Cell biology is the foundation of understanding how our bodies... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
114
•
Feb 13, 2026
•
Giana Lynch
@gianalynch_dpez
Cell biology is the foundation of understanding how our bodies... Show more









Ever wonder how a microscopic cell can perform all the functions needed to keep you alive? Cells contain specialized structures called organelles that each have specific jobs. The nucleus serves as the control center, housing most of the cell's DNA and genetic information. Surrounding the nucleus is the nuclear membrane, which separates it from the rest of the cell.
The cell membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that determines what enters and leaves the cell. Inside the cell, the cytoplasm consists of the gel-like cytosol and various organelles. Mitochondria, known as the "power plants" of cells, produce most of the energy (ATP) the cell needs to function.
Protein production involves several organelles working together. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is dotted with ribosomes that synthesize proteins, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) focuses on lipid and steroid synthesis. The Golgi apparatus finishes and packages proteins for export from the cell, and lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that "clean house" within the cell.
💡 Think of the cell as a tiny city: the nucleus is the city hall (control center), mitochondria are power plants, lysosomes are the sanitation department, and the cell membrane is the city limits with controlled entry points.
The cell also has structural components like microtubules that maintain cell shape and assist with movement. External projections such as cilia (short) and flagella (long) help cells move or move substances around them. Finally, centrioles play an important role during cell division.

How do substances move into and out of cells? Cells use various transport mechanisms to maintain balance and function. Diffusion is the most common method, where molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without using energy.
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion where water moves across a membrane from an area with more water to an area with less water. When cells need help moving certain molecules across the membrane, they use facilitated diffusion, which uses helper molecules but still doesn't require energy. These three methods are all forms of passive transport, meaning they don't require energy.
Sometimes cells need to move substances against their concentration gradient, which requires energy. The active transport pump uses ATP to move molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. For example, cells must actively pump potassium into the cell even when there's already more potassium inside than outside.
🔑 Understanding transport mechanisms is crucial for explaining many biological processes, from how medicines enter cells to why drinking salt water causes dehydration!
Cells can also transport larger materials through processes like phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), and exocytosis (cellular export). Filtration is another transport mechanism where pressure forces water and dissolved substances across a membrane, as happens in your kidneys and blood vessels.
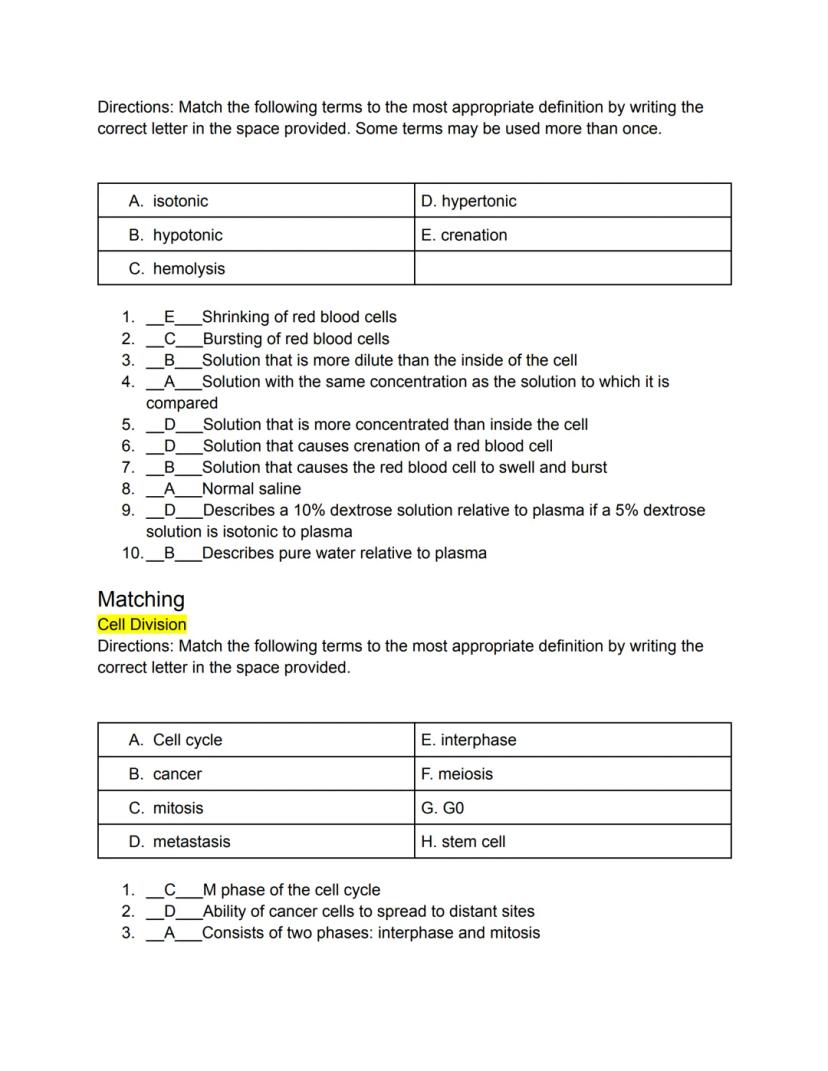
The concentration of solutions affects how cells interact with their environment. Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutions and how they affect cells. An isotonic solution has the same concentration as the cell's interior (like normal saline), causing no net movement of water.
