Bone tissue is much more than just a rigid support... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
75
•
Feb 12, 2026
•
Jorden Forrester
@jordenforrester
Bone tissue is much more than just a rigid support... Show more







Your skeleton is far from the lifeless structure you might imagine - it's actually a complex, living system that's constantly changing. Bones are dynamic tissues filled with cells, nerves, and blood vessels that continuously rebuild themselves and interact with other body systems.
Osteology, the study of bone, reveals that these remarkable structures do much more than just provide support. They protect vital organs, enable movement, store minerals, produce blood cells, and even help maintain your body's acid-base balance.
Fun Fact: Your entire skeleton regenerates completely every 10 years! About 10% of your bone tissue is replaced annually through the process of bone remodeling.

Your skeletal system consists of more than just bones - it's a complex network of different tissues working together. Cartilage serves as the forerunner of most bones and continues to cover many joint surfaces in adults. Ligaments connect bones to other bones at joints (like the ACL in your knee), while tendons attach muscles to bones (like the Achilles tendon at your heel).
The skeleton serves six critical functions in your body. It provides structural support for your entire body and protects vital organs like your brain and heart. Your bones enable movement by serving as levers for your muscles to pull against and help maintain proper electrolyte and acid-base balance in your blood by storing and releasing minerals as needed.
Perhaps most surprisingly, your bones are responsible for blood formation - the red bone marrow inside certain bones produces most of your blood cells!

Bone (osseous tissue) is a specialized connective tissue with a matrix hardened by calcium phosphate and other minerals. This hardening process, called mineralization or calcification, gives bones their characteristic strength and rigidity.
Individual bones are complex organs containing multiple tissue types - not just bone tissue, but also blood vessels, bone marrow, cartilage, adipose tissue, nerves, and fibrous connective tissue all working together.
Bones come in four main shapes, each suited to different functions. Flat bones like your skull protect soft organs. Long bones in your limbs act as rigid levers for movement. Short bones like those in your wrist provide stability with mobility. Irregular bones like your vertebrae have complex shapes that serve specialized functions.
Remember: Bones are living organs, not just hard structural supports. They contain numerous tissues and constantly remodel themselves throughout your life.

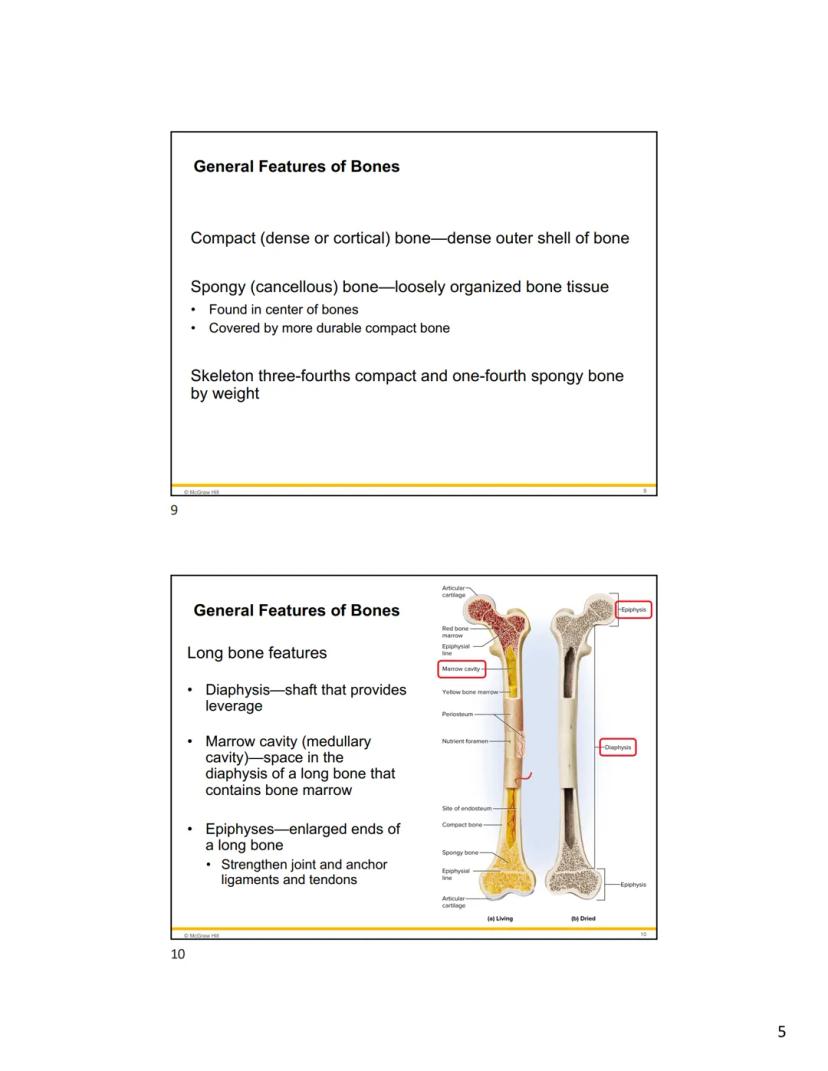
Looking at a cross-section of bone, you'll see two distinct arrangements. Compact bone (also called dense or cortical bone) forms the tough outer shell, while spongy bone (or cancellous bone) creates a lightweight, honeycomb-like internal structure. This smart design gives bones maximum strength with minimum weight - about three-fourths of your skeleton is compact bone and one-fourth is spongy bone.
