The Industrial Revolution transformed the world through technological innovation and... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
89
•
Feb 11, 2026
•
The Industrial Revolution transformed the world through technological innovation and... Show more








Ever wonder why the Industrial Revolution began in Britain? Several key advantages set the stage. Britain's thriving agricultural sector freed workers from farming, while abundant coal deposits provided crucial energy resources that supported iron production and powered steam engines. Meanwhile, China's coal regions were too far from its economic centers to spark similar development.
Britain's colonies played a critical role too. American territories supplied valuable raw materials like sugar and cotton while creating markets for manufactured goods. These overseas resources relieved pressure on European land and provided outlets for Europe's surplus population.
The textile industry became the first sector to truly industrialize. When British wool manufacturers felt threatened by cheap printed cotton fabrics (calicoes) from India, they pushed for protective laws. This ironically stimulated innovation in domestic cotton production. Inventors like John Kay (flying shuttle, 1733) and Samuel Crompton (spinning mule, 1779) created machines that dramatically increased production speed. By the 1820s, steam-powered looms had replaced hand weavers, allowing factories to produce enormous quantities of inexpensive goods.
Did you know? James Watt's 1765 steam engine revolutionized manufacturing by converting steam pressure into rotary motion. Originally designed for pumping water from coal mines, steam power soon transformed entire industries by providing reliable, powerful energy regardless of location.

The industrial landscape transformed through innovations in metals and transportation. In 1709, using coke instead of charcoal revolutionized iron production, making it cheaper and more plentiful. Later, Henry Bessemer's 1856 converter enabled mass production of steel, which was stronger and more versatile than iron.
Transportation advances connected markets in unprecedented ways. George Stephenson's steam locomotive and steamships dramatically reduced shipping costs. These new networks connected remote regions to urban centers, creating truly national and international markets.
The factory system replaced earlier production methods like the "putting out" system where people worked from home. Factories centralized production, bringing workers together under one roof where they performed specialized tasks. This arrangement gave managers strict control over work discipline and production efficiency.
Factory life was harsh for workers. They faced dangerous machinery, strict supervision, and repetitive tasks. A clear separation emerged between owners who provided the capital and workers who depended on wages. This led to protests like the Luddite movement (1811-1816), where workers destroyed textile machines they blamed for unemployment and low wages.
Important! While Luddites are often portrayed as anti-technology, they were actually protesting unfair economic conditions. They targeted machines that threatened their livelihoods, not technology itself.

Industrial innovation didn't stay in Britain for long! By the mid-19th century, industrialization spread to France, Germany, Belgium, and the United States. The French Revolution helped prepare western Europe by eliminating internal trade barriers and dismantling restrictive guilds. France soon developed its own refinements, while Germany's industrialization accelerated after 1871 under Bismarck's government, which promoted heavy industry and the formation of huge businesses.
North America's abundant resources but limited workforce created unique conditions for industrialization. Starting in the 1820s, entrepreneurs built cotton textile industries in New England by recruiting British workers. By 1900, the United States had become an economic powerhouse, with railroads connecting its vast territory.
Mass production revolutionized manufacturing through standardization. Eli Whitney pioneered using machine tools to create interchangeable parts for firearms in 1793. This approach allowed unskilled workers to make identical components that could fit any musket of the same model. By the mid-19th century, standardized production became the hallmark of industrial societies, culminating in Henry Ford's 1913 assembly line.
Big business emerged as the dominant form of industrial organization. The modern corporation became legally established in the 1850s-60s, and by the late 19th century, most major industries were corporate-controlled. Companies sought to eliminate competition through monopolies, trusts, and cartels that could control prices and markets, though some governments eventually took action against these combinations.
Think about it: Mass production made goods cheaper and more available, but also created more repetitive, less skilled work. How did this tradeoff affect society?

Industrialization dramatically transformed population patterns. Before industrialization, high birth rates were offset by high death rates from famines and epidemics. As industrial societies developed, medical advances like Jenner's vaccination helped control disease while better diets improved overall health, causing death rates to drop sharply.
