generally can't issue an unmodified opinion on a component if they've issued an adverse or disclaimer on the complete set.
Summary financial statements provide condensed information derived from audited financial statements. The auditor's report on summaries must:
Prospective financial information engagements examine future-oriented financial data:
When examining prospective information, auditors assess the reasonableness of assumptions but don't provide assurance on whether results will be achieved. Their report should clearly indicate the purpose and any limitations.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_8.webp&w=2048&q=75)
The Philippine Accountancy Act of 2004 (RA 9298) established the framework for regulating the accounting profession in the Philippines. This law standardizes accounting education, governs CPA examinations, and regulates professional practice.
Accountancy encompasses several major areas:
The scope of practice can include:
The Professional Regulatory Board of Accountancy consists of a chairman and six members appointed by the President. Members must be natural-born citizens with 10 years of experience in any scope of practice and good moral character.
Career Insight: To maintain your CPA license, you must complete at least 120 CPD units every three years, with a minimum of 20 units annually. After age 65, this requirement becomes optional.
Fraud and error represent significant concerns in financial reporting. While both can lead to misstatements, fraud involves intentional deception while errors are unintentional mistakes. Fraud typically requires more extensive audit procedures performed closer to year-end with larger sample sizes.
The fraud triangle identifies three factors present in fraud cases:
Management is primarily responsible for preventing and detecting fraud, while auditors must identify risks, obtain evidence, and respond appropriately to identified fraud. If significant fraud is discovered, auditors must report it to the appropriate level of management and those charged with governance.
Non-compliance with laws and regulations (NOCLAR) presents another important area. Laws with direct effect on financial statements (like tax laws) require specific audit procedures, while those with indirect effect (like environmental regulations) may require different approaches. When auditors discover NOCLAR, they must determine appropriate reporting based on the severity and circumstances.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_9.webp&w=2048&q=75)
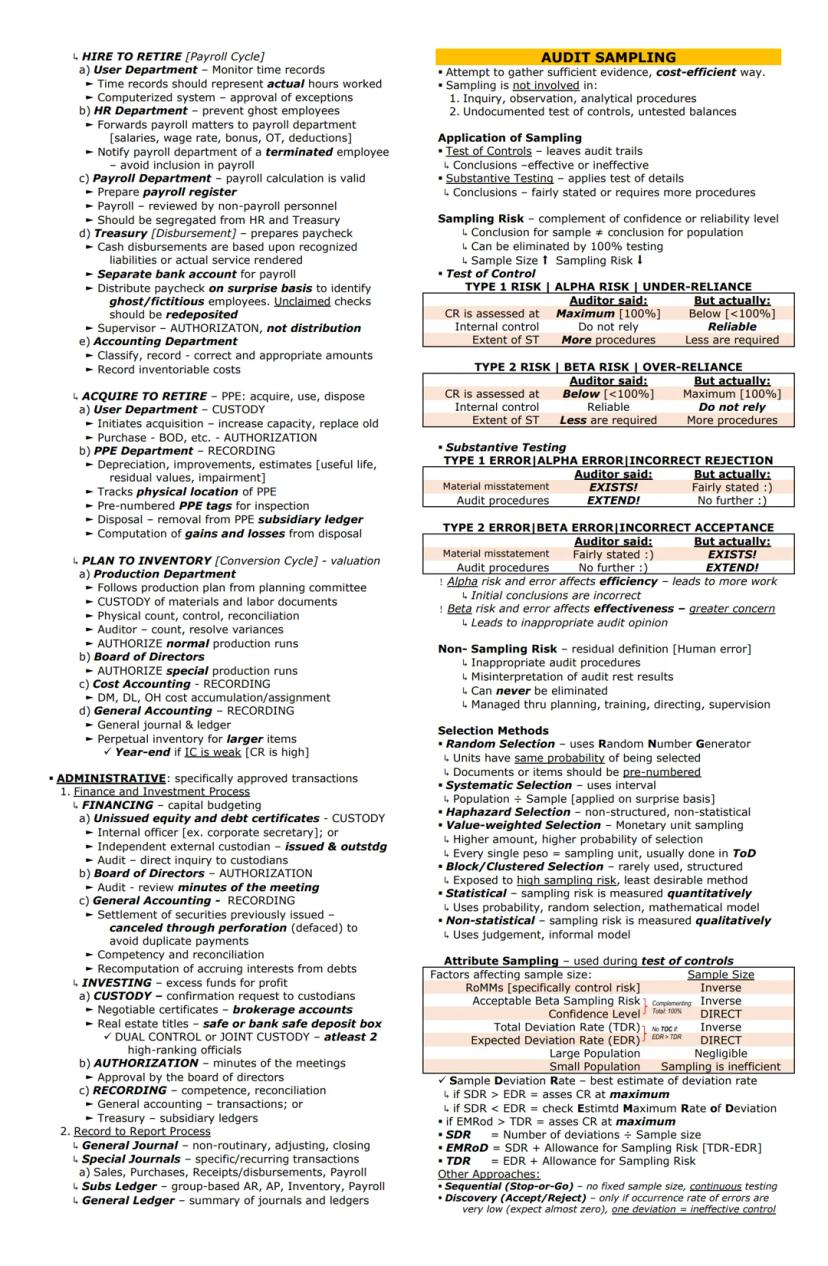
Understanding business transaction cycles helps auditors identify risks and design effective procedures. These cycles represent how accounting systems process related activities.
The Revenue and Receipt Process (Order to Cash) includes:
The Expenditure and Disbursement Process (Purchase to Pay) includes:
Control Insight: The three-way match (purchase order, receiving report, and vendor invoice) is a critical control in the expenditure cycle that helps prevent payment for goods not ordered or received.