Long bones like your femur (thigh bone) have specific structural features that help them function. The diaphysis is the central shaft that provides leverage. Inside this shaft is the marrow cavity (medullary cavity) containing bone marrow. At each end of a long bone is an epiphysis, which strengthens the joint and anchors ligaments and tendons.
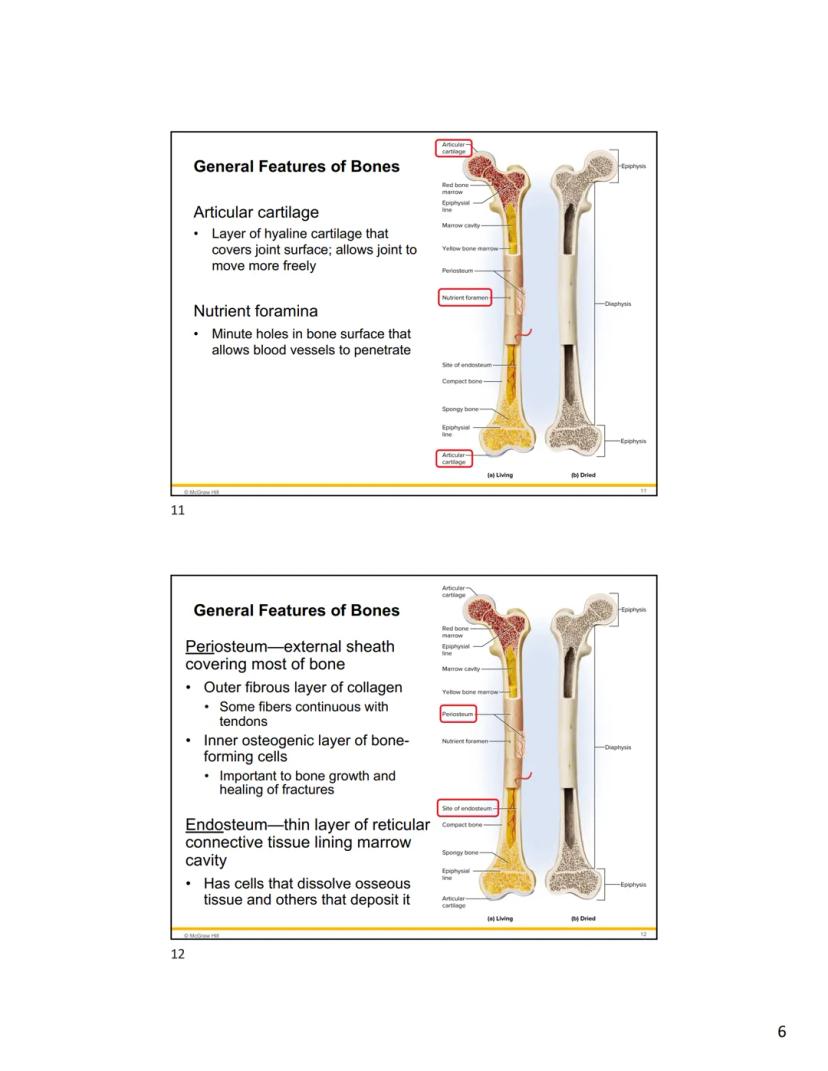
Joint surfaces are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth layer of hyaline cartilage that allows for frictionless movement. Throughout the bone's surface, you'll find tiny nutrient foramina - small holes that allow blood vessels to enter the bone and supply it with nutrients.