Birth rates eventually declined too, partly due to birth control methods like condoms and partly because industrial society changed how families viewed children. Parents began having fewer children but investing more in each one—a major shift in family strategy.
Cities exploded in size as people migrated from the countryside seeking factory work. These early urban environments were often dangerous and polluted, with death rates exceeding birth rates. Only constant migration kept cities growing. Wealth determined where you lived—the wealthy escaped to newly growing suburbs while the poor remained in crowded city centers.
Migration wasn't limited to local moves. Transcontinental migration brought millions of Europeans to America. British workers fled dangerous factories, Irish families escaped the potato famine of the 1840s, and Russian Jews fled anti-Semitic policies in the 1890s. These newcomers fueled America's rapid industrialization in the late 19th century.
Industrialization also undermined traditional institutions like slavery. Factory owners preferred free wage laborers who could spend their earnings on manufactured products, making slavery increasingly incompatible with industrial economies.
Fascinating fact: Early industrial cities were so unhealthy that they couldn't sustain their own populations through natural growth. Without constant migration from rural areas, these cities would have shrunk despite being the engines of economic growth!

Industrialization created distinct new social classes. At the top, captains of industry accumulated incredible wealth. The middle class expanded dramatically and became the principal beneficiaries of industrialization. Meanwhile, the working class gradually gained political influence by the mid-19th century.
Family life transformed as production moved outside the home. The family, once the basic productive unit, became divided as members led increasingly separate lives. Work and home became distinctly separate spheres, with men's identities increasingly defined by their wage-earning occupations. Despite long hours and harsh conditions, workers carved out leisure time, giving rise to popular pastimes like European soccer and American baseball.
Women's roles shifted dramatically during industrialization. Working-class women typically worked until marriage or even after, though they received lower wages than men. In early factories, women were actually preferred workers—their smaller hands gave them superior dexterity with certain machines. By mid-19th century, women made up the majority of Britain's industrial workforce.
Middle-class women experienced a different transformation. Industrialization confined them more strictly to domestic roles, creating new pressures to conform to idealized models of behavior centered on home and family management.
Child labor became increasingly controversial. While children had always worked in and around family homes, industrial child labor was particularly exploitative. Reform movements gained momentum, and by the 1840s, British Parliament began regulating child labor. By 1881, education became mandatory for children aged 5-10 in England.
Consider this: Industrial society created a sharp division between "work" and "home" that hadn't existed before. How might this separation have changed how people viewed their identities and relationships?

As industrialization created vast wealth alongside severe poverty, socialist thinkers emerged to challenge the capitalist system. The term "socialism" first appeared around 1830, with early "utopian socialists" like Charles Fourier (1772-1837) proposing communities based on love rather than competition, and businessman Robert Owen (1771-1858) demonstrating that caring for workers could be both humane and profitable.
Karl Marx (1818-83) and Friedrich Engels (1820-95) developed a more revolutionary analysis. They argued that capitalism inevitably divided society into two opposing classes: capitalists who owned the means of production and the proletariat who sold their labor. In their influential "Communist Manifesto" (1848), they predicted that workers would eventually overthrow capitalism and establish a radically egalitarian society without private property.
Socialist parties grew rapidly in the 19th century but disagreed on strategy. Some advocated for revolution, while others believed in working through democratic institutions. Though socialists didn't win control of any government until the Russian Revolution of 1917, their critiques pushed many governments to address industrial abuses.
Social reform movements gained momentum even without socialist governments. Facing pressure from voters and labor unions, countries began accepting that the state had responsibility for citizens' welfare. Germany led the way in establishing programs that formed the foundation of the modern welfare state.
Trade unions struggled against legal restrictions to improve workers' lives. Initially considered illegal associations, unions gradually gained acceptance and fought for higher wages and better working conditions, making employers more responsive to employees' needs over the long run.
Remember this: While socialism didn't immediately transform governments, it raised important questions about fairness in industrial societies that led to gradual reforms benefiting workers.