The Payroll Cycle (Hire to Retire) encompasses:
Other important cycles include:
Audit sampling allows auditors to draw conclusions about a population by testing only a portion of items. The two main types are:
Sample size is affected by factors like risk assessment, expected deviation/misstatement rates, and tolerable rates. Higher risk generally requires larger samples, while more effective alternative procedures may allow smaller samples.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_10.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Attribute sampling helps auditors evaluate the rate of deviations in control procedures. Sample size is inversely related to acceptable risk and the tolerable deviation rate—as these decrease, sample size increases. After testing, auditors compare the sample deviation rate to their expectations and determine whether controls can be relied upon.
Variable sampling techniques for substantive testing include:
When missing or voided documents are encountered, auditors must determine if they were properly handled according to internal control procedures. If not, they're considered deviations or misstatements.
Sampling Insight: While sampling introduces risk, it's often the only practical way to gather audit evidence. The key is managing sampling risk through appropriate sample selection methods and evaluation techniques.
Auditing in a computerized information system (CIS) environment requires understanding three key IT elements:
IT controls operate at different levels:
Automated controls are generally more reliable than manual controls since they're less prone to human error and cannot be easily bypassed. However, auditors must ensure these controls are properly designed and operating effectively.
Auditors can use two main approaches:
CAATs can include program analysis, test data, integrated test facility, parallel simulation, and many other techniques that help auditors test controls and verify data processing accuracy in complex IT environments.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
studywithnessa
@studywithnessa
Auditing is the systematic process of examining financial statements to determine if they are presented fairly and in accordance with appropriate financial reporting frameworks. This complex field requires understanding fundamental principles, methodologies, and professional responsibilities that govern how auditors evaluate... Show more
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_1.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
An assurance engagement involves three essential parties: the practitioner (governed by professional competence), the responsible party (accountable for the subject matter), and the intended users (identified by agreement).
The subject matter is what's being evaluated—like financial statements—while the subject matter information is the outcome of this evaluation against specific criteria. For example, in a financial audit, the financial statements themselves are the subject matter information.