A hypertonic solution is more concentrated than the cell's interior, causing water to move out of the cell. In red blood cells, this leads to crenation or shrinking. Conversely, a hypotonic solution is more dilute than the cell's interior, causing water to flow into the cell. In red blood cells, this can lead to swelling and eventually hemolysis (bursting).
Cell division is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and mitosis. During interphase (G₁, S, and G₂ phases), the cell grows and replicates its DNA. Mitosis (the M phase) is the actual division process with four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
📌 Remember: Regular cells divide by mitosis (resulting in identical copies), while reproductive cells divide by meiosis (resulting in cells with half the genetic material).
Some cells enter a G₀ phase where they stop dividing. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can specialize into different cell types through a process called differentiation. When cell division becomes uncontrolled, cancer can develop, which may lead to metastasis (spreading to other parts of the body).

Transport mechanisms are constantly at work in your body to maintain homeostasis. When you smell a skunk's spray, you're experiencing diffusion as the odor molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration. This passive transport happens without energy expenditure, making it efficient but limited by concentration gradients.
The active transport pump is crucial for cellular function, particularly the sodium-potassium pump. Unlike passive mechanisms, active transport requires ATP energy to move substances against their concentration gradients. This process is essential for nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and maintaining cell volume.
Cell membranes are selectively permeable, allowing some substances to pass while blocking others. This selective nature is vital for maintaining the internal environment of cells. The membrane contains specialized structures like microvilli and cilia that help with absorption and movement of substances around the cell.
⚡ Active transport is like pushing a boulder uphill—it requires energy input—while diffusion is like rolling downhill, happening naturally without energy.
Specialized cells have adapted their transport mechanisms for specific functions. For example, intestinal cells have extensive microvilli to increase surface area for absorption, while respiratory cells use cilia to move mucus and trapped particles away from the lungs. These specialized structures highlight how cell function follows cell structure.

Have you ever wondered how cells specialize for different jobs in your body? Differentiation is the process where unspecialized cells develop into specialized types like muscle, nerve, or blood cells. This remarkable transformation allows our bodies to perform countless complex functions with specialized cells.
The cell membrane serves as a gatekeeper for the cell. It's not just a simple barrier but a complex, selectively permeable structure that controls what enters and exits. This selective nature is crucial for maintaining the cell's internal environment and allowing communication with other cells.
Inside the cell, numerous organelles work together like a well-organized factory. Ribosomes are protein-making factories found either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or floating freely in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria are the cell's power plants, producing energy through cellular respiration. Lysosomes serve as the cell's cleanup crew, containing enzymes that break down cellular waste.
🧪 Imagine lysosomes as tiny recycling centers within the cell—they break down waste materials and damaged organelles so the components can be reused!