Industrialization created a new international division of labor that reshaped economies worldwide. Resource-rich regions increasingly oriented toward exporting raw materials to industrial countries, though they often had little control over these resources since industrial nations dominated commercial and financial institutions.
The global impact varied dramatically. By the mid-20th century, industrialization remained largely limited to Europe, Japan, and North America. Places like India struggled to industrialize despite having the potential—they lacked government support and sufficient investment capital to build industrial infrastructure at scale.
Transportation improvements—both on sea and land—dramatically increased global trade volumes. Some regions benefited more than others from this new economic order. Places settled by European colonists often parlayed their production and export of primary goods into broader economic development. Their relatively high incomes created flourishing markets and incentivized labor-saving technologies.
Other regions faced more challenging circumstances. Plantation economies with low-wage workers couldn't generate enough consumer demand for manufactured goods. Wealth remained concentrated in small elite groups that contributed little to broader economic development. Additionally, free trade policies allowed unrestricted entry of foreign manufactures, making it difficult for local industries to develop and compete.
This uneven development created new forms of economic interdependence between industrialized and non-industrialized regions. While some areas used their resource wealth as a stepping stone to industrialization, others found themselves locked into subordinate economic roles that were difficult to escape.
Think bigger: The industrial revolution didn't just transform factories—it reorganized the entire world economy. The prosperity of industrialized nations became linked to resources and markets in non-industrialized regions, creating relationships of both opportunity and dependency.
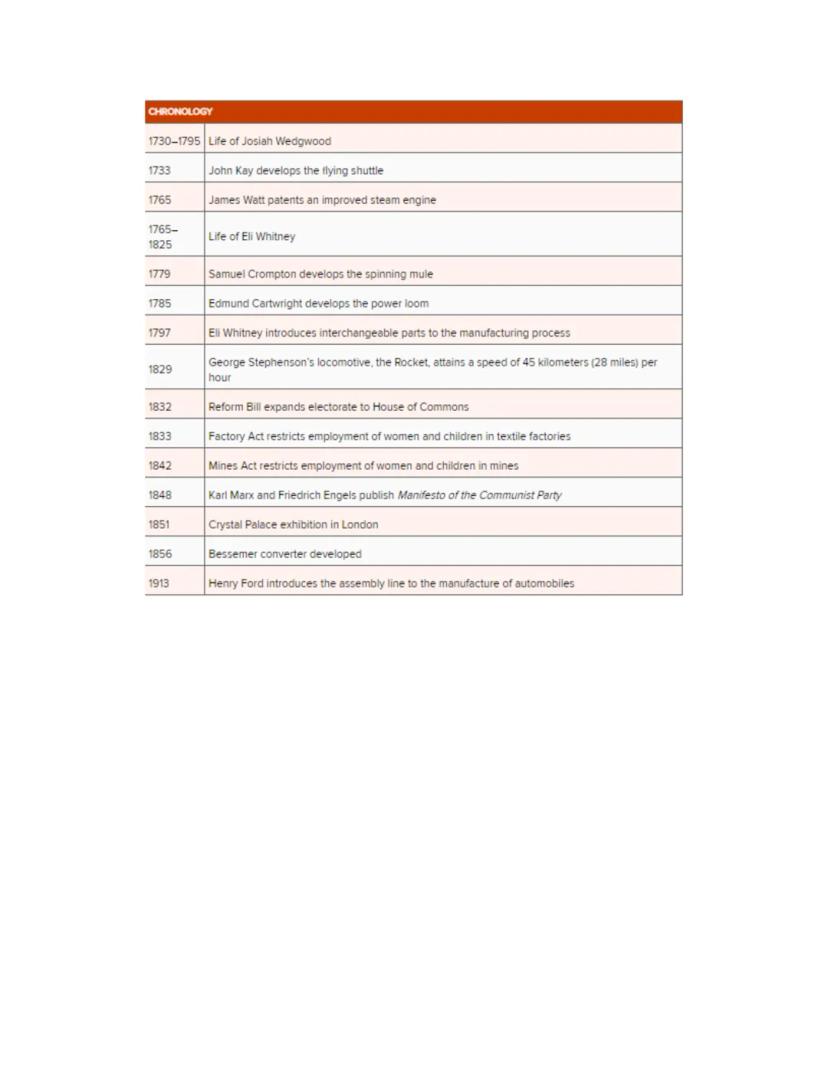
The Industrial Revolution unfolded through a series of key innovations and policy changes spanning nearly two centuries. Early textile inventions like John Kay's flying shuttle (1733) and Samuel Crompton's spinning mule (1779) revolutionized production methods, while James Watt's improved steam engine (1765) provided the power to drive these new machines.