When gathering evidence, auditors must consider both sufficiency (quantity) and appropriateness (quality). Remember that more evidence may be needed when risk is higher, but simply getting more low-quality evidence doesn't compensate for poor quality. Evidence is more reliable when:
Pro Tip: Professional skepticism is crucial throughout an engagement. Maintaining a questioning mindset helps you avoid overlooking suspicious circumstances and strengthens your ability to gather appropriate evidence.
Assurance engagements vary by level and structure. Reasonable assurance engagements (like audits) provide high assurance with positive opinions, while limited assurance engagements (like reviews) offer moderate assurance with negative opinions. The procedures differ significantly—audits require more extensive procedures beyond inquiry and analytics.
The structure can be either attestation-based (practitioner evaluates assertions made by the responsible party) or direct (practitioner directly reports on the subject matter).
Non-assurance engagements include agreed-upon procedures (reporting findings without conclusions), compilations (organizing financial information without assurance), tax services, and management consulting. These services don't provide the same level of confidence as assurance engagements.
Professional standards are established by various boards under the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC), with corresponding Philippine Standards covering auditing (PSAs), review engagements (PSREs), assurance engagements (PSAEs), related services (PSRSs), and quality control (PSQCs).
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_2.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
A financial statement audit is a systematic process where auditors obtain and evaluate evidence about management's assertions to determine if they match established criteria. This verification process forms the backbone of financial reporting credibility.
The theoretical framework for audits rests on several key principles. Auditors must maintain their independence to provide objective opinions, and the reliability of financial statements increases with effective internal controls and consistent application of accounting policies.
Businesses require audits due to several factors that create demand:
Important: Companies with gross annual sales of ₱3 million or more (vatable businesses) must undergo BIR-required audits, while SEC requirements vary based on entity type and asset/liability thresholds.
When examining financial statements, auditors focus on specific assertions made by management. These are organized into three categories:
All audits face inherent limitations. These include sampling risk (testing only a portion of transactions), judgment limitations, internal control weaknesses, and evidence that is persuasive rather than conclusive.
The audit process follows a structured approach: preliminary engagement activities, planning, internal control evaluation, substantive testing, completion, report issuance, and post-audit responsibilities. Preliminary activities focus on client acceptance considerations, including the auditor's competence and independence, client integrity, and establishing audit preconditions through an engagement letter.
For recurring audits, new engagement letters aren't required unless significant changes have occurred in circumstances, terms, or management. If a client requests changing the engagement's nature, auditors must carefully evaluate whether there's reasonable justification before proceeding.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_3.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Planning is essential for an effective audit. According to PSA 300, proper planning helps coordinate work, assign responsibilities, facilitate supervision, and identify problems early. The nature and extent of planning varies based on the entity's size, complexity, prior experience with the entity, and circumstances.
The planning process produces three key outputs:
When identifying and assessing risks of material misstatements (RoMMs), auditors consider both:
Materiality directly impacts the extent of audit procedures. Lower materiality levels require more extensive procedures, while higher levels allow for less extensive testing. Remember this key relationship: materiality and audit risk have an inverse relationship, while audit risk and audit procedures have a direct relationship.
Remember: When control risk and inherent risk are both high, detection risk must be at its lowest level to maintain an acceptable overall audit risk. This means you'll need to perform more extensive substantive testing.
Internal control is a process established by management to provide reasonable assurance about operations, reporting, and compliance. Effective internal controls can significantly improve audit efficiency by allowing for reduced substantive testing.
Internal controls face inherent limitations (COCCHA):
The five components of internal control (CRIME) include:
After evaluating the design and implementation of controls, auditors make a preliminary assessment of control risk. If control risk is assessed at less than maximum, auditors perform tests of controls to confirm operating effectiveness. If controls aren't effective or it's inefficient to test them, the control risk is set at maximum, requiring more extensive substantive testing.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_4.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Tests of Controls evaluate whether internal controls operate effectively in preventing, detecting, or correcting material misstatements. These tests go beyond just understanding the design—they confirm that controls actually work in practice.
For high-volume transactions, tests of controls combined with substantive analytics provide more persuasive evidence than substantive testing alone. Key procedures include inquiry, observation, inspection, and reperformance, with inquiry alone never being sufficient.
