Anatomy and physiology are the building blocks for understanding how... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
82
•
Dec 28, 2025
•
Francenuyen Reyes
@francenuyenreye
Anatomy and physiology are the building blocks for understanding how... Show more










Ever wondered how your body maintains balance despite constant changes in your environment? The answer lies in understanding anatomy and physiology, two sciences that work hand-in-hand to explain the marvel that is the human body.
Anatomy is the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. Derived from Greek words meaning "to cut apart," it examines body structures through various methods like regional anatomy (studying specific areas like the abdomen) and systemic anatomy (focusing on entire systems like the muscular system). Modern imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans have revolutionized how we study anatomy without dissection.
Physiology explores how the body and its parts function. It applies principles of chemistry and physics to understand biological functions, like how sweat glands work to cool the body. While anatomy looks at what structures are, physiology investigates what they do.
Did you know? Understanding anatomy and physiology isn't just for healthcare professionals! This knowledge helps you make sense of medical procedures, communicate effectively with doctors, and better understand both infectious and non-infectious diseases.
The relationship between structure and function is inseparable. Your body's form is precisely designed for its function - from the molecular level to entire organ systems. For example, the branching pattern of blood vessels efficiently delivers nutrients throughout the body, while serous membranes create fluid-filled spaces that reduce friction as organs move. This harmony between form and function is evident throughout the entire body, demonstrating how structure enables specific functions in all living systems.

Your body constantly moves materials from one area to another, a process essential for life. This movement, called flow, is always driven by gradients - differences in variables between two areas.
Three main types of gradients power movement in your body:
The rate of flow depends on two key factors. First, the size of the gradient matters - a larger difference creates faster flow, similar to water flowing down a steeper hill. Second, resistance slows flow - just as a narrower pipe restricts water movement, smaller blood vessels increase resistance to blood flow.
Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions despite changing external environments. Your body actively regulates conditions like temperature, pH, and oxygen levels around specific setpoints - the ideal values for optimal function. For instance, your body temperature has a setpoint of approximately 98.6°F (37°C), though it naturally fluctuates slightly throughout the day.
Remember this! Homeostasis doesn't mean conditions remain static - they're dynamically stable. Your body continuously makes small adjustments to stay within acceptable ranges, keeping your cells functioning properly despite external changes.
Maintaining these balanced conditions is crucial for survival. Your cells can only function properly within specific internal conditions, which is why your body works constantly to maintain homeostasis despite the varying environments you encounter.

Your body maintains homeostasis primarily through negative feedback loops - systems designed to resist changes from setpoints. These mechanisms work like your home thermostat, detecting deviations and triggering responses to correct them.
Every negative feedback loop has three essential components:
Consider blood glucose regulation: When you eat a candy bar, your blood glucose rises above its setpoint. The pancreas (acting as both sensor and control center) detects this increase and releases insulin (the effector response). Insulin causes cells to absorb glucose and the liver to store excess as glycogen, bringing your blood glucose levels back toward normal.
While negative feedback preserves stability, positive feedback does the opposite - it amplifies changes, pushing the system further from the normal range. This mechanism is less common in the body but proves useful for processes that need rapid completion.
Childbirth exemplifies positive feedback: When a baby's head pushes against the cervix, nerves signal the brain to release oxytocin. This hormone intensifies uterine contractions, pushing the baby further down and increasing pressure on the cervix, which triggers even more oxytocin release. This escalating cycle continues until birth occurs, at which point the feedback loop naturally terminates.
Think about it: Without feedback mechanisms, your body would struggle to maintain the stable internal environment necessary for survival. These systems work continuously, usually without your awareness, to keep you alive and functioning optimally.
Both negative and positive feedback mechanisms are crucial for bodily function, with negative feedback maintaining stability and positive feedback accelerating processes that need to reach completion quickly.

The human body is organized in a hierarchical structure, with each level building upon the previous one. This organization creates a logical progression from the simplest components to the complete organism.
At the chemical level, atoms and molecules like oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen combine to form the building blocks of life. These molecules join to create larger structures, each with specific functions - like collagen providing skin with strength and flexibility.
The cellular level represents the smallest independent units of life. Different cell types - nerve cells, fat cells, epithelial cells - have specialized structures that support their unique functions. These cells are the fundamental working units of the body.
When similar cells work together, they form tissues. The four basic tissue types - epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous - each perform specific functions based on their cellular makeup. For example, muscle tissue contains cells specialized for contraction and movement.