Manufacturing evolved through innovations like Eli Whitney's interchangeable parts (1797) and Edmund Cartwright's power loom (1785), making mass production increasingly efficient. Transportation transformed with George Stephenson's locomotive reaching impressive speeds by 1829.
The second half of the industrial period saw important social and political developments alongside technological ones. The Reform Bill of 1832 expanded voting rights, while the Factory Act (1833) and Mines Act (1842) began restricting the exploitation of women and children in industrial settings.
Marx and Engels published their influential "Communist Manifesto" in 1848, presenting a radical critique of industrial capitalism. Technical innovation continued with the Bessemer converter (1856) revolutionizing steel production, and Henry Ford's assembly line (1913) transforming manufacturing efficiency.
These developments collectively represent not just technological changes but a complete transformation in how society organized work, family, and economic relations across the world.
Connect the dots: Notice how innovations in one area often sparked changes in others. Textile machines created demand for better power sources, which then enabled transportation advances, which opened new markets—creating an accelerating cycle of change.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The Industrial Revolution transformed the world through technological innovation and economic reorganization. Starting in Britain and later spreading globally, this period saw the rise of factories, mass production, and new social classes. These changes dramatically altered how people lived, worked,... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wonder why the Industrial Revolution began in Britain? Several key advantages set the stage. Britain's thriving agricultural sector freed workers from farming, while abundant coal deposits provided crucial energy resources that supported iron production and powered steam engines. Meanwhile, China's coal regions were too far from its economic centers to spark similar development.
Britain's colonies played a critical role too. American territories supplied valuable raw materials like sugar and cotton while creating markets for manufactured goods. These overseas resources relieved pressure on European land and provided outlets for Europe's surplus population.
The textile industry became the first sector to truly industrialize. When British wool manufacturers felt threatened by cheap printed cotton fabrics (calicoes) from India, they pushed for protective laws. This ironically stimulated innovation in domestic cotton production. Inventors like John Kay (flying shuttle, 1733) and Samuel Crompton (spinning mule, 1779) created machines that dramatically increased production speed. By the 1820s, steam-powered looms had replaced hand weavers, allowing factories to produce enormous quantities of inexpensive goods.
Did you know? James Watt's 1765 steam engine revolutionized manufacturing by converting steam pressure into rotary motion. Originally designed for pumping water from coal mines, steam power soon transformed entire industries by providing reliable, powerful energy regardless of location.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The industrial landscape transformed through innovations in metals and transportation. In 1709, using coke instead of charcoal revolutionized iron production, making it cheaper and more plentiful. Later, Henry Bessemer's 1856 converter enabled mass production of steel, which was stronger and more versatile than iron.
Transportation advances connected markets in unprecedented ways. George Stephenson's steam locomotive and steamships dramatically reduced shipping costs. These new networks connected remote regions to urban centers, creating truly national and international markets.
The factory system replaced earlier production methods like the "putting out" system where people worked from home. Factories centralized production, bringing workers together under one roof where they performed specialized tasks. This arrangement gave managers strict control over work discipline and production efficiency.
Factory life was harsh for workers. They faced dangerous machinery, strict supervision, and repetitive tasks. A clear separation emerged between owners who provided the capital and workers who depended on wages. This led to protests like the Luddite movement (1811-1816), where workers destroyed textile machines they blamed for unemployment and low wages.