When controls aren't operating effectively, auditors must rely more heavily on substantive procedures, testing closer to year-end with larger sample sizes.
Substantive testing focuses on gathering evidence about the accuracy of account balances and transactions. Without sufficient evidence, an auditor cannot express an opinion. This evidence must be both persuasive and relevant to the assertions being tested.
Audit Insight: Evidence quality matters more than quantity. Evidence obtained from independent external sources is generally more reliable than information generated internally, and original documents are more reliable than copies.
Substantive testing can be performed as:
The nature, timing, and extent of substantive procedures depend on the assessed risk levels. Lower detection risk requires more effective procedures, testing closer to year-end, and larger sample sizes.
Specific substantive procedures include the "trifecta" (inquiry, observation, inspection) plus recalculation, analytical procedures, and confirmations. External confirmations are particularly valuable as they provide evidence directly from third parties.
For positive confirmations:
For negative confirmations:
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_5.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
As the audit nears completion, auditors perform crucial wrap-up procedures to ensure all material matters are properly addressed before issuing their opinion.
Searching for unrecorded liabilities is a critical step since companies tend to understate liabilities. Auditors review subsequent cash disbursements, examine unapproved invoices, and perform analytical procedures to detect missing obligations.
When evaluating litigation and claims, auditors:
Warning: If management refuses to allow communication with the entity's external legal counsel, this may result in a qualified opinion or disclaimer of opinion.
Related party disclosures require special attention. Auditors must identify relationships, evaluate unusual transactions, and assess whether disclosures comply with accounting standards. Failure to obtain sufficient evidence about related parties may lead to a qualified or adverse opinion.
Assessing going concern is another critical element. Management must evaluate the entity's ability to continue operating for at least 12 months from the financial statement date. If significant doubt exists, auditors must:
If going concern is appropriate but material uncertainty exists, an unqualified opinion with an Emphasis of Matter paragraph is required. If going concern is not appropriate and financial statements are prepared on a going concern basis, an adverse opinion is warranted.
For subsequent events, auditors must distinguish between:
If management amends financial statements to reflect subsequent events, the auditor must extend procedures to cover these changes and issue a new report. If management refuses to make necessary amendments, the auditor may need to modify their opinion or seek legal advice.
Before finalizing the audit, auditors perform analytical procedures to help form an overall conclusion about whether the financial statements are consistent with their understanding of the entity.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_6.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Effective communication and thorough documentation are essential components of a quality audit. A key communication tool is the Management Representation Letter, which:
However, remember that written representations aren't substitutes for other audit procedures—they're like inquiries and should be supported by additional evidence.
Important Distinction: Don't confuse a Management Representation Letter (from the client to the auditor) with a Management Letter (from the auditor to the client). The latter contains recommendations for improving internal controls and operations.
Audit documentation (working papers) provides a record of procedures performed and conclusions reached. It should be sufficient for an experienced auditor with no previous connection to understand the work performed, significant findings, and conclusions reached.
Documentation typically includes:
Working papers should be properly indexed, cross-referenced, and marked with tick marks to show procedures performed. They remain the property of the auditor and must be completed within 60 days after the audit report date.
Audit reporting communicates the results to users. The standard auditor's report follows a structured format (TAOB MA SAD):
The type of opinion depends on the circumstances:
Additional paragraphs may include Key Audit Matters (most significant matters for listed entities), Emphasis of Matter (drawing attention to disclosed issues), and Other Matter paragraphs (addressing matters not presented in the financial statements).
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_7.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
When auditors encounter other information , they must consider whether it's consistent with the audited financial statements. If material inconsistencies or misstatements exist, auditors must request management to make corrections or, if management refuses, modify their report accordingly.
Comparative information presents special considerations. Two approaches exist:
The approach determines how the auditor addresses prior period matters and whether separate opinions are expressed on each period.
