Accounting principles can seem complex, but understanding the fundamentals is... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
1,068
•
Jan 31, 2026
•
studywithnessa
@studywithnessa
Accounting principles can seem complex, but understanding the fundamentals is... Show more
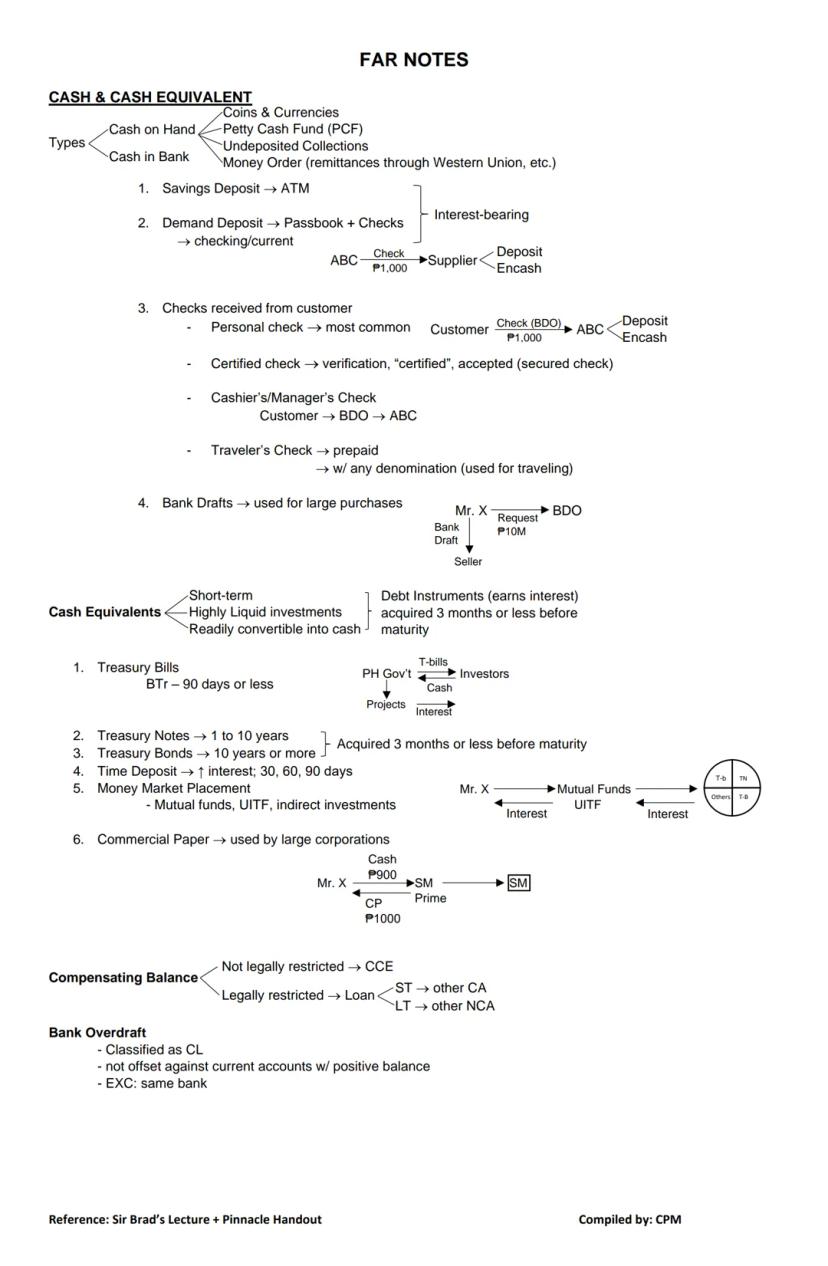


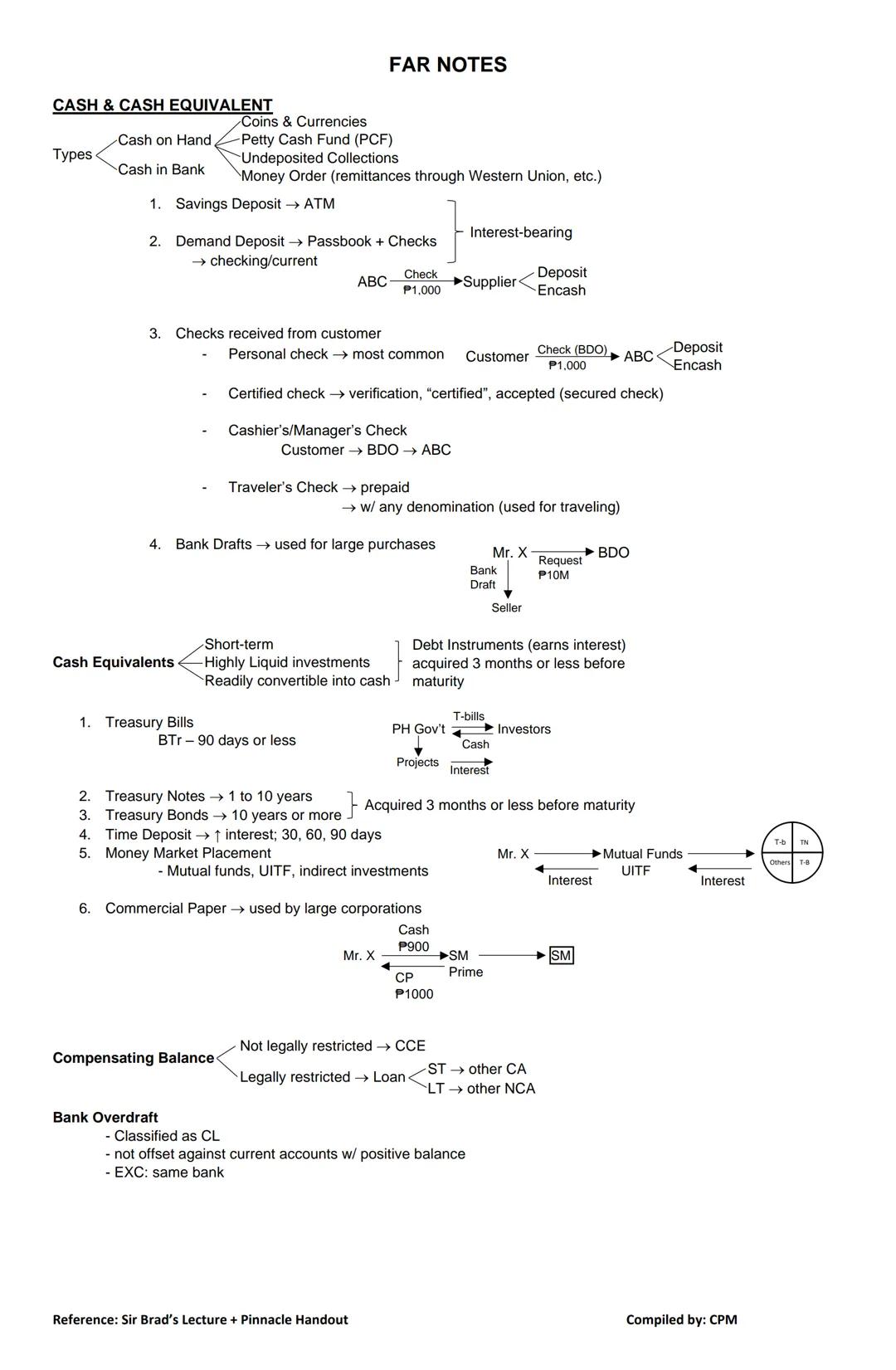
Cash is more than just the coins and bills in your register. It encompasses all immediately available funds that a business can use without restriction.
Cash includes coins & currencies (cash on hand, petty cash), cash in bank (savings and demand deposits), and undeposited collections (money orders, remittances). Demand deposits are particularly important for businesses as they allow for both passbook access and check writing privileges.
When dealing with checks, understand the differences:
💡 Bank drafts are helpful for large purchases, as they provide guaranteed payment like a cashier's check but for much larger amounts.
Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that can be readily converted into cash. To qualify as a cash equivalent, investments must be debt instruments acquired three months or less before maturity. Examples include Treasury bills, short-term Treasury notes/bonds, time deposits, and money market placements.
Remember that legally restricted funds (like compensating balances for loans) aren't classified as cash equivalents. They're either classified as other current assets or other non-current assets .