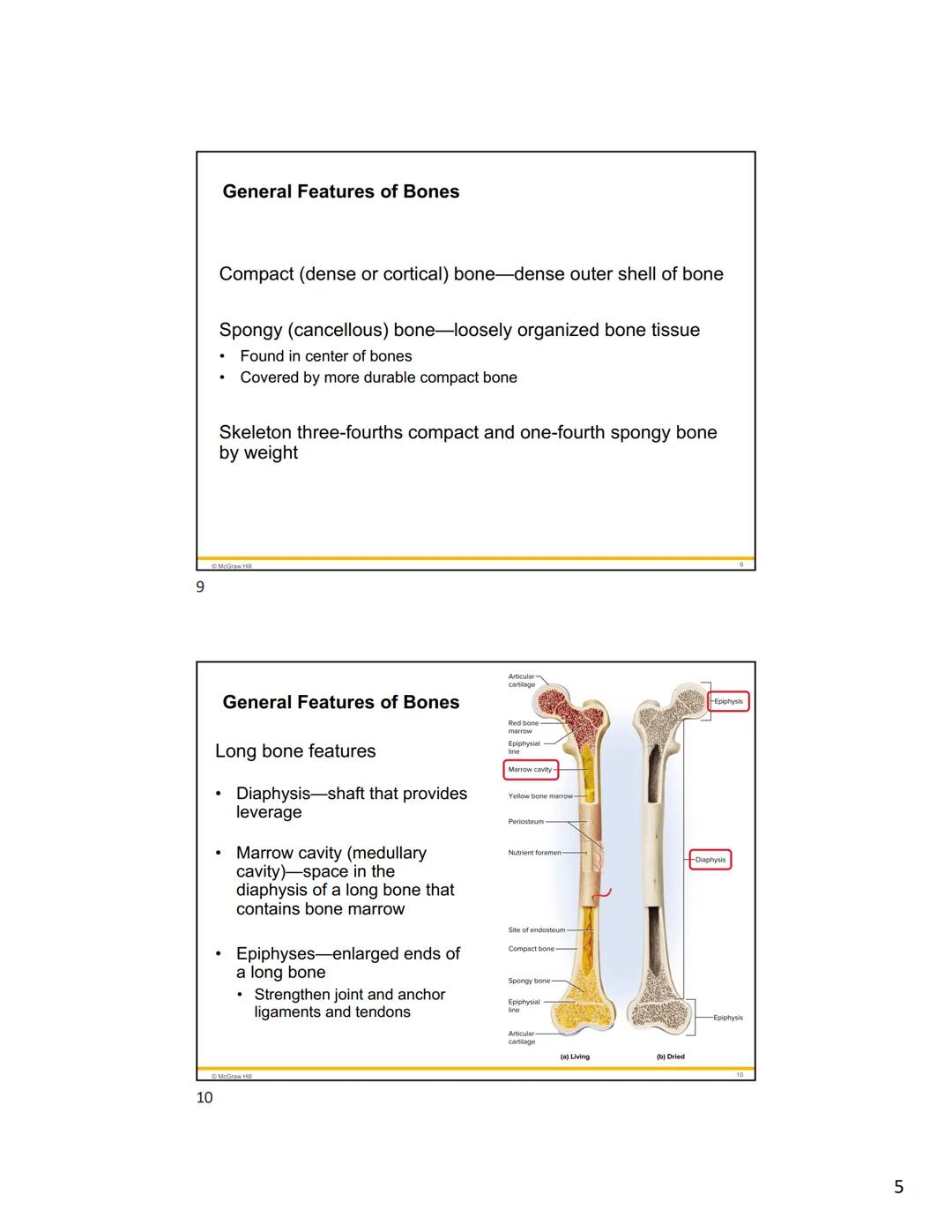
Your bones are wrapped in protective coverings that are essential for their health and growth. The periosteum is a tough external sheath covering most of the bone's surface. It has two layers: an outer fibrous layer made of collagen (some fibers connect with tendons) and an inner osteogenic layer containing bone-forming cells that are crucial for bone growth and fracture healing.
Inside the bone, a thin layer of tissue called the endosteum lines the marrow cavity. This layer contains both cells that dissolve bone tissue and others that deposit new bone, allowing for internal remodeling.