Special purpose engagements address the specific needs of certain users:
For single financial statements or specific elements, auditors may express separate opinions, but generally can't issue an unmodified opinion on a component if they've issued an adverse or disclaimer on the complete set.
Summary financial statements provide condensed information derived from audited financial statements. The auditor's report on summaries must:
Prospective financial information engagements examine future-oriented financial data:
When examining prospective information, auditors assess the reasonableness of assumptions but don't provide assurance on whether results will be achieved. Their report should clearly indicate the purpose and any limitations.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_8.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The Philippine Accountancy Act of 2004 (RA 9298) established the framework for regulating the accounting profession in the Philippines. This law standardizes accounting education, governs CPA examinations, and regulates professional practice.
Accountancy encompasses several major areas:
The scope of practice can include:
The Professional Regulatory Board of Accountancy consists of a chairman and six members appointed by the President. Members must be natural-born citizens with 10 years of experience in any scope of practice and good moral character.
Career Insight: To maintain your CPA license, you must complete at least 120 CPD units every three years, with a minimum of 20 units annually. After age 65, this requirement becomes optional.
Fraud and error represent significant concerns in financial reporting. While both can lead to misstatements, fraud involves intentional deception while errors are unintentional mistakes. Fraud typically requires more extensive audit procedures performed closer to year-end with larger sample sizes.
The fraud triangle identifies three factors present in fraud cases:
Management is primarily responsible for preventing and detecting fraud, while auditors must identify risks, obtain evidence, and respond appropriately to identified fraud. If significant fraud is discovered, auditors must report it to the appropriate level of management and those charged with governance.
Non-compliance with laws and regulations (NOCLAR) presents another important area. Laws with direct effect on financial statements (like tax laws) require specific audit procedures, while those with indirect effect (like environmental regulations) may require different approaches. When auditors discover NOCLAR, they must determine appropriate reporting based on the severity and circumstances.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_9.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Understanding business transaction cycles helps auditors identify risks and design effective procedures. These cycles represent how accounting systems process related activities.
The Revenue and Receipt Process (Order to Cash) includes:
The Expenditure and Disbursement Process (Purchase to Pay) includes:
Control Insight: The three-way match (purchase order, receiving report, and vendor invoice) is a critical control in the expenditure cycle that helps prevent payment for goods not ordered or received.
The Payroll Cycle (Hire to Retire) encompasses:
Other important cycles include:
Audit sampling allows auditors to draw conclusions about a population by testing only a portion of items. The two main types are:
Sample size is affected by factors like risk assessment, expected deviation/misstatement rates, and tolerable rates. Higher risk generally requires larger samples, while more effective alternative procedures may allow smaller samples.
![# FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
Elements of Assurance Engagement [3SECC]
• Three-party relationship
✓ Practitioner
governed by professional compet](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent-eu-central-1.knowunity.com%2FCONTENT%2F019aa5aa-efe5-7638-8470-89e5a1254c7e_image_page_10.webp&w=2048&q=75)
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Attribute sampling helps auditors evaluate the rate of deviations in control procedures. Sample size is inversely related to acceptable risk and the tolerable deviation rate—as these decrease, sample size increases. After testing, auditors compare the sample deviation rate to their expectations and determine whether controls can be relied upon.
Variable sampling techniques for substantive testing include:
When missing or voided documents are encountered, auditors must determine if they were properly handled according to internal control procedures. If not, they're considered deviations or misstatements.
Sampling Insight: While sampling introduces risk, it's often the only practical way to gather audit evidence. The key is managing sampling risk through appropriate sample selection methods and evaluation techniques.
Auditing in a computerized information system (CIS) environment requires understanding three key IT elements:
IT controls operate at different levels:
Automated controls are generally more reliable than manual controls since they're less prone to human error and cannot be easily bypassed. However, auditors must ensure these controls are properly designed and operating effectively.
Auditors can use two main approaches:
CAATs can include program analysis, test data, integrated test facility, parallel simulation, and many other techniques that help auditors test controls and verify data processing accuracy in complex IT environments.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
7
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user