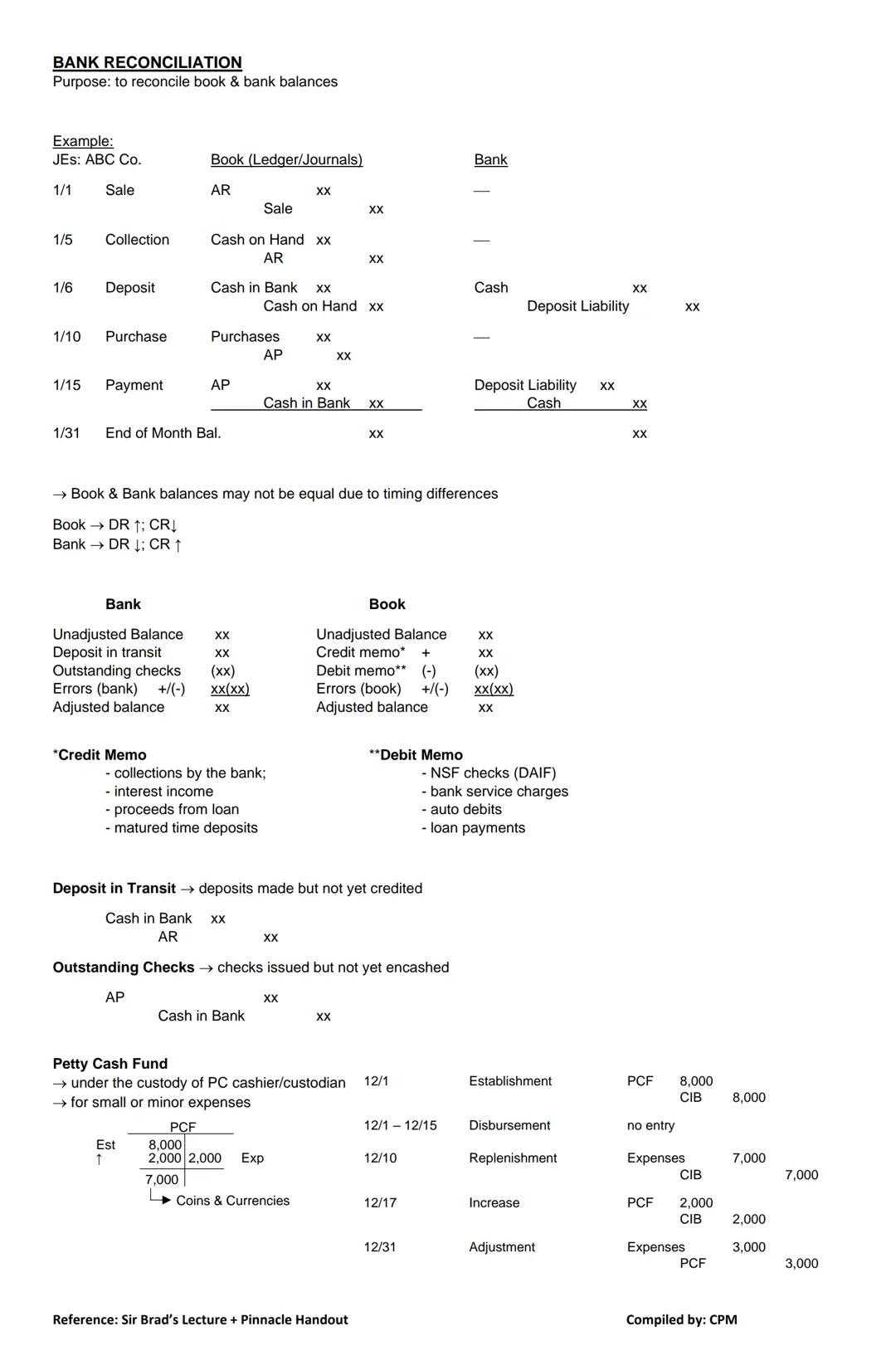
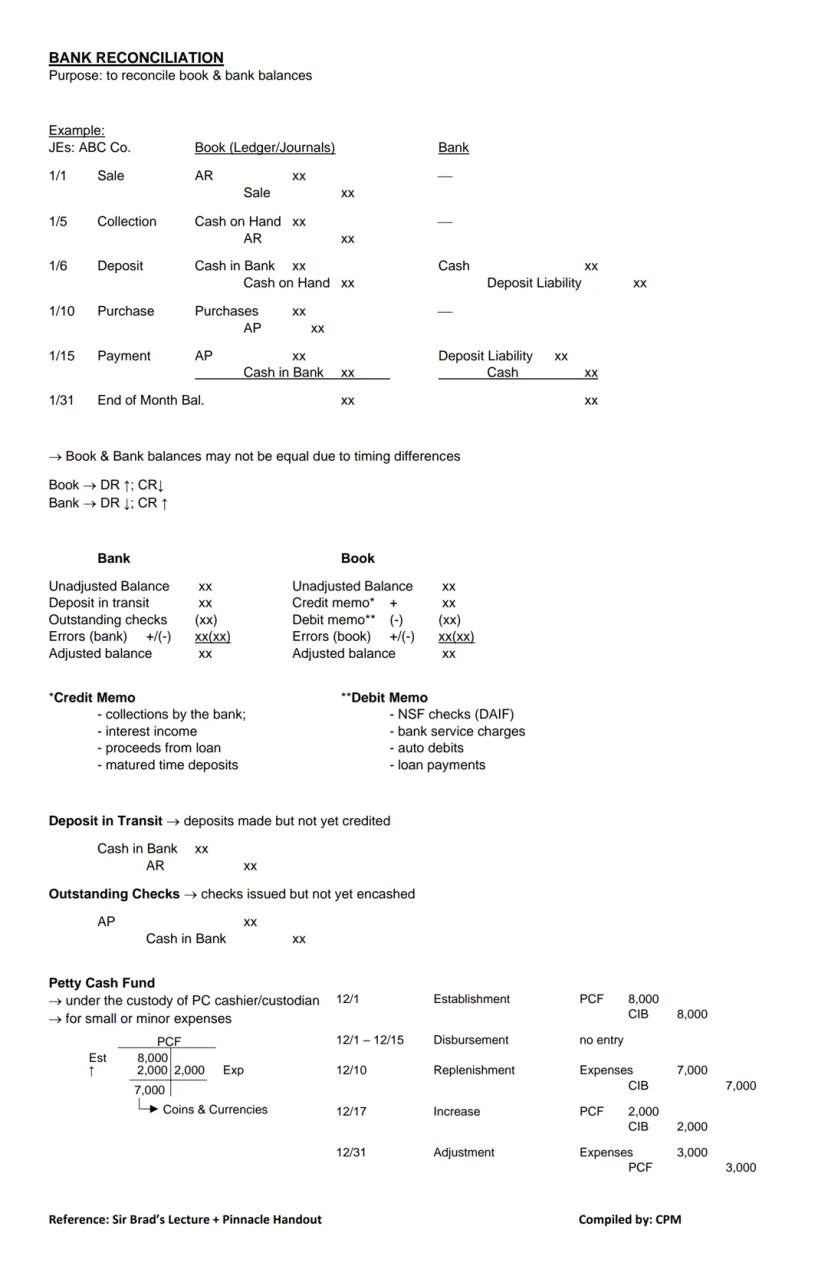
Bank reconciliation helps you match your book balance (what you've recorded) with your bank balance (what the bank shows). These two figures often differ due to timing differences.
Think of it this way: your books record cash increasing when you receive it, while the bank records increases when you deposit it. Similarly, your books show decreases when you write checks, but the bank only records them when they're presented for payment.
To reconcile your accounts, start with:
Key terms to understand:
💡 Remember that bank and book entries work in opposite directions! In your books, debits increase your cash balance while credits decrease it. On your bank statement, credits increase your balance while debits decrease it.
Petty Cash Fund Management: Managing petty cash requires three key steps:
If you need to increase the fund later, simply issue another check for the additional amount. At year-end, adjust any remaining expenses that haven't been recorded.
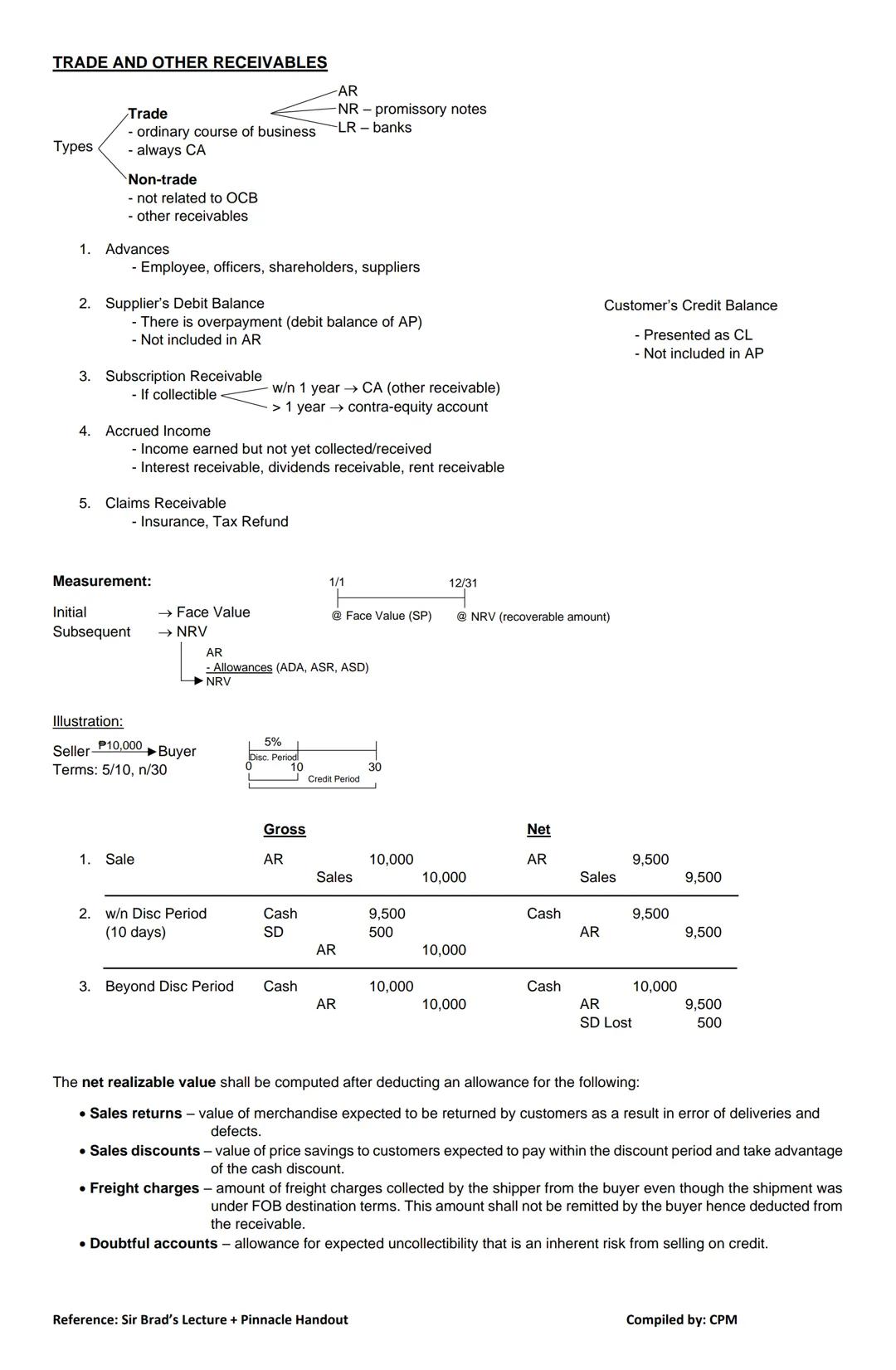