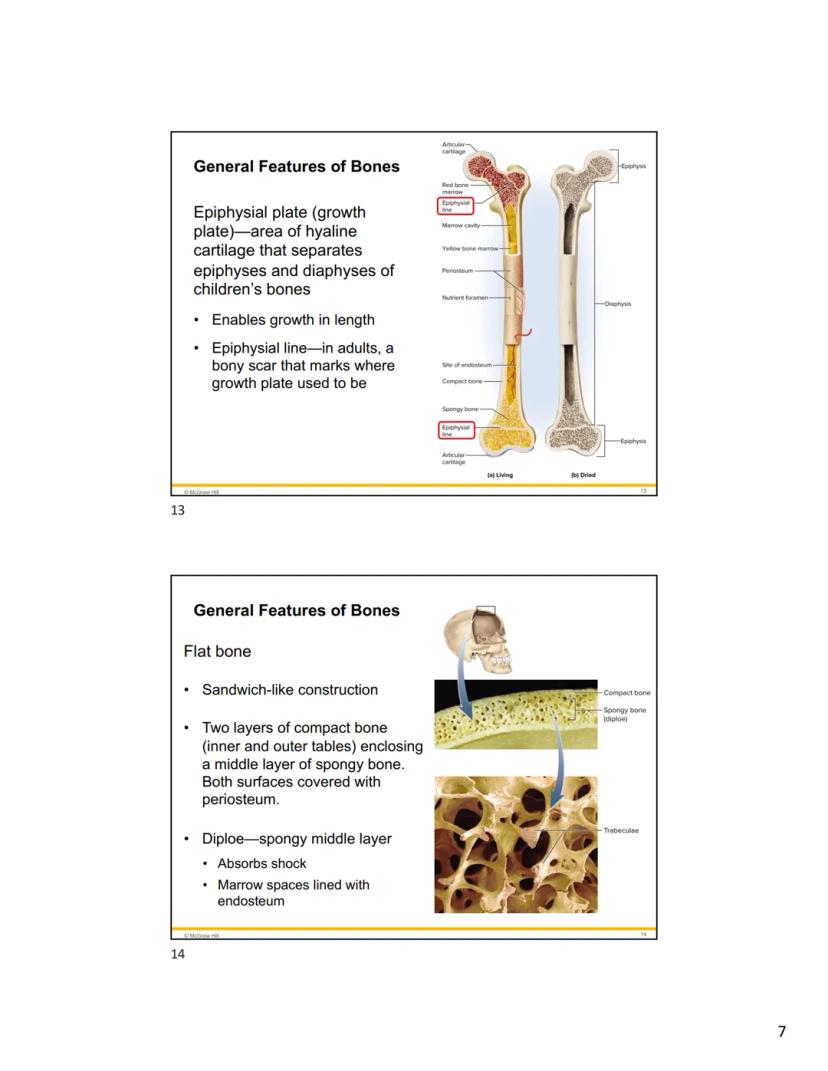
In children and adolescents, long bones have epiphysial plates (growth plates) - areas of hyaline cartilage between the epiphyses and diaphysis that enable the bone to grow in length. Once growth stops, these plates close and leave behind epiphysial lines - visible bony scars in adult bones.
Did you know? The growth plates in your bones close at different times. That's why some parts of your body may finish growing before others!