Cell division occurs through a carefully orchestrated process called mitosis, which includes four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Before division begins, the cell goes through interphase, which includes the G₁, S (DNA synthesis), and G₂ phases. Understanding this cycle is essential for comprehending both normal growth and abnormal conditions like cancer.

The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) functions as the cell's manufacturing and transport system. The rough endoplasmic reticulum contains ribosomes on its surface, giving it a bumpy appearance. This specialized structure is dedicated to protein synthesis and forms channels that guide newly created proteins through the cell.
When studying cellular transport, understanding concentration gradients is essential. Consider a beaker with two compartments: one with 25% glucose and one with 5% glucose. If the membrane allows both water and glucose to pass, diffusion will move glucose from high concentration (25%) to low concentration (5%). Simultaneously, water moves in the opposite direction through osmosis.
If the membrane only permits water to pass (not glucose), water will still move toward the higher glucose concentration through osmosis. This principle explains why drinking seawater dehydrates you—water leaves your cells to dilute the saltier external environment.
💧 Your cells constantly balance water movement through osmosis. This is why proper hydration is crucial—it helps maintain the right balance of water inside and outside your cells!
Sometimes cells need to move substances against concentration gradients, which requires active transport. Unlike diffusion, which moves substances from high to low concentration, active transport can move substances from low to high concentration but requires energy (ATP) to do so. This mechanism is essential for many cellular processes, including nutrient uptake and waste removal.

Blood vessels showcase fascinating transport principles at work. In capillaries, filtration occurs when blood pressure forces water and dissolved substances out of the vessels into surrounding tissues. This happens primarily at the arterial end of capillaries where pressure is higher (around 35 mm Hg). At the venous end, where pressure drops (to about 7 mm Hg), osmosis draws water back into the bloodstream, influenced by the plasma's oncotic pressure.
Understanding different transport mechanisms helps explain how medications work and why certain medical conditions develop. Passive transport (diffusion, osmosis) requires no energy, while active transport uses energy to move substances against concentration gradients. Knowing which mechanism is involved helps predict how substances will move throughout the body.
Cell abnormalities can lead to various conditions, including tumors. A neoplasm refers to any new and abnormal tissue growth, which can be benign or malignant. Benign neoplasms typically have well-differentiated cells that resemble their tissue of origin and don't spread to other body parts. In contrast, cancerous (malignant) neoplasms often have poorly differentiated cells and the ability to metastasize (spread to distant locations).
🔬 When doctors perform a biopsy, they're collecting tissue samples to examine cell characteristics. This helps determine if a tumor is benign or malignant, which guides treatment decisions.
Different cell types have specific characteristics that reflect their function. For example, muscle cells contain numerous mitochondria to provide energy for contraction, while cells that produce hormones have extensive RER and Golgi apparatus for protein synthesis and secretion. The number and type of organelles in a cell directly relate to its specialized function.

The cell membrane is a remarkable structure that determines what enters and leaves the cell. This selectively permeable barrier consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that act as channels, receptors, and identification markers. Unlike completely impermeable or freely permeable membranes, selective permeability allows cells to maintain their internal environment while interacting with surroundings.
Mitochondria are often called the powerhouses of the cell because they produce most of the cell's ATP (energy). Cells with higher metabolic demands, like muscle and liver cells, contain more mitochondria. In contrast, protein synthesis occurs primarily through the collaboration of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus—not in mitochondria as sometimes confused.
The nucleus contains most of the cell's DNA and serves as the control center. It's surrounded by a nuclear membrane with pores that allow communication with the cytoplasm. This organization keeps genetic material protected while allowing regulated access for processes like protein synthesis. The nucleus directs cellular activities by controlling which genes are expressed.
🧬 Your DNA contains approximately 20,000-25,000 genes, but each cell only uses a fraction of them. This selective gene expression explains how cells with identical DNA develop into different cell types!
The endoplasmic reticulum exists in two forms: rough and smooth. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached to its surface (making it "rough"), while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes. The RER focuses on protein synthesis, while the SER is involved in lipid production, detoxification, and calcium storage. This specialization allows cells to efficiently perform multiple complex functions simultaneously.