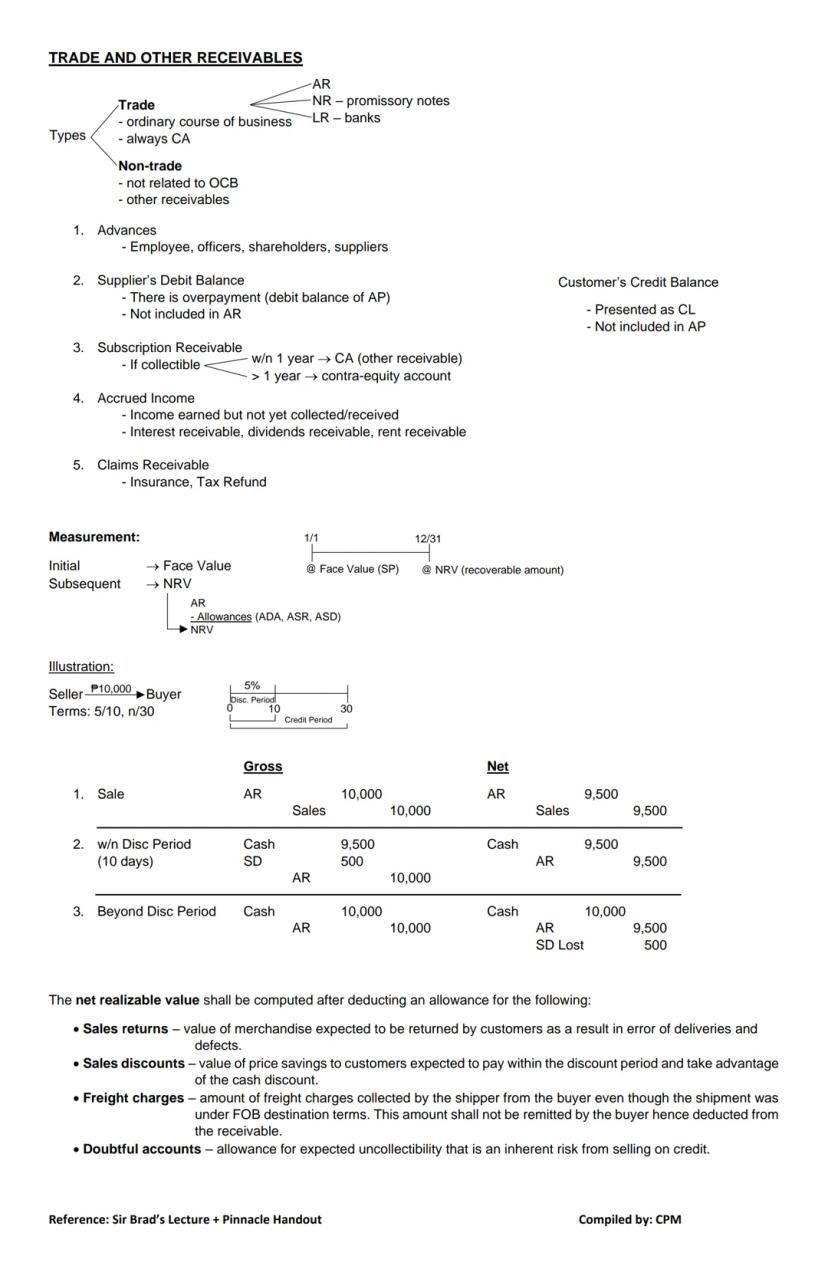
Receivables represent money owed to your business by others. Understanding how to classify and value them is crucial for accurate financial reporting.
Types of Receivables:
Within these categories, you'll find:
Other important receivables include:
💡 Customer credit balances are not receivables! They should be presented as current liabilities, not deducted from accounts receivable.
Measurement of Receivables: Initially, receivables are recorded at face value (selling price). Subsequently, they must be measured at net realizable value (NRV) – the amount you actually expect to collect.
To calculate NRV, you must deduct allowances for:
For example, if you offer terms of "5/10, n/30" (5% discount if paid within 10 days, net amount due within 30 days), you'll need to account for both gross and net methods of recording the transaction.
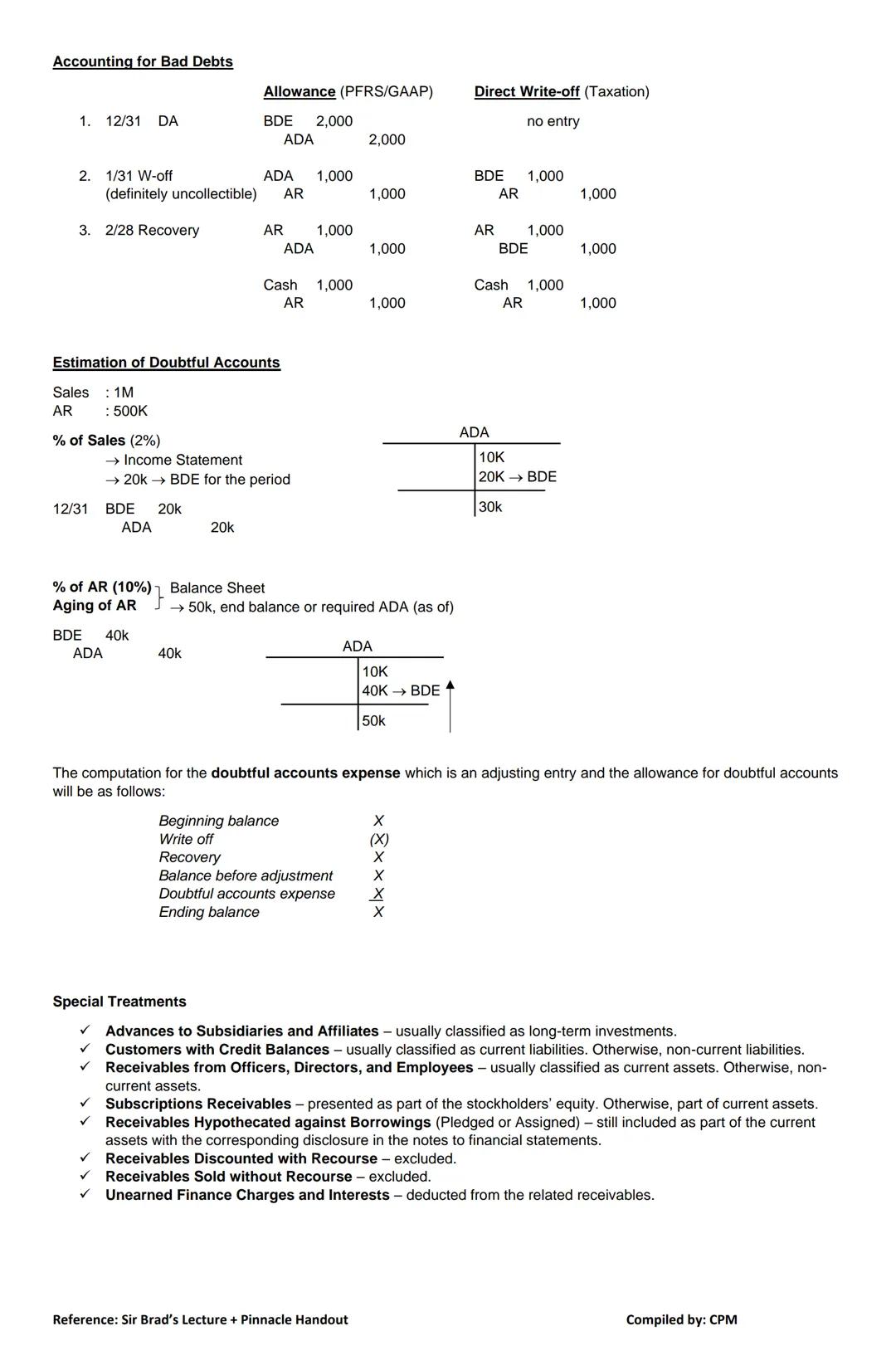
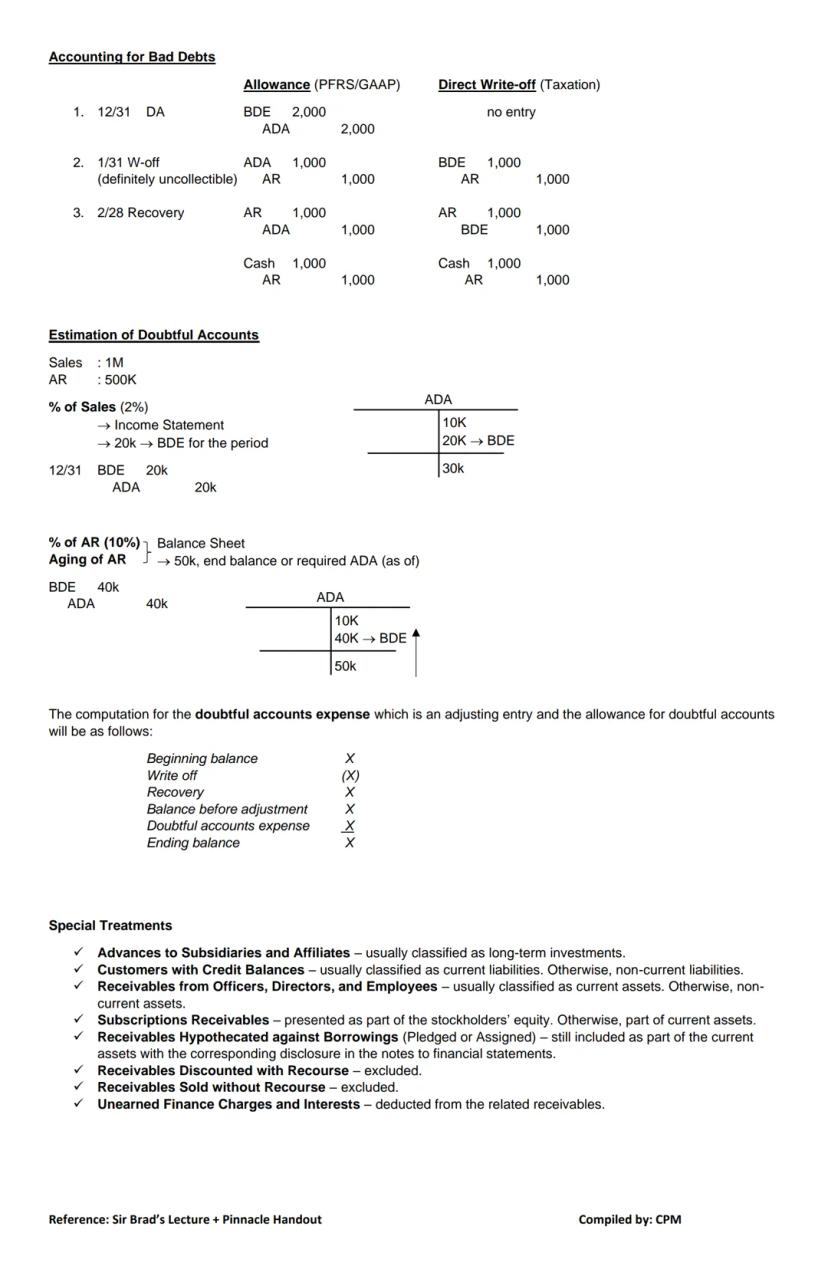
When customers fail to pay, you need a system to account for these losses. There are two main approaches: the allowance method and the direct write-off method.