Important! While Luddites are often portrayed as anti-technology, they were actually protesting unfair economic conditions. They targeted machines that threatened their livelihoods, not technology itself.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Industrial innovation didn't stay in Britain for long! By the mid-19th century, industrialization spread to France, Germany, Belgium, and the United States. The French Revolution helped prepare western Europe by eliminating internal trade barriers and dismantling restrictive guilds. France soon developed its own refinements, while Germany's industrialization accelerated after 1871 under Bismarck's government, which promoted heavy industry and the formation of huge businesses.
North America's abundant resources but limited workforce created unique conditions for industrialization. Starting in the 1820s, entrepreneurs built cotton textile industries in New England by recruiting British workers. By 1900, the United States had become an economic powerhouse, with railroads connecting its vast territory.
Mass production revolutionized manufacturing through standardization. Eli Whitney pioneered using machine tools to create interchangeable parts for firearms in 1793. This approach allowed unskilled workers to make identical components that could fit any musket of the same model. By the mid-19th century, standardized production became the hallmark of industrial societies, culminating in Henry Ford's 1913 assembly line.
Big business emerged as the dominant form of industrial organization. The modern corporation became legally established in the 1850s-60s, and by the late 19th century, most major industries were corporate-controlled. Companies sought to eliminate competition through monopolies, trusts, and cartels that could control prices and markets, though some governments eventually took action against these combinations.
Think about it: Mass production made goods cheaper and more available, but also created more repetitive, less skilled work. How did this tradeoff affect society?

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Industrialization dramatically transformed population patterns. Before industrialization, high birth rates were offset by high death rates from famines and epidemics. As industrial societies developed, medical advances like Jenner's vaccination helped control disease while better diets improved overall health, causing death rates to drop sharply.
Birth rates eventually declined too, partly due to birth control methods like condoms and partly because industrial society changed how families viewed children. Parents began having fewer children but investing more in each one—a major shift in family strategy.
Cities exploded in size as people migrated from the countryside seeking factory work. These early urban environments were often dangerous and polluted, with death rates exceeding birth rates. Only constant migration kept cities growing. Wealth determined where you lived—the wealthy escaped to newly growing suburbs while the poor remained in crowded city centers.
Migration wasn't limited to local moves. Transcontinental migration brought millions of Europeans to America. British workers fled dangerous factories, Irish families escaped the potato famine of the 1840s, and Russian Jews fled anti-Semitic policies in the 1890s. These newcomers fueled America's rapid industrialization in the late 19th century.
Industrialization also undermined traditional institutions like slavery. Factory owners preferred free wage laborers who could spend their earnings on manufactured products, making slavery increasingly incompatible with industrial economies.
Fascinating fact: Early industrial cities were so unhealthy that they couldn't sustain their own populations through natural growth. Without constant migration from rural areas, these cities would have shrunk despite being the engines of economic growth!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Industrialization created distinct new social classes. At the top, captains of industry accumulated incredible wealth. The middle class expanded dramatically and became the principal beneficiaries of industrialization. Meanwhile, the working class gradually gained political influence by the mid-19th century.
Family life transformed as production moved outside the home. The family, once the basic productive unit, became divided as members led increasingly separate lives. Work and home became distinctly separate spheres, with men's identities increasingly defined by their wage-earning occupations. Despite long hours and harsh conditions, workers carved out leisure time, giving rise to popular pastimes like European soccer and American baseball.
Women's roles shifted dramatically during industrialization. Working-class women typically worked until marriage or even after, though they received lower wages than men. In early factories, women were actually preferred workers—their smaller hands gave them superior dexterity with certain machines. By mid-19th century, women made up the majority of Britain's industrial workforce.
Middle-class women experienced a different transformation. Industrialization confined them more strictly to domestic roles, creating new pressures to conform to idealized models of behavior centered on home and family management.
Child labor became increasingly controversial. While children had always worked in and around family homes, industrial child labor was particularly exploitative. Reform movements gained momentum, and by the 1840s, British Parliament began regulating child labor. By 1881, education became mandatory for children aged 5-10 in England.
Consider this: Industrial society created a sharp division between "work" and "home" that hadn't existed before. How might this separation have changed how people viewed their identities and relationships?