Multiple tissue types collaborate to form organs - structures designed for specific functions. Your stomach, heart, and lungs are all organs composed of various tissues working in harmony.
Related organs working toward a common purpose create organ systems. For instance, the urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, all cooperating to produce, store, and eliminate urine.
Finally, all organ systems functioning together create the complete organism - you!
Amazing fact: Every level of organization enables new functions that couldn't exist at lower levels. This emergence of new properties with increased complexity is why understanding the body at multiple levels is so important.
Your body contains eleven major organ systems, each with specific functions - from the integumentary system that protects your body from the environment to the reproductive system responsible for producing offspring. All these systems work together in a remarkable display of biological coordination to maintain life.

Your body's organ systems work together in remarkable harmony, each handling specific functions while contributing to overall survival. Let's explore these systems and their primary roles.
The integumentary system (skin, hair, nails) creates a protective barrier against pathogens and fluid loss while providing sensory reception. Your skeletal system gives structural support and protection to vital organs, while working with the muscular system to create movement and help regulate body temperature.
Your nervous system serves as the body's command center, connecting your brain to every body part and acting as the sensor for homeostasis. The endocrine system secretes hormones that regulate many bodily processes, from metabolism to reproduction.
The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body while removing waste products and helping regulate temperature. Working alongside it, the lymphatic system balances fluid levels and houses immune cells that defend against pathogens.
The respiratory system exchanges air with the environment, providing surfaces for oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusion with the blood. The digestive system breaks down and absorbs nutrients, while the urinary system removes waste products and contributes to blood pressure and pH balance.
Finally, the reproductive system produces and exchanges gametes, houses the fetus during pregnancy, and in females, provides nourishment through lactation.
Remember: No system functions in isolation. Your body is an integrated whole, with each system depending on others. For example, the cardiovascular system transports hormones from the endocrine system and delivers oxygen acquired through the respiratory system.
Understanding how these systems interact helps explain how your body maintains the delicate balance needed for health and survival.

Have you ever wondered how medical professionals describe locations in the body with such precision? They use standardized anatomical terms based on the anatomical position - a universal reference point for all descriptions.
In the anatomical position, a person stands upright with feet parallel, arms at the sides, and palms facing forward. This standard position ensures that terms like "right" and "left" always refer to the patient's right and left, not the observer's. Other common positions include prone and supine .
Medical terminology often derives from Latin and Greek, and understanding common prefixes and suffixes can help decipher complex terms. For example, "appendicitis" combines "appendix" with "-itis" (inflammation), meaning inflammation of the appendix.
Directional terms are essential for describing relationships between body parts:
Pro tip: When you encounter an unfamiliar anatomical term, break it down into its root words and affixes. This linguistic detective work often reveals the meaning - for example, "infraspinous" means "below the spine."
Understanding these terms provides the foundation for discussing body locations precisely, whether you're describing an injury, understanding a medical diagnosis, or studying anatomy.

When describing specific areas of the body, healthcare professionals use standardized regional terms. The body is divided into the central region (head, neck, and trunk) and the limbs. The trunk further divides into the thorax (containing the heart and lungs), abdomen (housing the liver, stomach, and intestines), and pelvis (containing the bladder and reproductive organs).
Other key regions include the cephalic (head), cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), abdominal (abdomen), pelvic (pelvis), dorsal (back), carpal (wrist), tarsal (ankle), and pedal (foot) regions. These terms allow for precise communication about body locations.
To visualize internal structures, anatomists use body planes - imaginary flat surfaces passing through the body. These planes are essential for interpreting medical imaging like CT scans and MRIs.
The three main planes are:
Different types of sections through these planes include:
Medical imaging insight: Understanding these planes is crucial when interpreting medical images. For example, MRI scans often show "slices" of the body in different planes to provide comprehensive views of internal structures.