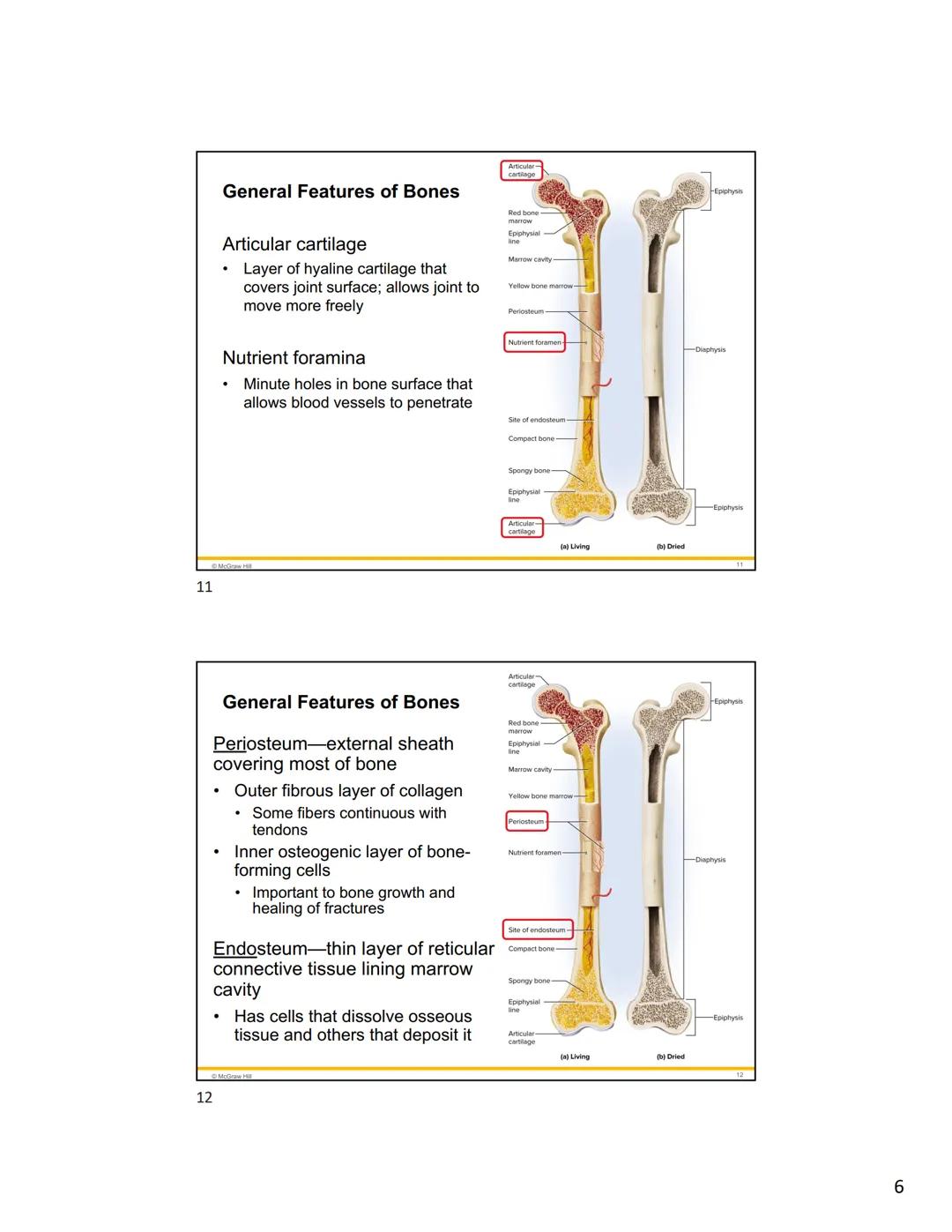
Flat bones like those in your skull have a sandwich-like construction that makes them both protective and lightweight. They consist of two layers of compact bone (called the inner and outer tables) with a middle layer of spongy bone between them. This spongy middle layer is called the diploe.
This clever design allows flat bones to absorb shock effectively while still being strong enough to protect vital organs like your brain. Both the inner and outer surfaces of flat bones are covered with periosteum, while the marrow spaces within the spongy bone are lined with endosteum.
The structure of bones perfectly matches their functions - flat bones protect, long bones provide leverage for movement, and all bones combine strength with relative lightness through their arrangement of compact and spongy bone.