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
As industrialization created vast wealth alongside severe poverty, socialist thinkers emerged to challenge the capitalist system. The term "socialism" first appeared around 1830, with early "utopian socialists" like Charles Fourier (1772-1837) proposing communities based on love rather than competition, and businessman Robert Owen (1771-1858) demonstrating that caring for workers could be both humane and profitable.
Karl Marx (1818-83) and Friedrich Engels (1820-95) developed a more revolutionary analysis. They argued that capitalism inevitably divided society into two opposing classes: capitalists who owned the means of production and the proletariat who sold their labor. In their influential "Communist Manifesto" (1848), they predicted that workers would eventually overthrow capitalism and establish a radically egalitarian society without private property.
Socialist parties grew rapidly in the 19th century but disagreed on strategy. Some advocated for revolution, while others believed in working through democratic institutions. Though socialists didn't win control of any government until the Russian Revolution of 1917, their critiques pushed many governments to address industrial abuses.
Social reform movements gained momentum even without socialist governments. Facing pressure from voters and labor unions, countries began accepting that the state had responsibility for citizens' welfare. Germany led the way in establishing programs that formed the foundation of the modern welfare state.
Trade unions struggled against legal restrictions to improve workers' lives. Initially considered illegal associations, unions gradually gained acceptance and fought for higher wages and better working conditions, making employers more responsive to employees' needs over the long run.
Remember this: While socialism didn't immediately transform governments, it raised important questions about fairness in industrial societies that led to gradual reforms benefiting workers.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Industrialization created a new international division of labor that reshaped economies worldwide. Resource-rich regions increasingly oriented toward exporting raw materials to industrial countries, though they often had little control over these resources since industrial nations dominated commercial and financial institutions.
The global impact varied dramatically. By the mid-20th century, industrialization remained largely limited to Europe, Japan, and North America. Places like India struggled to industrialize despite having the potential—they lacked government support and sufficient investment capital to build industrial infrastructure at scale.
Transportation improvements—both on sea and land—dramatically increased global trade volumes. Some regions benefited more than others from this new economic order. Places settled by European colonists often parlayed their production and export of primary goods into broader economic development. Their relatively high incomes created flourishing markets and incentivized labor-saving technologies.