The allowance method anticipates bad debts before they occur:
The direct write-off method (used for tax purposes) only recognizes bad debts when they're definitely uncollectible:
Estimating Doubtful Accounts:
You can estimate bad debts using either:
💡 When calculating your bad debt expense for the year, start with your existing allowance, adjust for write-offs and recoveries, then determine how much additional expense is needed to reach your required ending balance.
Special Treatment of Receivables:
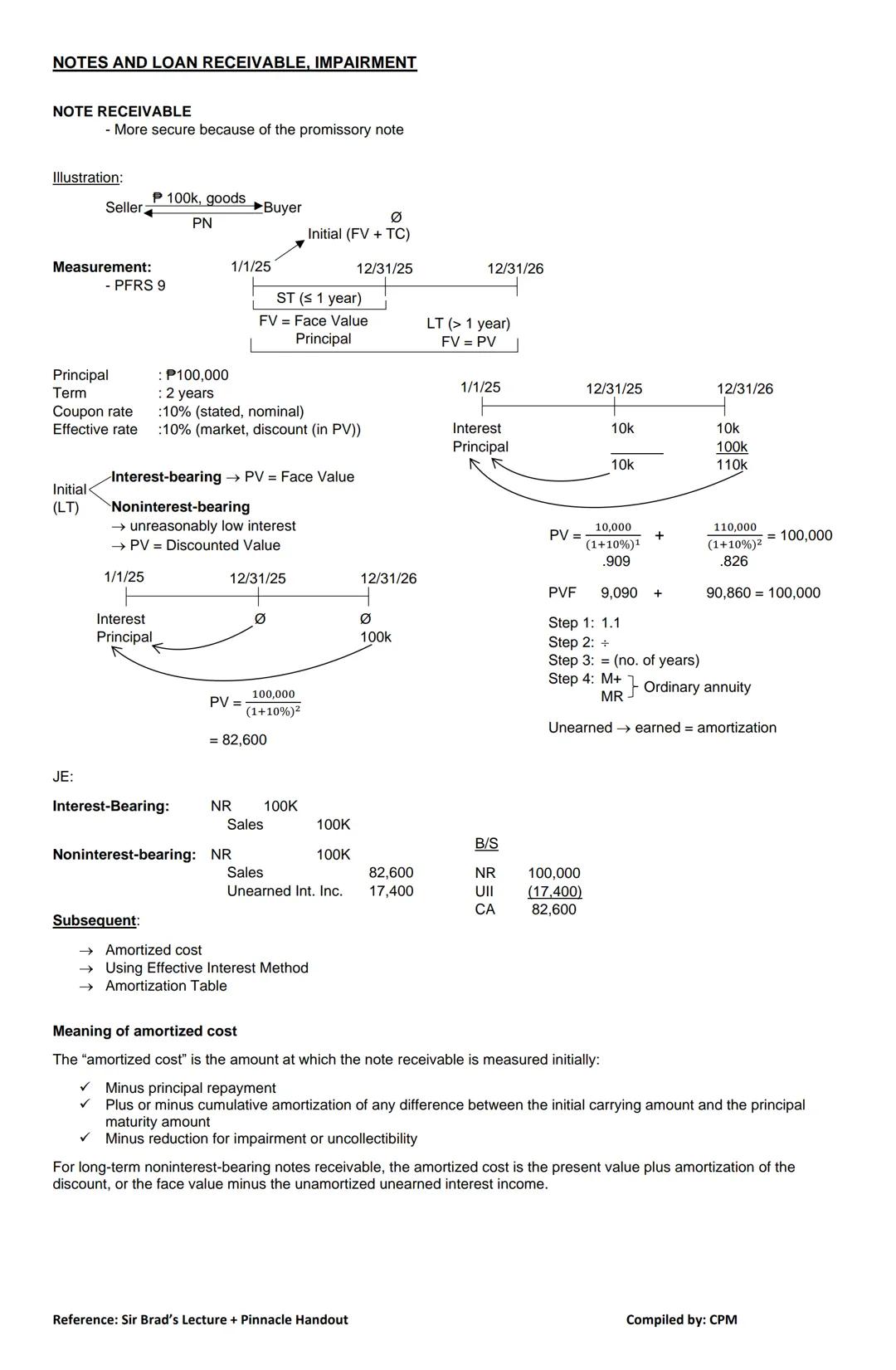
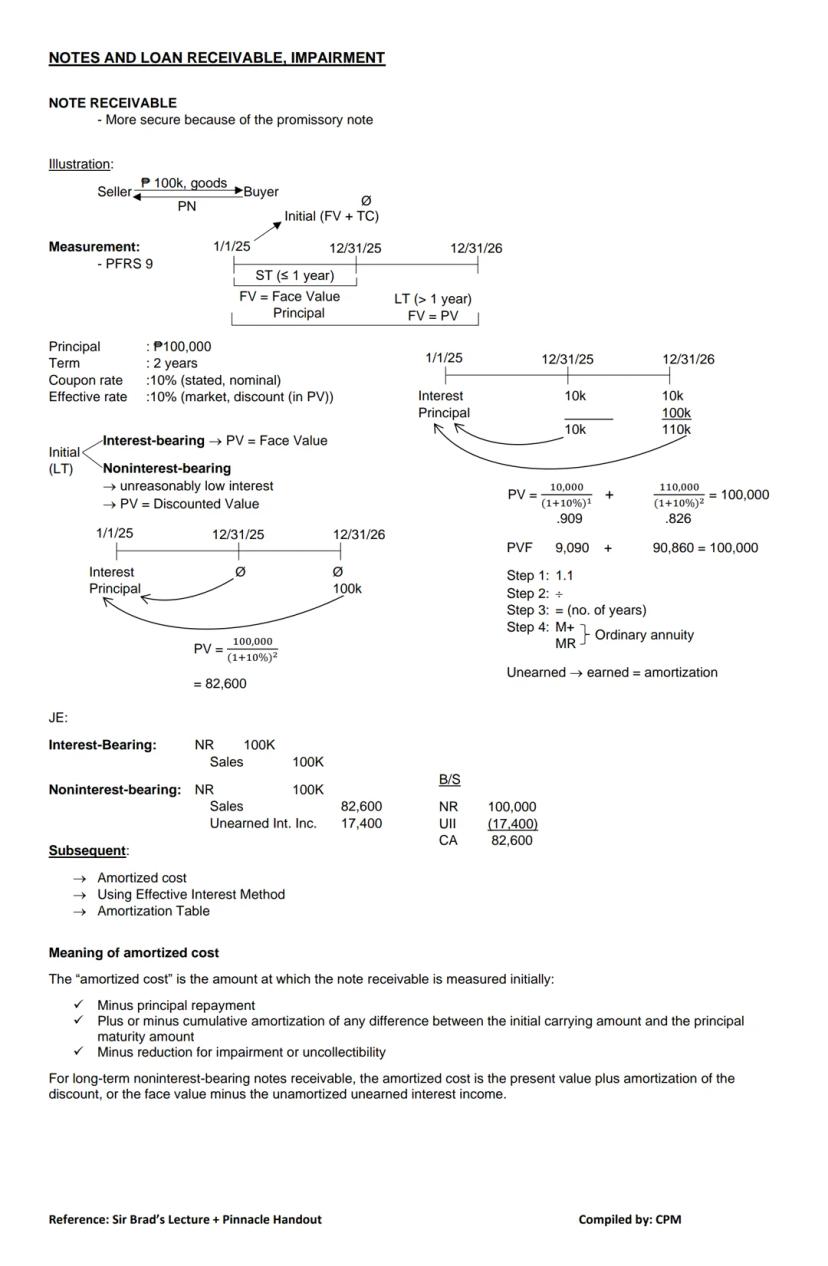
Notes receivable are more secure than accounts receivable because they're formalized with a promissory note that specifies payment terms.