When stem cells develop into specialized cells like muscle or nerve cells, they undergo differentiation. This fascinating process doesn't change the cell's DNA, but rather changes which genes are expressed. Through differentiation, cells with identical genetic material can develop completely different structures and functions.
Understanding tonicity has important medical applications. If pure water were administered intravenously, it would act as a hypotonic solution relative to blood, causing red blood cells to absorb water and undergo hemolysis (bursting). This demonstrates why medical fluids must have appropriate tonicity—typically isotonic to blood—to prevent cellular damage.
The study of cells, known as cytology, reveals how cellular processes impact health and disease. For example, in capillaries, filtration occurs when blood pressure forces water and dissolved substances out of the blood vessels into tissues. At the venous end of capillaries, osmosis draws fluid back into the bloodstream due to osmotic pressure from plasma proteins.
⚕️ Medical treatments often depend on cellular principles. Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cancer cells, dialysis uses diffusion and filtration to clean the blood, and many medications work by affecting specific cellular transport mechanisms.
Cellular aging occurs primarily due to damage to DNA over time. As cells replicate, small errors accumulate in genetic material, leading to reduced function and efficiency. This helps explain why organs function less efficiently with age and why some diseases become more common in older populations. Understanding these cellular mechanisms continues to drive advances in medical treatments and anti-aging research.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Giana Lynch
@gianalynch_dpez
Cell biology is the foundation of understanding how our bodies work. From basic structures to complex processes, cells are the building blocks of life. Let's explore the key components and mechanisms of cells that will help you ace your biology... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wonder how a microscopic cell can perform all the functions needed to keep you alive? Cells contain specialized structures called organelles that each have specific jobs. The nucleus serves as the control center, housing most of the cell's DNA and genetic information. Surrounding the nucleus is the nuclear membrane, which separates it from the rest of the cell.
The cell membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that determines what enters and leaves the cell. Inside the cell, the cytoplasm consists of the gel-like cytosol and various organelles. Mitochondria, known as the "power plants" of cells, produce most of the energy (ATP) the cell needs to function.
Protein production involves several organelles working together. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is dotted with ribosomes that synthesize proteins, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) focuses on lipid and steroid synthesis. The Golgi apparatus finishes and packages proteins for export from the cell, and lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that "clean house" within the cell.
💡 Think of the cell as a tiny city: the nucleus is the city hall (control center), mitochondria are power plants, lysosomes are the sanitation department, and the cell membrane is the city limits with controlled entry points.
The cell also has structural components like microtubules that maintain cell shape and assist with movement. External projections such as cilia (short) and flagella (long) help cells move or move substances around them. Finally, centrioles play an important role during cell division.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
How do substances move into and out of cells? Cells use various transport mechanisms to maintain balance and function. Diffusion is the most common method, where molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without using energy.
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion where water moves across a membrane from an area with more water to an area with less water. When cells need help moving certain molecules across the membrane, they use facilitated diffusion, which uses helper molecules but still doesn't require energy. These three methods are all forms of passive transport, meaning they don't require energy.
Sometimes cells need to move substances against their concentration gradient, which requires energy. The active transport pump uses ATP to move molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. For example, cells must actively pump potassium into the cell even when there's already more potassium inside than outside.
🔑 Understanding transport mechanisms is crucial for explaining many biological processes, from how medicines enter cells to why drinking salt water causes dehydration!