Other regions faced more challenging circumstances. Plantation economies with low-wage workers couldn't generate enough consumer demand for manufactured goods. Wealth remained concentrated in small elite groups that contributed little to broader economic development. Additionally, free trade policies allowed unrestricted entry of foreign manufactures, making it difficult for local industries to develop and compete.
This uneven development created new forms of economic interdependence between industrialized and non-industrialized regions. While some areas used their resource wealth as a stepping stone to industrialization, others found themselves locked into subordinate economic roles that were difficult to escape.
Think bigger: The industrial revolution didn't just transform factories—it reorganized the entire world economy. The prosperity of industrialized nations became linked to resources and markets in non-industrialized regions, creating relationships of both opportunity and dependency.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
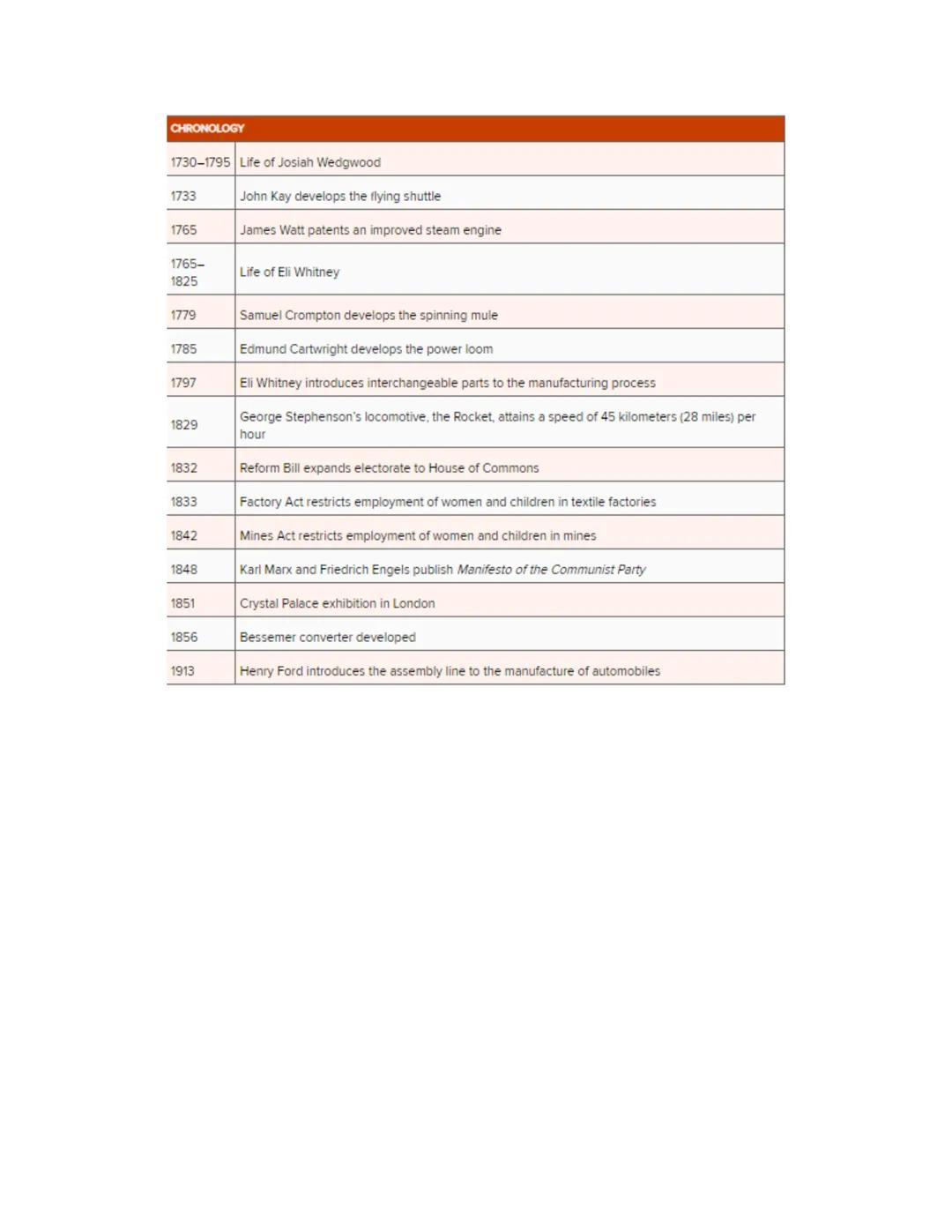
The Industrial Revolution unfolded through a series of key innovations and policy changes spanning nearly two centuries. Early textile inventions like John Kay's flying shuttle (1733) and Samuel Crompton's spinning mule (1779) revolutionized production methods, while James Watt's improved steam engine (1765) provided the power to drive these new machines.
Manufacturing evolved through innovations like Eli Whitney's interchangeable parts (1797) and Edmund Cartwright's power loom (1785), making mass production increasingly efficient. Transportation transformed with George Stephenson's locomotive reaching impressive speeds by 1829.
The second half of the industrial period saw important social and political developments alongside technological ones. The Reform Bill of 1832 expanded voting rights, while the Factory Act (1833) and Mines Act (1842) began restricting the exploitation of women and children in industrial settings.
Marx and Engels published their influential "Communist Manifesto" in 1848, presenting a radical critique of industrial capitalism. Technical innovation continued with the Bessemer converter (1856) revolutionizing steel production, and Henry Ford's assembly line (1913) transforming manufacturing efficiency.
These developments collectively represent not just technological changes but a complete transformation in how society organized work, family, and economic relations across the world.
Connect the dots: Notice how innovations in one area often sparked changes in others. Textile machines created demand for better power sources, which then enabled transportation advances, which opened new markets—creating an accelerating cycle of change.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
4
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
Quick and detailed notes for unit 5.8 and 5.9 of AP world history
Imperial powers expanded to states, and how those states responded.
AP World Unit 6 Notes
unit 6 notes
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user