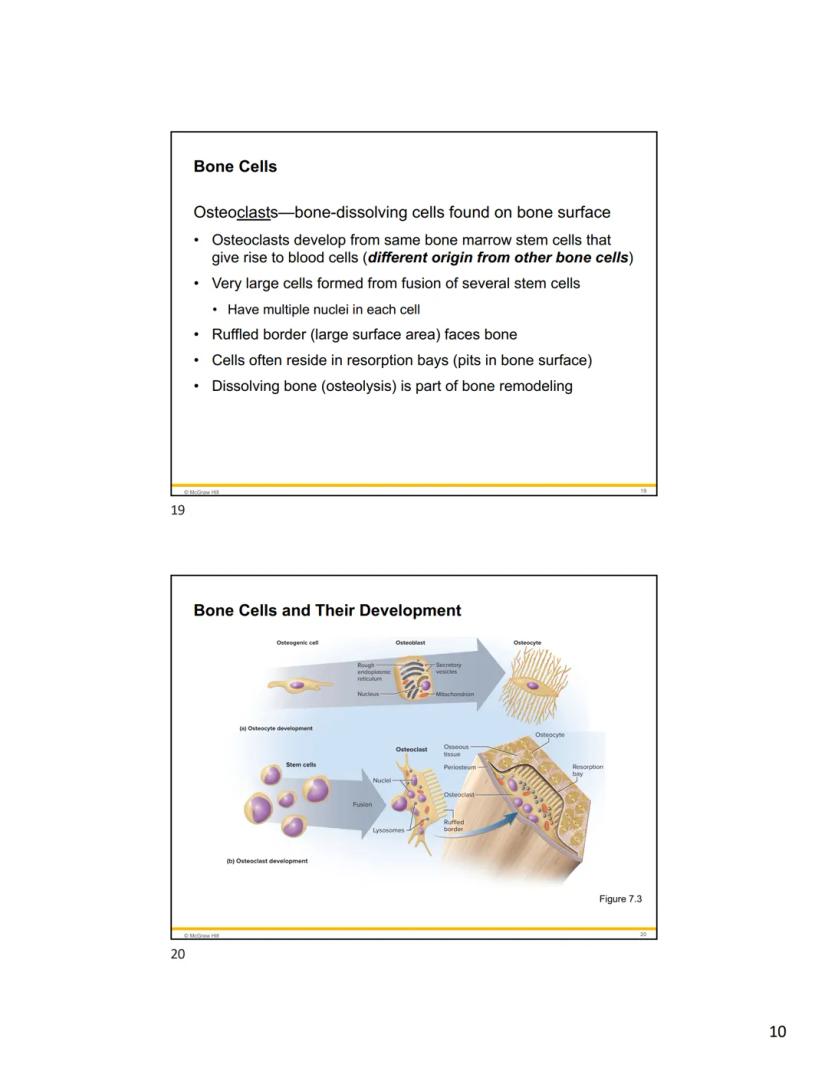
Bone tissue contains four specialized cell types that work together to build, maintain, and remodel your skeleton. Osteogenic cells are stem cells found in the endosteum and inner layer of periosteum. These cells continuously divide and give rise to most other bone cell types.
Osteoblasts are the bone-forming cells that line up on bone surfaces. They synthesize the soft organic matrix of bone, which then hardens through mineral deposition (osteogenesis). When you experience physical stress on a bone, osteogenic cells multiply rapidly and increase the number of osteoblasts to reinforce the bone.
Osteocytes are former osteoblasts that have become trapped in the matrix they created. They reside in tiny cavities called lacunae connected by small channels called canaliculi. Their cellular processes extend through these channels, allowing neighboring cells to communicate and exchange nutrients. Osteocytes function as strain sensors - when bone is stressed, they produce signals that regulate bone remodeling.
Important: Your bones aren't static structures - they're constantly being reshaped by these specialized cells in response to the stresses placed on them. That's why exercise strengthens bones!

Osteoclasts are the large, multinucleated cells responsible for dissolving bone tissue. Unlike other bone cells, they develop from the same bone marrow stem cells that produce blood cells. With their distinctive ruffled border facing the bone surface, osteoclasts create resorption bays (small pits) as they break down bone matrix. This process of bone dissolution (osteolysis) is a crucial part of normal bone remodeling.
The matrix of bone tissue contains both organic and inorganic components that give it its unique properties. The organic portion, synthesized by osteoblasts, consists of collagen and carbohydrate-protein complexes. The inorganic portion includes minerals like hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate salt), calcium carbonate, and trace amounts of other minerals.
Bone is essentially a composite material - combining a ceramic component (minerals) that provides compression strength with a polymer component (collagen) that provides flexibility. This combination allows bones to support your body weight without sagging while still having some flexibility to prevent easy fracturing.

The balance between mineral and protein components in bone is crucial for proper function. When either component is deficient, serious bone disorders can result. Rickets is caused by mineral deficiency, resulting in soft, deformed bones that cannot properly support body weight. Conversely, osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease) results from a defect in collagen deposition, making bones dangerously fragile.
The microscopic structure of compact bone reveals osteons (haversian systems) - cylindrical units running lengthwise through the bone. Each osteon consists of concentric rings of bone matrix (lamellae) surrounding a central canal that contains blood vessels and nerves. Between osteons are irregular regions filled with interstitial lamellae, while the outer region of dense bone contains circumferential lamellae.
Throughout this structure, tiny cavities called lacunae house the osteocytes, with microscopic channels (canaliculi) connecting these spaces and allowing for cellular communication and nutrient exchange.