Measurement of Notes Receivable:
For example, if you receive a 2-year, $100,000 note with 10% interest payable annually:
💡 The difference between face value and present value is called "unearned interest income" and must be amortized over the life of the note.
Subsequent Measurement: After initial recognition, notes receivable are measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Amortized cost equals:
For non-interest bearing notes, amortized cost equals the present value plus amortization of the discount (or face value minus unamortized unearned interest income).
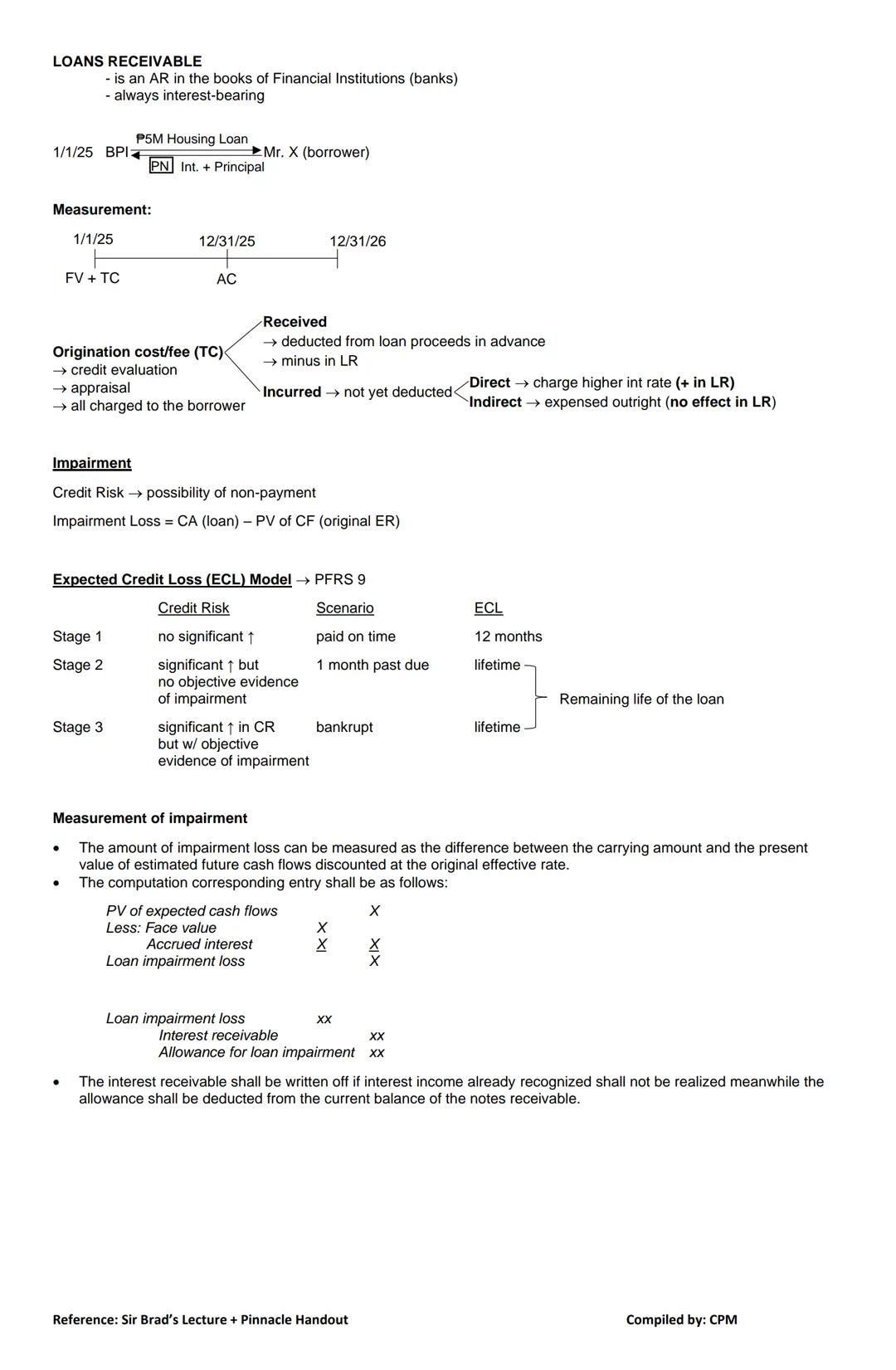
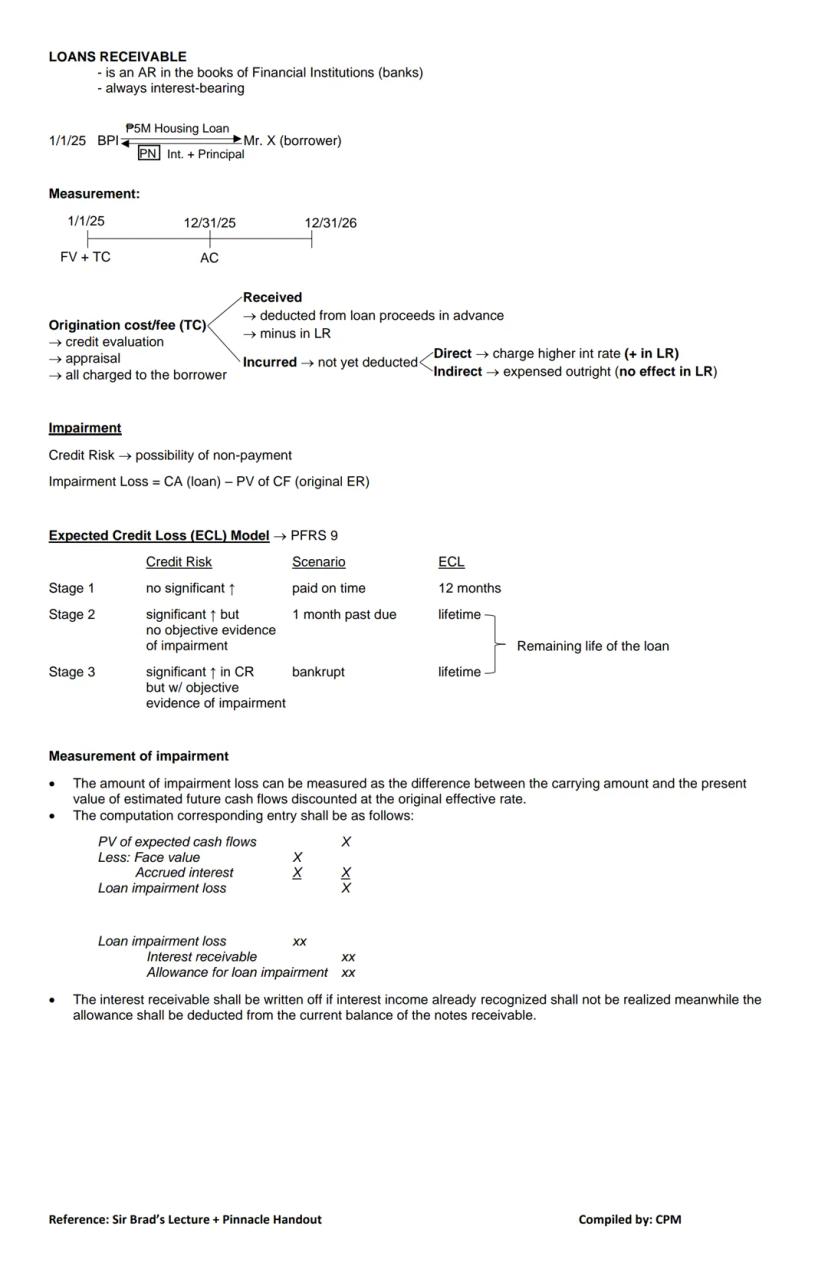
Loans receivable are a special category of receivables found in financial institutions' books (like banks). Unlike regular notes receivable, loans receivable always include interest.
When a bank issues a loan, it records several important elements:
Origination costs include expenses like credit evaluation and appraisal fees. These can be handled in two ways:
Impairment Assessment: Under PFRS 9, lenders must assess credit risk and potential impairment using the Expected Credit Loss (ECL) model. This involves three stages:
💡 Impairment loss is calculated as the difference between the carrying amount of the loan and the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the original effective rate.
The journal entry for impairment typically involves:
Loan impairment loss XX
Interest receivable XX
Allowance for loan impairment XX
This write-down adjusts both the interest receivable that won't be collected and creates an allowance against the loan balance.