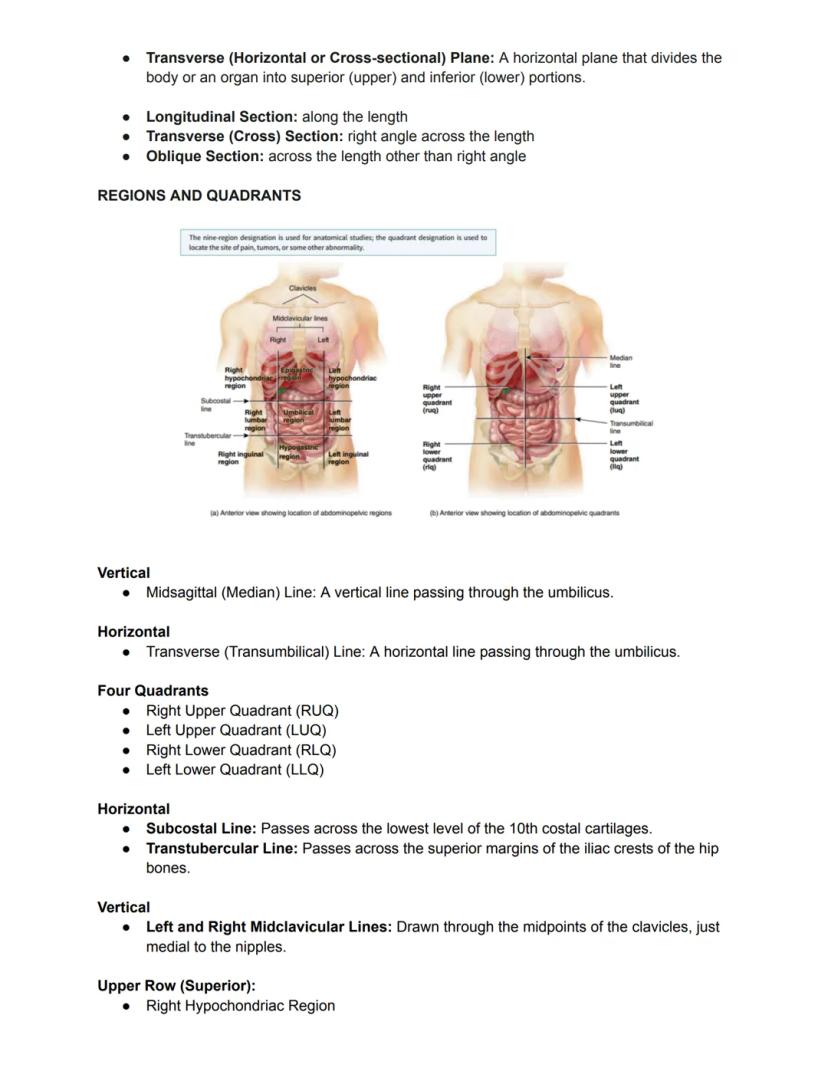
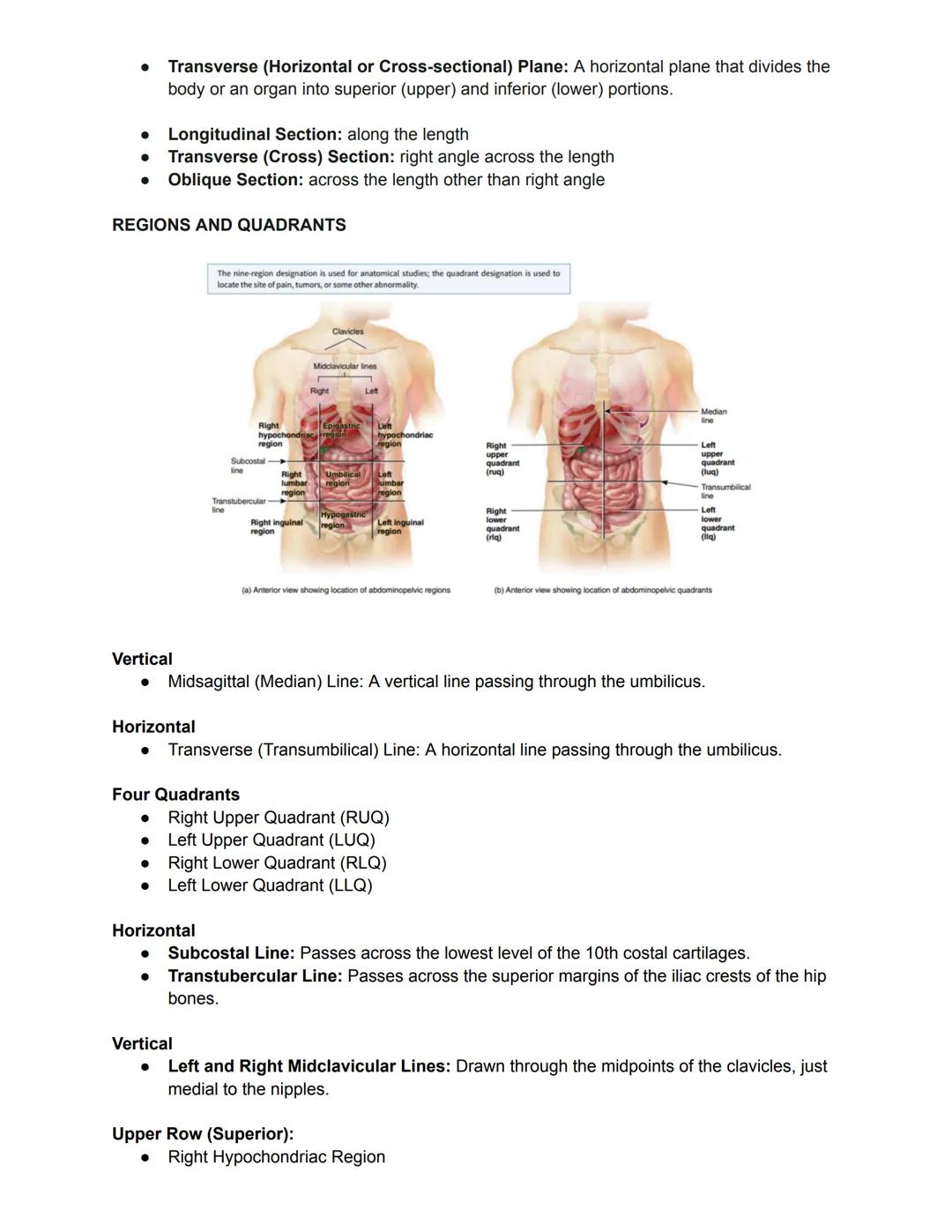
When locating specific regions in the abdominopelvic area, healthcare professionals use either a four-quadrant system (divided by vertical and horizontal lines through the navel) or a more detailed nine-region system. These standardized reference systems help precisely communicate the location of pain, tumors, or other abnormalities.

Your body contains several hollow spaces called cavities that house and protect vital organs. These cavities are lined with membranes that provide additional protection and support.
In the trunk, the thoracic cavity contains your heart and lungs and is divided by the mediastinum into left and right sections. Below the diaphragm, the abdominal cavity houses digestive organs, while the pelvic cavity contains the urinary bladder and reproductive organs. Together, these lower two areas form the abdominopelvic cavity, sometimes called the peritoneal cavity.
Serous membranes are thin, double-layered structures that line these body cavities and cover organs. They consist of:
These membranes create fluid-filled spaces that reduce friction as organs move. In the thoracic cavity, the pericardium surrounds the heart, while the pleura encloses the lungs. In the abdominopelvic cavity, the peritoneum wraps around the abdominal organs.
The structure of these membranes is perfect for their function. The smooth, wet surfaces allow organs to slide against each other and cavity walls without damage during movements like breathing or digestion. The fluid between the membranes acts as both lubricant and shock absorber.
Fascinating fact: The total surface area of all serous membranes in your body is approximately equal to the surface area of your skin! This extensive coverage highlights how important these membranes are for protecting internal organs.
Understanding these cavities and membranes helps explain how your internal organs are organized and protected while still allowing the movement necessary for functions like breathing, digestion, and circulation.
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, forms the boundary between a cell's internal environment and the outside world. More than just a barrier, this remarkable structure controls what enters and leaves the cell, maintaining the specific internal conditions cells need to function.
The fluid mosaic model best describes the cell membrane's structure - a dynamic arrangement of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in constant motion. By weight, it's approximately 50% phospholipids and 50% proteins, though there are many more lipid molecules than protein molecules since proteins are much larger.
The foundation of the membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. When placed in water, these molecules spontaneously arrange with their hydrophilic heads facing the watery environments inside and outside the cell, while their hydrophobic tails cluster in the middle, away from water.
Membrane proteins perform most of the membrane's specific functions. Integral proteins embed within or span the lipid bilayer, forming channels for specific substances, acting as carriers, binding to signaling molecules, or functioning as pumps. Peripheral proteins attach to the membrane's surface and often participate in cell signaling or structural support.
On the cell's outer surface, carbohydrates attach to proteins and lipids, forming a "sugar coat" called the glycocalyx. This structure helps cells recognize each other, facilitates cell adhesion, and provides protection.