Think about it: The microscopic architecture of bone is like a well-designed building - with support structures precisely positioned to handle stress while allowing for maintenance and communication throughout.

Spongy bone has a completely different structure from compact bone. Instead of organized osteons, it consists of a lattice of thin plates or beams called trabeculae covered with endosteum. The spaces between trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow.
Unlike compact bone, spongy bone doesn't contain central canals. Since all osteocytes are close to the bone marrow, they can receive nutrients directly from it. This design provides strength with minimal weight - trabeculae naturally develop along the bone's lines of stress, creating an internal framework optimized for the forces typically applied to that bone.
The femur (thigh bone) provides an excellent example of this adaptive structure. The trabeculae in the head of the femur form an elaborate pattern that perfectly aligns with the lines of stress created when you stand, walk, or run. This allows the bone to support tremendous weight while remaining relatively light.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Jorden Forrester
@jordenforrester
Bone tissue is much more than just a rigid support system for your body. It's a dynamic, living tissue full of cells, blood vessels, and nerves that constantly remodels itself. This chapter explores the composition of bone tissue, how it... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Your skeleton is far from the lifeless structure you might imagine - it's actually a complex, living system that's constantly changing. Bones are dynamic tissues filled with cells, nerves, and blood vessels that continuously rebuild themselves and interact with other body systems.
Osteology, the study of bone, reveals that these remarkable structures do much more than just provide support. They protect vital organs, enable movement, store minerals, produce blood cells, and even help maintain your body's acid-base balance.
Fun Fact: Your entire skeleton regenerates completely every 10 years! About 10% of your bone tissue is replaced annually through the process of bone remodeling.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Your skeletal system consists of more than just bones - it's a complex network of different tissues working together. Cartilage serves as the forerunner of most bones and continues to cover many joint surfaces in adults. Ligaments connect bones to other bones at joints (like the ACL in your knee), while tendons attach muscles to bones (like the Achilles tendon at your heel).
The skeleton serves six critical functions in your body. It provides structural support for your entire body and protects vital organs like your brain and heart. Your bones enable movement by serving as levers for your muscles to pull against and help maintain proper electrolyte and acid-base balance in your blood by storing and releasing minerals as needed.
Perhaps most surprisingly, your bones are responsible for blood formation - the red bone marrow inside certain bones produces most of your blood cells!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Bone (osseous tissue) is a specialized connective tissue with a matrix hardened by calcium phosphate and other minerals. This hardening process, called mineralization or calcification, gives bones their characteristic strength and rigidity.
Individual bones are complex organs containing multiple tissue types - not just bone tissue, but also blood vessels, bone marrow, cartilage, adipose tissue, nerves, and fibrous connective tissue all working together.
Bones come in four main shapes, each suited to different functions. Flat bones like your skull protect soft organs. Long bones in your limbs act as rigid levers for movement. Short bones like those in your wrist provide stability with mobility. Irregular bones like your vertebrae have complex shapes that serve specialized functions.
Remember: Bones are living organs, not just hard structural supports. They contain numerous tissues and constantly remodel themselves throughout your life.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Looking at a cross-section of bone, you'll see two distinct arrangements. Compact bone (also called dense or cortical bone) forms the tough outer shell, while spongy bone (or cancellous bone) creates a lightweight, honeycomb-like internal structure. This smart design gives bones maximum strength with minimum weight - about three-fourths of your skeleton is compact bone and one-fourth is spongy bone.
Long bones like your femur (thigh bone) have specific structural features that help them function. The diaphysis is the central shaft that provides leverage. Inside this shaft is the marrow cavity (medullary cavity) containing bone marrow. At each end of a long bone is an epiphysis, which strengthens the joint and anchors ligaments and tendons.
Joint surfaces are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth layer of hyaline cartilage that allows for frictionless movement. Throughout the bone's surface, you'll find tiny nutrient foramina - small holes that allow blood vessels to enter the bone and supply it with nutrients.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Your bones are wrapped in protective coverings that are essential for their health and growth. The periosteum is a tough external sheath covering most of the bone's surface. It has two layers: an outer fibrous layer made of collagen (some fibers connect with tendons) and an inner osteogenic layer containing bone-forming cells that are crucial for bone growth and fracture healing.
Inside the bone, a thin layer of tissue called the endosteum lines the marrow cavity. This layer contains both cells that dissolve bone tissue and others that deposit new bone, allowing for internal remodeling.