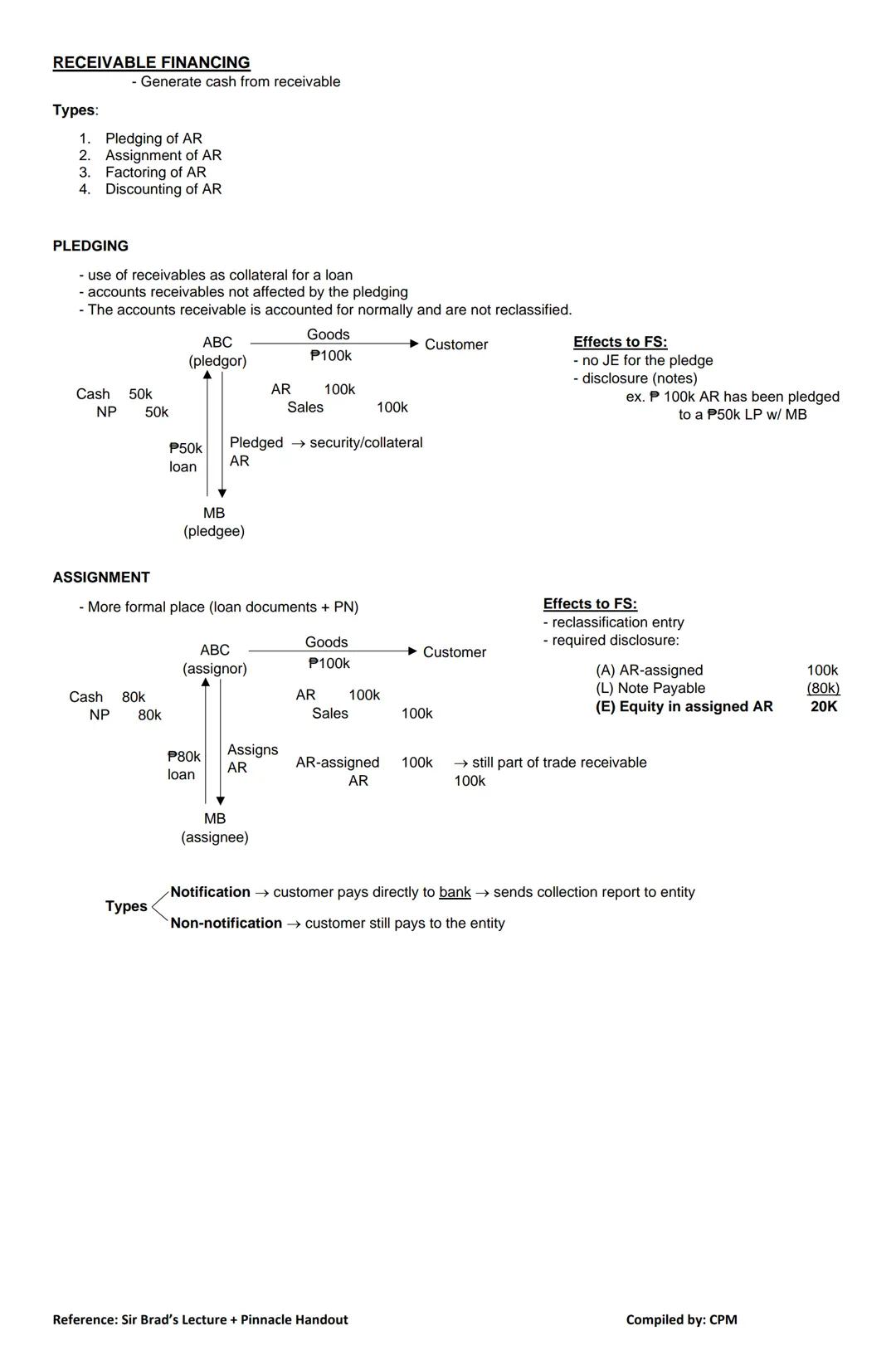
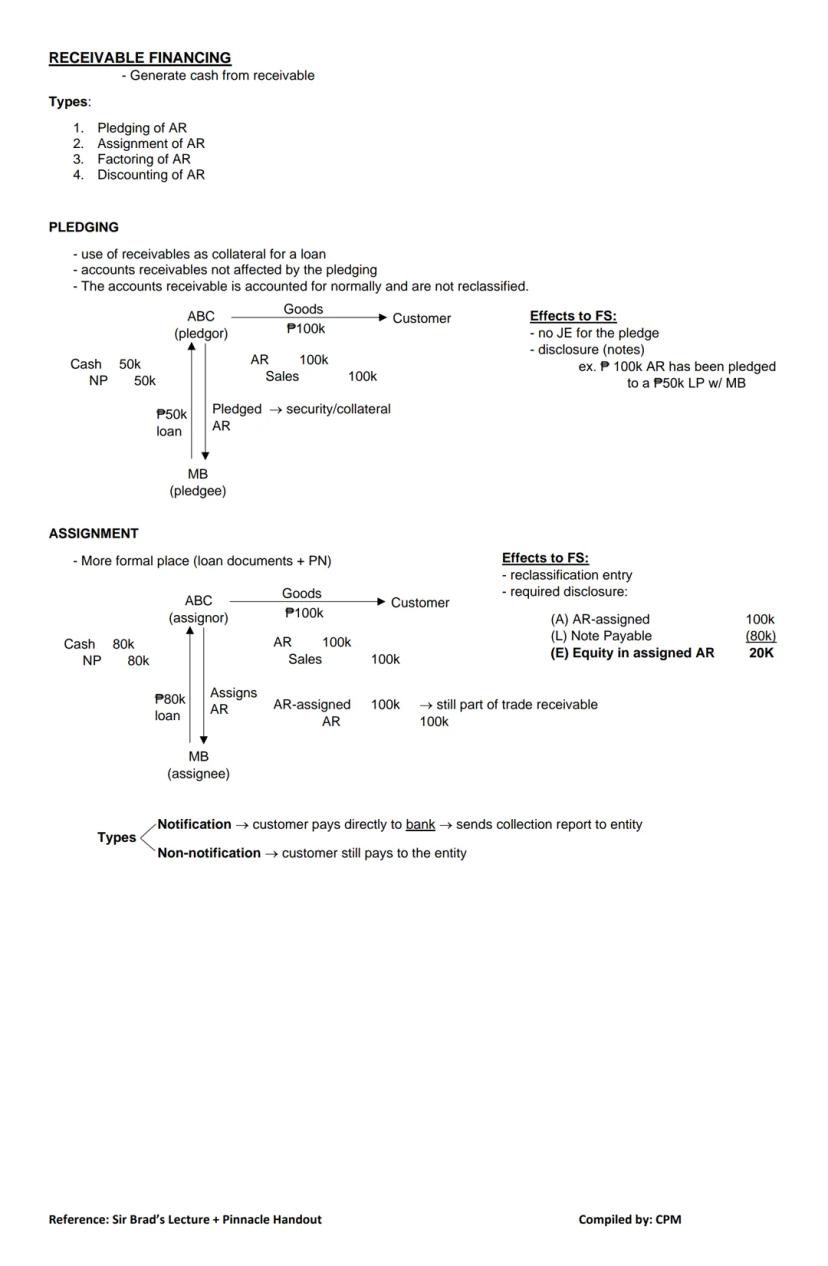
Receivable financing helps businesses generate immediate cash from their receivables. There are four main methods, each with different accounting implications.
1. Pledging of AR When pledging receivables:
For example, if you pledge $100,000 in receivables to secure a $50,000 loan from MB Bank, your receivables stay on your books while you record the loan as normal.
2. Assignment of AR Assignment is more formal than pledging:
With assignment, your financial statements must disclose:
(A) AR-assigned $100,000
(L) Note Payable ($80,000)
(E) Equity in assigned AR $20,000
💡 Unlike pledging, assignment requires you to reclassify your receivables as "AR-assigned," though they remain part of your total trade receivables.