Think about it: Your cell membranes process thousands of substances every second, deciding what stays out and what comes in. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining the precise internal conditions cells need to function.
This complex membrane structure elegantly serves its function - creating a selective barrier that maintains cellular homeostasis while allowing necessary communication and transport with the environment.

Every cell constantly exchanges materials with its surroundings to maintain homeostasis. This movement of substances across the cell membrane occurs through several mechanisms, driven primarily by concentration gradients - the difference in concentration of a substance between two areas.
Transport mechanisms fall into two main categories based on energy requirements:
Passive transport doesn't require energy (ATP) expenditure. Substances move down their concentration gradient from higher to lower concentration:
Active transport requires energy (ATP) expenditure to move substances against their concentration gradient:
Cellular wisdom: Your cells are constantly making energy decisions - using passive transport whenever possible to conserve ATP, but investing energy in active transport when necessary to maintain crucial concentration gradients that keep you alive.
For very large particles or volumes of material, cells use vesicular transport - energy-dependent processes that involve membrane-bound sacs. Endocytosis brings materials in through phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), or receptor-mediated endocytosis. Exocytosis expels materials through membrane fusion and release.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Francenuyen Reyes
@francenuyenreye
Anatomy and physiology are the building blocks for understanding how the human body works. Anatomy examines the structure and organization of body parts, while physiology studies how these parts function together. This fundamental relationship between structure and function is key... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Ever wondered how your body maintains balance despite constant changes in your environment? The answer lies in understanding anatomy and physiology, two sciences that work hand-in-hand to explain the marvel that is the human body.
Anatomy is the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. Derived from Greek words meaning "to cut apart," it examines body structures through various methods like regional anatomy (studying specific areas like the abdomen) and systemic anatomy (focusing on entire systems like the muscular system). Modern imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans have revolutionized how we study anatomy without dissection.
Physiology explores how the body and its parts function. It applies principles of chemistry and physics to understand biological functions, like how sweat glands work to cool the body. While anatomy looks at what structures are, physiology investigates what they do.
Did you know? Understanding anatomy and physiology isn't just for healthcare professionals! This knowledge helps you make sense of medical procedures, communicate effectively with doctors, and better understand both infectious and non-infectious diseases.
The relationship between structure and function is inseparable. Your body's form is precisely designed for its function - from the molecular level to entire organ systems. For example, the branching pattern of blood vessels efficiently delivers nutrients throughout the body, while serous membranes create fluid-filled spaces that reduce friction as organs move. This harmony between form and function is evident throughout the entire body, demonstrating how structure enables specific functions in all living systems.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body constantly moves materials from one area to another, a process essential for life. This movement, called flow, is always driven by gradients - differences in variables between two areas.
Three main types of gradients power movement in your body:
The rate of flow depends on two key factors. First, the size of the gradient matters - a larger difference creates faster flow, similar to water flowing down a steeper hill. Second, resistance slows flow - just as a narrower pipe restricts water movement, smaller blood vessels increase resistance to blood flow.
Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions despite changing external environments. Your body actively regulates conditions like temperature, pH, and oxygen levels around specific setpoints - the ideal values for optimal function. For instance, your body temperature has a setpoint of approximately 98.6°F (37°C), though it naturally fluctuates slightly throughout the day.
Remember this! Homeostasis doesn't mean conditions remain static - they're dynamically stable. Your body continuously makes small adjustments to stay within acceptable ranges, keeping your cells functioning properly despite external changes.
Maintaining these balanced conditions is crucial for survival. Your cells can only function properly within specific internal conditions, which is why your body works constantly to maintain homeostasis despite the varying environments you encounter.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body maintains homeostasis primarily through negative feedback loops - systems designed to resist changes from setpoints. These mechanisms work like your home thermostat, detecting deviations and triggering responses to correct them.
Every negative feedback loop has three essential components:
Consider blood glucose regulation: When you eat a candy bar, your blood glucose rises above its setpoint. The pancreas (acting as both sensor and control center) detects this increase and releases insulin (the effector response). Insulin causes cells to absorb glucose and the liver to store excess as glycogen, bringing your blood glucose levels back toward normal.
While negative feedback preserves stability, positive feedback does the opposite - it amplifies changes, pushing the system further from the normal range. This mechanism is less common in the body but proves useful for processes that need rapid completion.