In children and adolescents, long bones have epiphysial plates (growth plates) - areas of hyaline cartilage between the epiphyses and diaphysis that enable the bone to grow in length. Once growth stops, these plates close and leave behind epiphysial lines - visible bony scars in adult bones.
Did you know? The growth plates in your bones close at different times. That's why some parts of your body may finish growing before others!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Flat bones like those in your skull have a sandwich-like construction that makes them both protective and lightweight. They consist of two layers of compact bone (called the inner and outer tables) with a middle layer of spongy bone between them. This spongy middle layer is called the diploe.
This clever design allows flat bones to absorb shock effectively while still being strong enough to protect vital organs like your brain. Both the inner and outer surfaces of flat bones are covered with periosteum, while the marrow spaces within the spongy bone are lined with endosteum.
The structure of bones perfectly matches their functions - flat bones protect, long bones provide leverage for movement, and all bones combine strength with relative lightness through their arrangement of compact and spongy bone.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Bone tissue contains four specialized cell types that work together to build, maintain, and remodel your skeleton. Osteogenic cells are stem cells found in the endosteum and inner layer of periosteum. These cells continuously divide and give rise to most other bone cell types.
Osteoblasts are the bone-forming cells that line up on bone surfaces. They synthesize the soft organic matrix of bone, which then hardens through mineral deposition (osteogenesis). When you experience physical stress on a bone, osteogenic cells multiply rapidly and increase the number of osteoblasts to reinforce the bone.
Osteocytes are former osteoblasts that have become trapped in the matrix they created. They reside in tiny cavities called lacunae connected by small channels called canaliculi. Their cellular processes extend through these channels, allowing neighboring cells to communicate and exchange nutrients. Osteocytes function as strain sensors - when bone is stressed, they produce signals that regulate bone remodeling.
Important: Your bones aren't static structures - they're constantly being reshaped by these specialized cells in response to the stresses placed on them. That's why exercise strengthens bones!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Osteoclasts are the large, multinucleated cells responsible for dissolving bone tissue. Unlike other bone cells, they develop from the same bone marrow stem cells that produce blood cells. With their distinctive ruffled border facing the bone surface, osteoclasts create resorption bays (small pits) as they break down bone matrix. This process of bone dissolution (osteolysis) is a crucial part of normal bone remodeling.
The matrix of bone tissue contains both organic and inorganic components that give it its unique properties. The organic portion, synthesized by osteoblasts, consists of collagen and carbohydrate-protein complexes. The inorganic portion includes minerals like hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate salt), calcium carbonate, and trace amounts of other minerals.
Bone is essentially a composite material - combining a ceramic component (minerals) that provides compression strength with a polymer component (collagen) that provides flexibility. This combination allows bones to support your body weight without sagging while still having some flexibility to prevent easy fracturing.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The balance between mineral and protein components in bone is crucial for proper function. When either component is deficient, serious bone disorders can result. Rickets is caused by mineral deficiency, resulting in soft, deformed bones that cannot properly support body weight. Conversely, osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease) results from a defect in collagen deposition, making bones dangerously fragile.
The microscopic structure of compact bone reveals osteons (haversian systems) - cylindrical units running lengthwise through the bone. Each osteon consists of concentric rings of bone matrix (lamellae) surrounding a central canal that contains blood vessels and nerves. Between osteons are irregular regions filled with interstitial lamellae, while the outer region of dense bone contains circumferential lamellae.
Throughout this structure, tiny cavities called lacunae house the osteocytes, with microscopic channels (canaliculi) connecting these spaces and allowing for cellular communication and nutrient exchange.
Think about it: The microscopic architecture of bone is like a well-designed building - with support structures precisely positioned to handle stress while allowing for maintenance and communication throughout.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Spongy bone has a completely different structure from compact bone. Instead of organized osteons, it consists of a lattice of thin plates or beams called trabeculae covered with endosteum. The spaces between trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow.
Unlike compact bone, spongy bone doesn't contain central canals. Since all osteocytes are close to the bone marrow, they can receive nutrients directly from it. This design provides strength with minimal weight - trabeculae naturally develop along the bone's lines of stress, creating an internal framework optimized for the forces typically applied to that bone.
The femur (thigh bone) provides an excellent example of this adaptive structure. The trabeculae in the head of the femur form an elaborate pattern that perfectly aligns with the lines of stress created when you stand, walk, or run. This allows the bone to support tremendous weight while remaining relatively light.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
2
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user