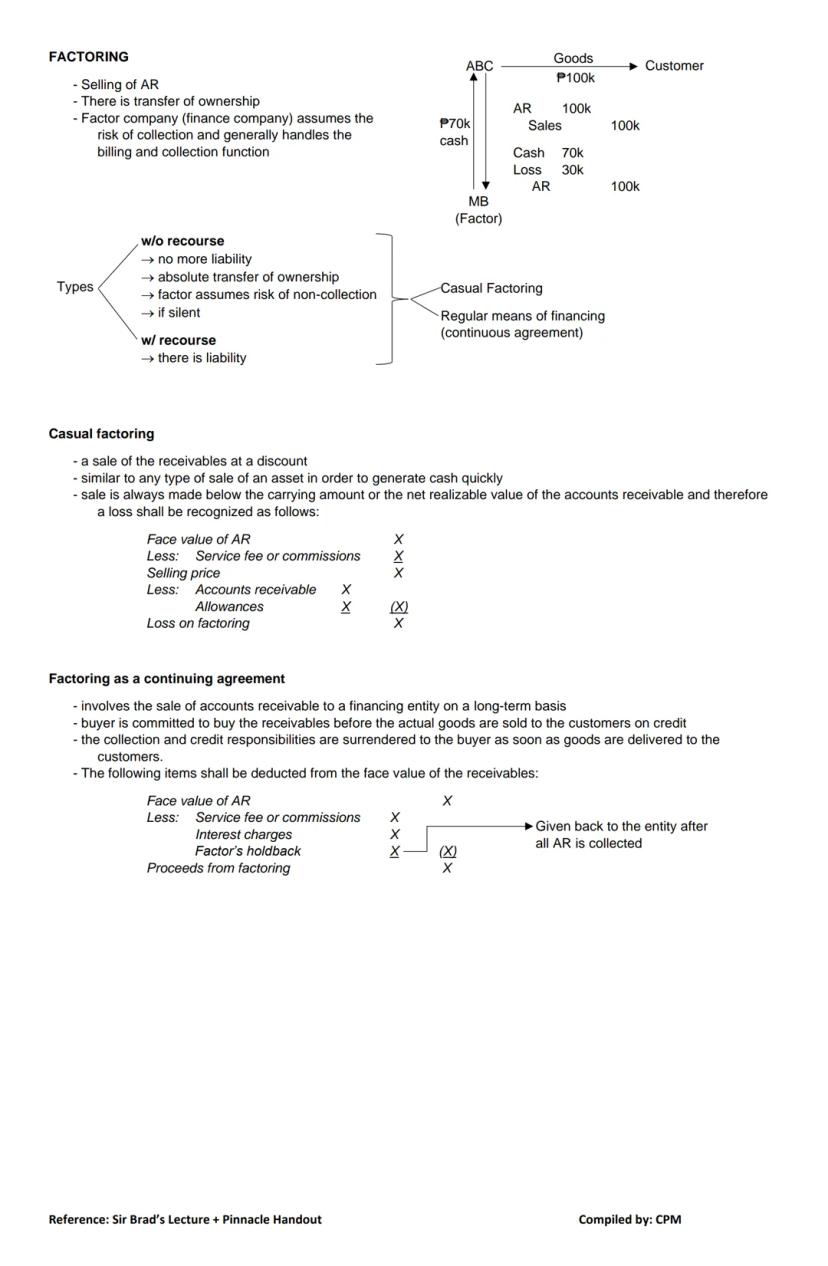
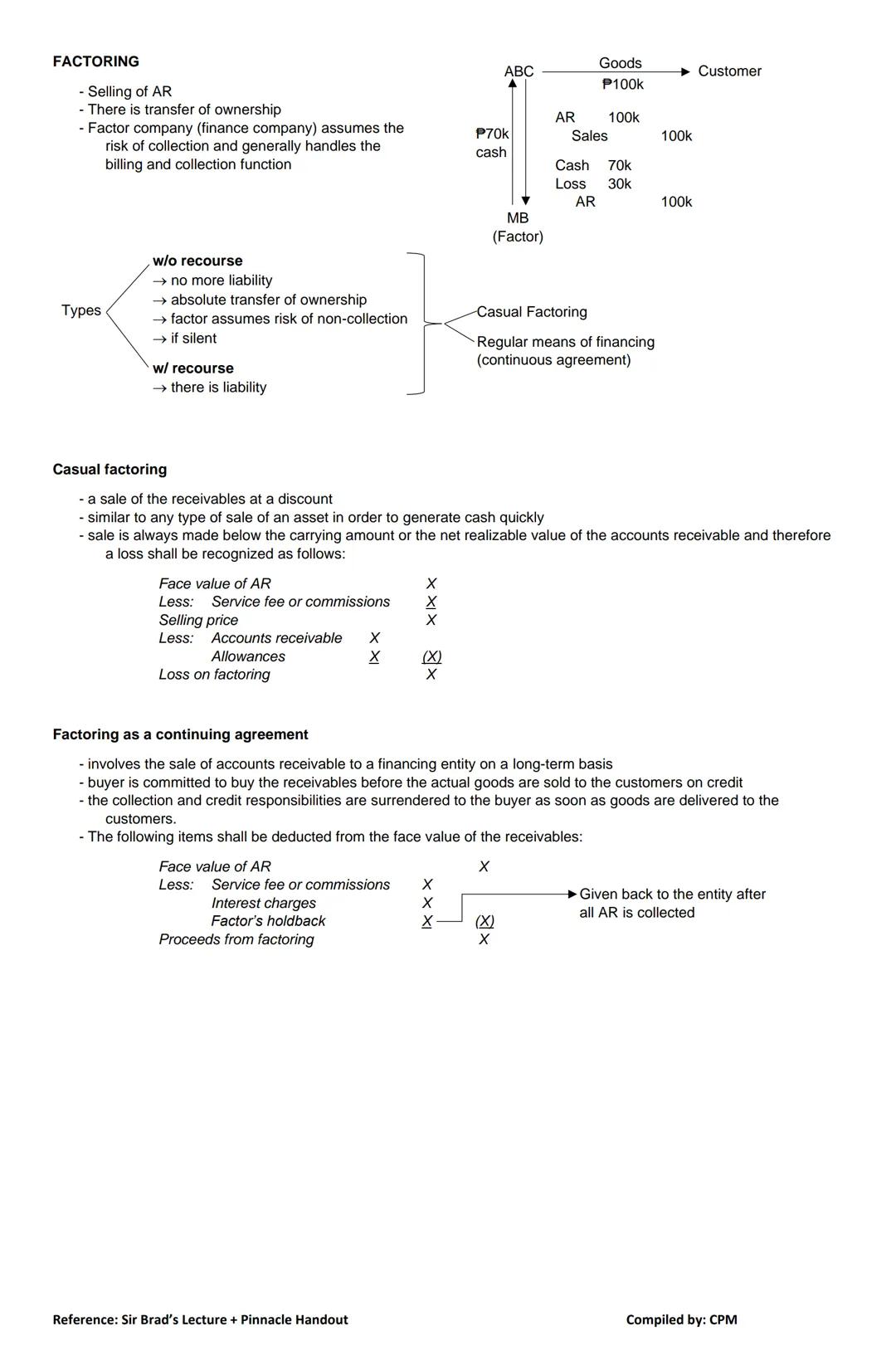
3. Factoring of AR Factoring involves selling your receivables:
When factoring receivables, you record:
Cash 70,000
Loss on factoring 30,000
Accounts Receivable 100,000
Factoring typically involves deductions for service fees, interest charges, and possibly a factor's holdback (returned after all receivables are collected).
Discounting is the process of selling a note receivable before its maturity date, typically to a bank at less than face value.
When you discount a note, you receive cash immediately rather than waiting for maturity. The bank deducts interest (the "discount") for the remaining time until maturity.
Types of Discounting:
For example, if you discount a $100,000 note to a bank for $80,000:
Under conditional sale accounting:
Cash 70,000
Loss on discounting 30,000
Notes receivable discounted 100,000
Under secured borrowing accounting:
Cash 70,000
Interest expense 30,000
Notes receivable discounted 100,000
💡 With recourse, "Notes receivable discounted" is a contra-asset account deducted from Notes Receivable on your balance sheet, reflecting your contingent liability.
Calculating Discount Proceeds:
Face value/principal X
Interest on maturity X
Maturity value X
Less: Discount (MV × DR × remaining term) (X)
Proceeds from discounting X
The discount rate is determined by the bank, but if not specified, use the same rate as on the note. The remaining term (or "discount period") is the time from discounting until maturity.
When recording the transaction, compare the total receivable (face value plus accrued interest) with the discounting proceeds and recognize the difference as a loss.

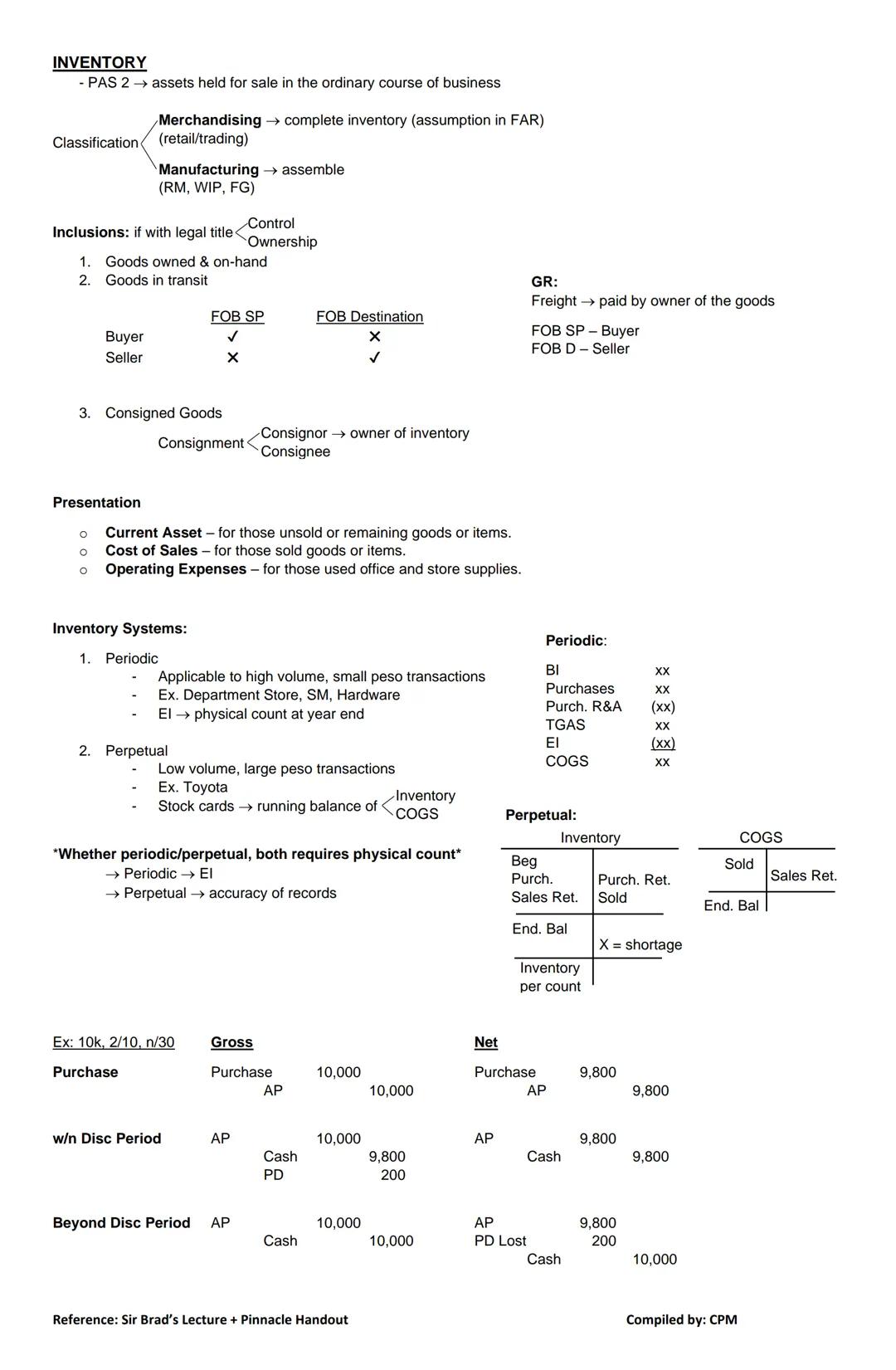
Inventory represents assets held for sale in the ordinary course of business. In merchandising businesses, inventory consists of goods purchased for resale.