Cells can also transport larger materials through processes like phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), and exocytosis (cellular export). Filtration is another transport mechanism where pressure forces water and dissolved substances across a membrane, as happens in your kidneys and blood vessels.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
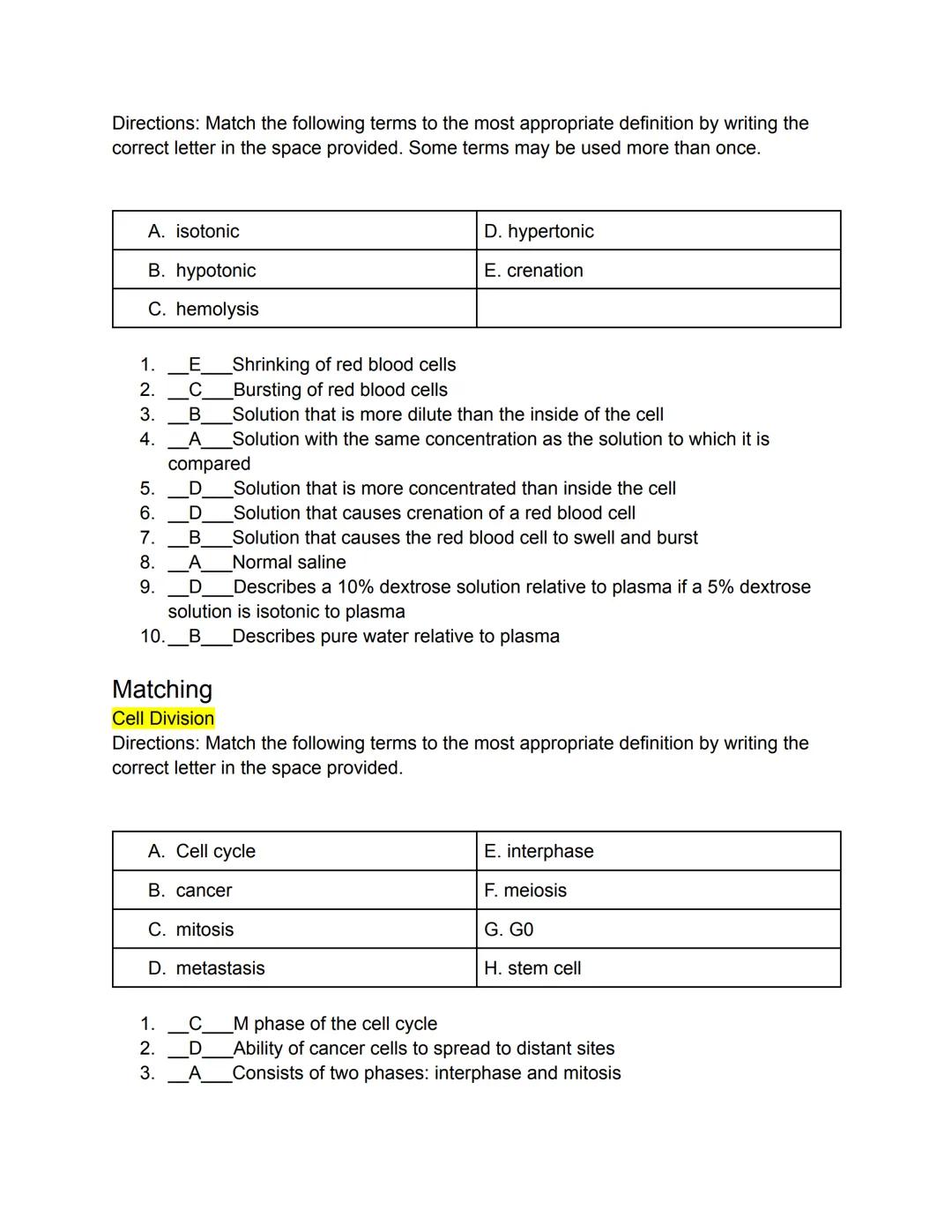
The concentration of solutions affects how cells interact with their environment. Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutions and how they affect cells. An isotonic solution has the same concentration as the cell's interior (like normal saline), causing no net movement of water.
A hypertonic solution is more concentrated than the cell's interior, causing water to move out of the cell. In red blood cells, this leads to crenation or shrinking. Conversely, a hypotonic solution is more dilute than the cell's interior, causing water to flow into the cell. In red blood cells, this can lead to swelling and eventually hemolysis (bursting).
Cell division is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and mitosis. During interphase (G₁, S, and G₂ phases), the cell grows and replicates its DNA. Mitosis (the M phase) is the actual division process with four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
📌 Remember: Regular cells divide by mitosis (resulting in identical copies), while reproductive cells divide by meiosis (resulting in cells with half the genetic material).