Childbirth exemplifies positive feedback: When a baby's head pushes against the cervix, nerves signal the brain to release oxytocin. This hormone intensifies uterine contractions, pushing the baby further down and increasing pressure on the cervix, which triggers even more oxytocin release. This escalating cycle continues until birth occurs, at which point the feedback loop naturally terminates.
Think about it: Without feedback mechanisms, your body would struggle to maintain the stable internal environment necessary for survival. These systems work continuously, usually without your awareness, to keep you alive and functioning optimally.
Both negative and positive feedback mechanisms are crucial for bodily function, with negative feedback maintaining stability and positive feedback accelerating processes that need to reach completion quickly.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The human body is organized in a hierarchical structure, with each level building upon the previous one. This organization creates a logical progression from the simplest components to the complete organism.
At the chemical level, atoms and molecules like oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen combine to form the building blocks of life. These molecules join to create larger structures, each with specific functions - like collagen providing skin with strength and flexibility.
The cellular level represents the smallest independent units of life. Different cell types - nerve cells, fat cells, epithelial cells - have specialized structures that support their unique functions. These cells are the fundamental working units of the body.
When similar cells work together, they form tissues. The four basic tissue types - epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous - each perform specific functions based on their cellular makeup. For example, muscle tissue contains cells specialized for contraction and movement.
Multiple tissue types collaborate to form organs - structures designed for specific functions. Your stomach, heart, and lungs are all organs composed of various tissues working in harmony.
Related organs working toward a common purpose create organ systems. For instance, the urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, all cooperating to produce, store, and eliminate urine.
Finally, all organ systems functioning together create the complete organism - you!
Amazing fact: Every level of organization enables new functions that couldn't exist at lower levels. This emergence of new properties with increased complexity is why understanding the body at multiple levels is so important.
Your body contains eleven major organ systems, each with specific functions - from the integumentary system that protects your body from the environment to the reproductive system responsible for producing offspring. All these systems work together in a remarkable display of biological coordination to maintain life.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body's organ systems work together in remarkable harmony, each handling specific functions while contributing to overall survival. Let's explore these systems and their primary roles.
The integumentary system (skin, hair, nails) creates a protective barrier against pathogens and fluid loss while providing sensory reception. Your skeletal system gives structural support and protection to vital organs, while working with the muscular system to create movement and help regulate body temperature.
Your nervous system serves as the body's command center, connecting your brain to every body part and acting as the sensor for homeostasis. The endocrine system secretes hormones that regulate many bodily processes, from metabolism to reproduction.
The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body while removing waste products and helping regulate temperature. Working alongside it, the lymphatic system balances fluid levels and houses immune cells that defend against pathogens.
The respiratory system exchanges air with the environment, providing surfaces for oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusion with the blood. The digestive system breaks down and absorbs nutrients, while the urinary system removes waste products and contributes to blood pressure and pH balance.
Finally, the reproductive system produces and exchanges gametes, houses the fetus during pregnancy, and in females, provides nourishment through lactation.
Remember: No system functions in isolation. Your body is an integrated whole, with each system depending on others. For example, the cardiovascular system transports hormones from the endocrine system and delivers oxygen acquired through the respiratory system.
Understanding how these systems interact helps explain how your body maintains the delicate balance needed for health and survival.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Have you ever wondered how medical professionals describe locations in the body with such precision? They use standardized anatomical terms based on the anatomical position - a universal reference point for all descriptions.
In the anatomical position, a person stands upright with feet parallel, arms at the sides, and palms facing forward. This standard position ensures that terms like "right" and "left" always refer to the patient's right and left, not the observer's. Other common positions include prone and supine .
Medical terminology often derives from Latin and Greek, and understanding common prefixes and suffixes can help decipher complex terms. For example, "appendicitis" combines "appendix" with "-itis" (inflammation), meaning inflammation of the appendix.
Directional terms are essential for describing relationships between body parts:
Pro tip: When you encounter an unfamiliar anatomical term, break it down into its root words and affixes. This linguistic detective work often reveals the meaning - for example, "infraspinous" means "below the spine."
Understanding these terms provides the foundation for discussing body locations precisely, whether you're describing an injury, understanding a medical diagnosis, or studying anatomy.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
When describing specific areas of the body, healthcare professionals use standardized regional terms. The body is divided into the central region (head, neck, and trunk) and the limbs. The trunk further divides into the thorax (containing the heart and lungs), abdomen (housing the liver, stomach, and intestines), and pelvis (containing the bladder and reproductive organs).