Inclusions in Inventory: Items are included in inventory when you have both:
This means inventory includes:
Shipping Terms Matter:
Inventory Systems:
Periodic System:
Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inventory = COGS
Perpetual System:
💡 Both systems require physical inventory counts, but for different purposes. Periodic systems need counts to determine ending inventory, while perpetual systems use counts to verify accuracy of records.
Purchase Discounts: When recording purchases with terms like "10k, 2/10, n/30" (2% discount if paid within 10 days), you can use either:
Remember: Whether using periodic or perpetual inventory, freight costs paid by the owner of the goods (according to shipping terms) should be added to the cost of inventory.
Assigning costs to inventory is a critical accounting task. Three main methods are available under PAS 2:
1. Specific Identification
2. First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
3. Weighted Average (WAVE)
💡 In FIFO, inventory costs flow in the same order as physical goods, while in weighted average, all costs are blended together.
Inventory Measurement: Inventory must be measured at the Lower of Cost and Net Realizable Value (LCNRV):
This approach is conservative, ensuring inventory isn't overstated.
Purchase Commitments: When you enter agreements to buy inventory at fixed future prices:
Remember that purchase commitments are used to minimize risk of price increases but can result in losses if prices drop significantly.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
studywithnessa
@studywithnessa
Accounting principles can seem complex, but understanding the fundamentals is essential for tracking finances and making business decisions. This summary covers key accounting concepts from financial statement elements to specialized accounting treatments, providing clear explanations of how to record transactions... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Cash is more than just the coins and bills in your register. It encompasses all immediately available funds that a business can use without restriction.
Cash includes coins & currencies (cash on hand, petty cash), cash in bank (savings and demand deposits), and undeposited collections (money orders, remittances). Demand deposits are particularly important for businesses as they allow for both passbook access and check writing privileges.
When dealing with checks, understand the differences:
💡 Bank drafts are helpful for large purchases, as they provide guaranteed payment like a cashier's check but for much larger amounts.
Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that can be readily converted into cash. To qualify as a cash equivalent, investments must be debt instruments acquired three months or less before maturity. Examples include Treasury bills, short-term Treasury notes/bonds, time deposits, and money market placements.
Remember that legally restricted funds (like compensating balances for loans) aren't classified as cash equivalents. They're either classified as other current assets or other non-current assets .

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Bank reconciliation helps you match your book balance (what you've recorded) with your bank balance (what the bank shows). These two figures often differ due to timing differences.
Think of it this way: your books record cash increasing when you receive it, while the bank records increases when you deposit it. Similarly, your books show decreases when you write checks, but the bank only records them when they're presented for payment.
To reconcile your accounts, start with:
Key terms to understand:
💡 Remember that bank and book entries work in opposite directions! In your books, debits increase your cash balance while credits decrease it. On your bank statement, credits increase your balance while debits decrease it.
Petty Cash Fund Management: Managing petty cash requires three key steps:
If you need to increase the fund later, simply issue another check for the additional amount. At year-end, adjust any remaining expenses that haven't been recorded.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Receivables represent money owed to your business by others. Understanding how to classify and value them is crucial for accurate financial reporting.
Types of Receivables:
Within these categories, you'll find:
Other important receivables include:
💡 Customer credit balances are not receivables! They should be presented as current liabilities, not deducted from accounts receivable.
Measurement of Receivables: Initially, receivables are recorded at face value (selling price). Subsequently, they must be measured at net realizable value (NRV) – the amount you actually expect to collect.
To calculate NRV, you must deduct allowances for:
For example, if you offer terms of "5/10, n/30" (5% discount if paid within 10 days, net amount due within 30 days), you'll need to account for both gross and net methods of recording the transaction.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
When customers fail to pay, you need a system to account for these losses. There are two main approaches: the allowance method and the direct write-off method.
The allowance method anticipates bad debts before they occur:
The direct write-off method (used for tax purposes) only recognizes bad debts when they're definitely uncollectible:
Estimating Doubtful Accounts:
You can estimate bad debts using either:
💡 When calculating your bad debt expense for the year, start with your existing allowance, adjust for write-offs and recoveries, then determine how much additional expense is needed to reach your required ending balance.
Special Treatment of Receivables:

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Notes receivable are more secure than accounts receivable because they're formalized with a promissory note that specifies payment terms.
Measurement of Notes Receivable:
For example, if you receive a 2-year, $100,000 note with 10% interest payable annually:
💡 The difference between face value and present value is called "unearned interest income" and must be amortized over the life of the note.
Subsequent Measurement: After initial recognition, notes receivable are measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Amortized cost equals:
For non-interest bearing notes, amortized cost equals the present value plus amortization of the discount (or face value minus unamortized unearned interest income).

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Loans receivable are a special category of receivables found in financial institutions' books (like banks). Unlike regular notes receivable, loans receivable always include interest.
When a bank issues a loan, it records several important elements:
Origination costs include expenses like credit evaluation and appraisal fees. These can be handled in two ways:
Impairment Assessment: Under PFRS 9, lenders must assess credit risk and potential impairment using the Expected Credit Loss (ECL) model. This involves three stages:
💡 Impairment loss is calculated as the difference between the carrying amount of the loan and the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the original effective rate.
The journal entry for impairment typically involves:
Loan impairment loss XX
Interest receivable XX
Allowance for loan impairment XX
This write-down adjusts both the interest receivable that won't be collected and creates an allowance against the loan balance.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Receivable financing helps businesses generate immediate cash from their receivables. There are four main methods, each with different accounting implications.
1. Pledging of AR When pledging receivables:
For example, if you pledge $100,000 in receivables to secure a $50,000 loan from MB Bank, your receivables stay on your books while you record the loan as normal.
2. Assignment of AR Assignment is more formal than pledging:
With assignment, your financial statements must disclose:
(A) AR-assigned $100,000
(L) Note Payable ($80,000)
(E) Equity in assigned AR $20,000
💡 Unlike pledging, assignment requires you to reclassify your receivables as "AR-assigned," though they remain part of your total trade receivables.
3. Factoring of AR Factoring involves selling your receivables:
When factoring receivables, you record:
Cash 70,000
Loss on factoring 30,000
Accounts Receivable 100,000
Factoring typically involves deductions for service fees, interest charges, and possibly a factor's holdback (returned after all receivables are collected).

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Discounting is the process of selling a note receivable before its maturity date, typically to a bank at less than face value.
When you discount a note, you receive cash immediately rather than waiting for maturity. The bank deducts interest (the "discount") for the remaining time until maturity.
Types of Discounting:
For example, if you discount a $100,000 note to a bank for $80,000:
Under conditional sale accounting:
Cash 70,000
Loss on discounting 30,000
Notes receivable discounted 100,000
Under secured borrowing accounting:
Cash 70,000
Interest expense 30,000
Notes receivable discounted 100,000
💡 With recourse, "Notes receivable discounted" is a contra-asset account deducted from Notes Receivable on your balance sheet, reflecting your contingent liability.
Calculating Discount Proceeds:
Face value/principal X
Interest on maturity X
Maturity value X
Less: Discount (MV × DR × remaining term) (X)
Proceeds from discounting X
The discount rate is determined by the bank, but if not specified, use the same rate as on the note. The remaining term (or "discount period") is the time from discounting until maturity.
When recording the transaction, compare the total receivable (face value plus accrued interest) with the discounting proceeds and recognize the difference as a loss.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Inventory represents assets held for sale in the ordinary course of business. In merchandising businesses, inventory consists of goods purchased for resale.
Inclusions in Inventory: Items are included in inventory when you have both:
This means inventory includes:
Shipping Terms Matter:
Inventory Systems:
Periodic System:
Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inventory = COGS
Perpetual System:
💡 Both systems require physical inventory counts, but for different purposes. Periodic systems need counts to determine ending inventory, while perpetual systems use counts to verify accuracy of records.
Purchase Discounts: When recording purchases with terms like "10k, 2/10, n/30" (2% discount if paid within 10 days), you can use either:
Remember: Whether using periodic or perpetual inventory, freight costs paid by the owner of the goods (according to shipping terms) should be added to the cost of inventory.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Assigning costs to inventory is a critical accounting task. Three main methods are available under PAS 2:
1. Specific Identification
2. First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
3. Weighted Average (WAVE)
💡 In FIFO, inventory costs flow in the same order as physical goods, while in weighted average, all costs are blended together.
Inventory Measurement: Inventory must be measured at the Lower of Cost and Net Realizable Value (LCNRV):
This approach is conservative, ensuring inventory isn't overstated.
Purchase Commitments: When you enter agreements to buy inventory at fixed future prices:
Remember that purchase commitments are used to minimize risk of price increases but can result in losses if prices drop significantly.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
30
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user