Some cells enter a G₀ phase where they stop dividing. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can specialize into different cell types through a process called differentiation. When cell division becomes uncontrolled, cancer can develop, which may lead to metastasis (spreading to other parts of the body).

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Transport mechanisms are constantly at work in your body to maintain homeostasis. When you smell a skunk's spray, you're experiencing diffusion as the odor molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration. This passive transport happens without energy expenditure, making it efficient but limited by concentration gradients.
The active transport pump is crucial for cellular function, particularly the sodium-potassium pump. Unlike passive mechanisms, active transport requires ATP energy to move substances against their concentration gradients. This process is essential for nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and maintaining cell volume.
Cell membranes are selectively permeable, allowing some substances to pass while blocking others. This selective nature is vital for maintaining the internal environment of cells. The membrane contains specialized structures like microvilli and cilia that help with absorption and movement of substances around the cell.
⚡ Active transport is like pushing a boulder uphill—it requires energy input—while diffusion is like rolling downhill, happening naturally without energy.
Specialized cells have adapted their transport mechanisms for specific functions. For example, intestinal cells have extensive microvilli to increase surface area for absorption, while respiratory cells use cilia to move mucus and trapped particles away from the lungs. These specialized structures highlight how cell function follows cell structure.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Have you ever wondered how cells specialize for different jobs in your body? Differentiation is the process where unspecialized cells develop into specialized types like muscle, nerve, or blood cells. This remarkable transformation allows our bodies to perform countless complex functions with specialized cells.
The cell membrane serves as a gatekeeper for the cell. It's not just a simple barrier but a complex, selectively permeable structure that controls what enters and exits. This selective nature is crucial for maintaining the cell's internal environment and allowing communication with other cells.
Inside the cell, numerous organelles work together like a well-organized factory. Ribosomes are protein-making factories found either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or floating freely in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria are the cell's power plants, producing energy through cellular respiration. Lysosomes serve as the cell's cleanup crew, containing enzymes that break down cellular waste.
🧪 Imagine lysosomes as tiny recycling centers within the cell—they break down waste materials and damaged organelles so the components can be reused!
Cell division occurs through a carefully orchestrated process called mitosis, which includes four main phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Before division begins, the cell goes through interphase, which includes the G₁, S (DNA synthesis), and G₂ phases. Understanding this cycle is essential for comprehending both normal growth and abnormal conditions like cancer.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) functions as the cell's manufacturing and transport system. The rough endoplasmic reticulum contains ribosomes on its surface, giving it a bumpy appearance. This specialized structure is dedicated to protein synthesis and forms channels that guide newly created proteins through the cell.
When studying cellular transport, understanding concentration gradients is essential. Consider a beaker with two compartments: one with 25% glucose and one with 5% glucose. If the membrane allows both water and glucose to pass, diffusion will move glucose from high concentration (25%) to low concentration (5%). Simultaneously, water moves in the opposite direction through osmosis.
If the membrane only permits water to pass (not glucose), water will still move toward the higher glucose concentration through osmosis. This principle explains why drinking seawater dehydrates you—water leaves your cells to dilute the saltier external environment.
💧 Your cells constantly balance water movement through osmosis. This is why proper hydration is crucial—it helps maintain the right balance of water inside and outside your cells!
Sometimes cells need to move substances against concentration gradients, which requires active transport. Unlike diffusion, which moves substances from high to low concentration, active transport can move substances from low to high concentration but requires energy (ATP) to do so. This mechanism is essential for many cellular processes, including nutrient uptake and waste removal.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Blood vessels showcase fascinating transport principles at work. In capillaries, filtration occurs when blood pressure forces water and dissolved substances out of the vessels into surrounding tissues. This happens primarily at the arterial end of capillaries where pressure is higher (around 35 mm Hg). At the venous end, where pressure drops (to about 7 mm Hg), osmosis draws water back into the bloodstream, influenced by the plasma's oncotic pressure.
Understanding different transport mechanisms helps explain how medications work and why certain medical conditions develop. Passive transport (diffusion, osmosis) requires no energy, while active transport uses energy to move substances against concentration gradients. Knowing which mechanism is involved helps predict how substances will move throughout the body.