Other key regions include the cephalic (head), cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), abdominal (abdomen), pelvic (pelvis), dorsal (back), carpal (wrist), tarsal (ankle), and pedal (foot) regions. These terms allow for precise communication about body locations.
To visualize internal structures, anatomists use body planes - imaginary flat surfaces passing through the body. These planes are essential for interpreting medical imaging like CT scans and MRIs.
The three main planes are:
Different types of sections through these planes include:
Medical imaging insight: Understanding these planes is crucial when interpreting medical images. For example, MRI scans often show "slices" of the body in different planes to provide comprehensive views of internal structures.
When locating specific regions in the abdominopelvic area, healthcare professionals use either a four-quadrant system (divided by vertical and horizontal lines through the navel) or a more detailed nine-region system. These standardized reference systems help precisely communicate the location of pain, tumors, or other abnormalities.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body contains several hollow spaces called cavities that house and protect vital organs. These cavities are lined with membranes that provide additional protection and support.
In the trunk, the thoracic cavity contains your heart and lungs and is divided by the mediastinum into left and right sections. Below the diaphragm, the abdominal cavity houses digestive organs, while the pelvic cavity contains the urinary bladder and reproductive organs. Together, these lower two areas form the abdominopelvic cavity, sometimes called the peritoneal cavity.
Serous membranes are thin, double-layered structures that line these body cavities and cover organs. They consist of:
These membranes create fluid-filled spaces that reduce friction as organs move. In the thoracic cavity, the pericardium surrounds the heart, while the pleura encloses the lungs. In the abdominopelvic cavity, the peritoneum wraps around the abdominal organs.
The structure of these membranes is perfect for their function. The smooth, wet surfaces allow organs to slide against each other and cavity walls without damage during movements like breathing or digestion. The fluid between the membranes acts as both lubricant and shock absorber.
Fascinating fact: The total surface area of all serous membranes in your body is approximately equal to the surface area of your skin! This extensive coverage highlights how important these membranes are for protecting internal organs.
Understanding these cavities and membranes helps explain how your internal organs are organized and protected while still allowing the movement necessary for functions like breathing, digestion, and circulation.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, forms the boundary between a cell's internal environment and the outside world. More than just a barrier, this remarkable structure controls what enters and leaves the cell, maintaining the specific internal conditions cells need to function.
The fluid mosaic model best describes the cell membrane's structure - a dynamic arrangement of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in constant motion. By weight, it's approximately 50% phospholipids and 50% proteins, though there are many more lipid molecules than protein molecules since proteins are much larger.
The foundation of the membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. When placed in water, these molecules spontaneously arrange with their hydrophilic heads facing the watery environments inside and outside the cell, while their hydrophobic tails cluster in the middle, away from water.
Membrane proteins perform most of the membrane's specific functions. Integral proteins embed within or span the lipid bilayer, forming channels for specific substances, acting as carriers, binding to signaling molecules, or functioning as pumps. Peripheral proteins attach to the membrane's surface and often participate in cell signaling or structural support.
On the cell's outer surface, carbohydrates attach to proteins and lipids, forming a "sugar coat" called the glycocalyx. This structure helps cells recognize each other, facilitates cell adhesion, and provides protection.
Think about it: Your cell membranes process thousands of substances every second, deciding what stays out and what comes in. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining the precise internal conditions cells need to function.
This complex membrane structure elegantly serves its function - creating a selective barrier that maintains cellular homeostasis while allowing necessary communication and transport with the environment.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Every cell constantly exchanges materials with its surroundings to maintain homeostasis. This movement of substances across the cell membrane occurs through several mechanisms, driven primarily by concentration gradients - the difference in concentration of a substance between two areas.
Transport mechanisms fall into two main categories based on energy requirements:
Passive transport doesn't require energy (ATP) expenditure. Substances move down their concentration gradient from higher to lower concentration:
Active transport requires energy (ATP) expenditure to move substances against their concentration gradient:
Cellular wisdom: Your cells are constantly making energy decisions - using passive transport whenever possible to conserve ATP, but investing energy in active transport when necessary to maintain crucial concentration gradients that keep you alive.
For very large particles or volumes of material, cells use vesicular transport - energy-dependent processes that involve membrane-bound sacs. Endocytosis brings materials in through phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), or receptor-mediated endocytosis. Exocytosis expels materials through membrane fusion and release.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
0
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user