Cell abnormalities can lead to various conditions, including tumors. A neoplasm refers to any new and abnormal tissue growth, which can be benign or malignant. Benign neoplasms typically have well-differentiated cells that resemble their tissue of origin and don't spread to other body parts. In contrast, cancerous (malignant) neoplasms often have poorly differentiated cells and the ability to metastasize (spread to distant locations).
🔬 When doctors perform a biopsy, they're collecting tissue samples to examine cell characteristics. This helps determine if a tumor is benign or malignant, which guides treatment decisions.
Different cell types have specific characteristics that reflect their function. For example, muscle cells contain numerous mitochondria to provide energy for contraction, while cells that produce hormones have extensive RER and Golgi apparatus for protein synthesis and secretion. The number and type of organelles in a cell directly relate to its specialized function.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The cell membrane is a remarkable structure that determines what enters and leaves the cell. This selectively permeable barrier consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that act as channels, receptors, and identification markers. Unlike completely impermeable or freely permeable membranes, selective permeability allows cells to maintain their internal environment while interacting with surroundings.
Mitochondria are often called the powerhouses of the cell because they produce most of the cell's ATP (energy). Cells with higher metabolic demands, like muscle and liver cells, contain more mitochondria. In contrast, protein synthesis occurs primarily through the collaboration of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus—not in mitochondria as sometimes confused.
The nucleus contains most of the cell's DNA and serves as the control center. It's surrounded by a nuclear membrane with pores that allow communication with the cytoplasm. This organization keeps genetic material protected while allowing regulated access for processes like protein synthesis. The nucleus directs cellular activities by controlling which genes are expressed.
🧬 Your DNA contains approximately 20,000-25,000 genes, but each cell only uses a fraction of them. This selective gene expression explains how cells with identical DNA develop into different cell types!
The endoplasmic reticulum exists in two forms: rough and smooth. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached to its surface (making it "rough"), while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes. The RER focuses on protein synthesis, while the SER is involved in lipid production, detoxification, and calcium storage. This specialization allows cells to efficiently perform multiple complex functions simultaneously.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
When stem cells develop into specialized cells like muscle or nerve cells, they undergo differentiation. This fascinating process doesn't change the cell's DNA, but rather changes which genes are expressed. Through differentiation, cells with identical genetic material can develop completely different structures and functions.
Understanding tonicity has important medical applications. If pure water were administered intravenously, it would act as a hypotonic solution relative to blood, causing red blood cells to absorb water and undergo hemolysis (bursting). This demonstrates why medical fluids must have appropriate tonicity—typically isotonic to blood—to prevent cellular damage.
The study of cells, known as cytology, reveals how cellular processes impact health and disease. For example, in capillaries, filtration occurs when blood pressure forces water and dissolved substances out of the blood vessels into tissues. At the venous end of capillaries, osmosis draws fluid back into the bloodstream due to osmotic pressure from plasma proteins.
⚕️ Medical treatments often depend on cellular principles. Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cancer cells, dialysis uses diffusion and filtration to clean the blood, and many medications work by affecting specific cellular transport mechanisms.
Cellular aging occurs primarily due to damage to DNA over time. As cells replicate, small errors accumulate in genetic material, leading to reduced function and efficiency. This helps explain why organs function less efficiently with age and why some diseases become more common in older populations. Understanding these cellular mechanisms continues to drive advances in medical treatments and anti-aging research.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
0
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
Explore Gregor Mendel's groundbreaking experiments with pea plants that established the principles of genetic inheritance. This summary covers key concepts such as dominant and recessive alleles, the law of segregation, and the significance of Mendel's findings in modern genetics. Ideal for students studying genetics and inheritance patterns.
Explore the foundational principles of Mendelian genetics through Gregor Mendel's groundbreaking experiments with pea plants. This summary covers key concepts such as the Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation, and Law of Independent Assortment, along with Mendel's methodology and significant findings in genetic inheritance. Ideal for students studying genetics and heredity.
history of genetics
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 10 Study Guide
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user