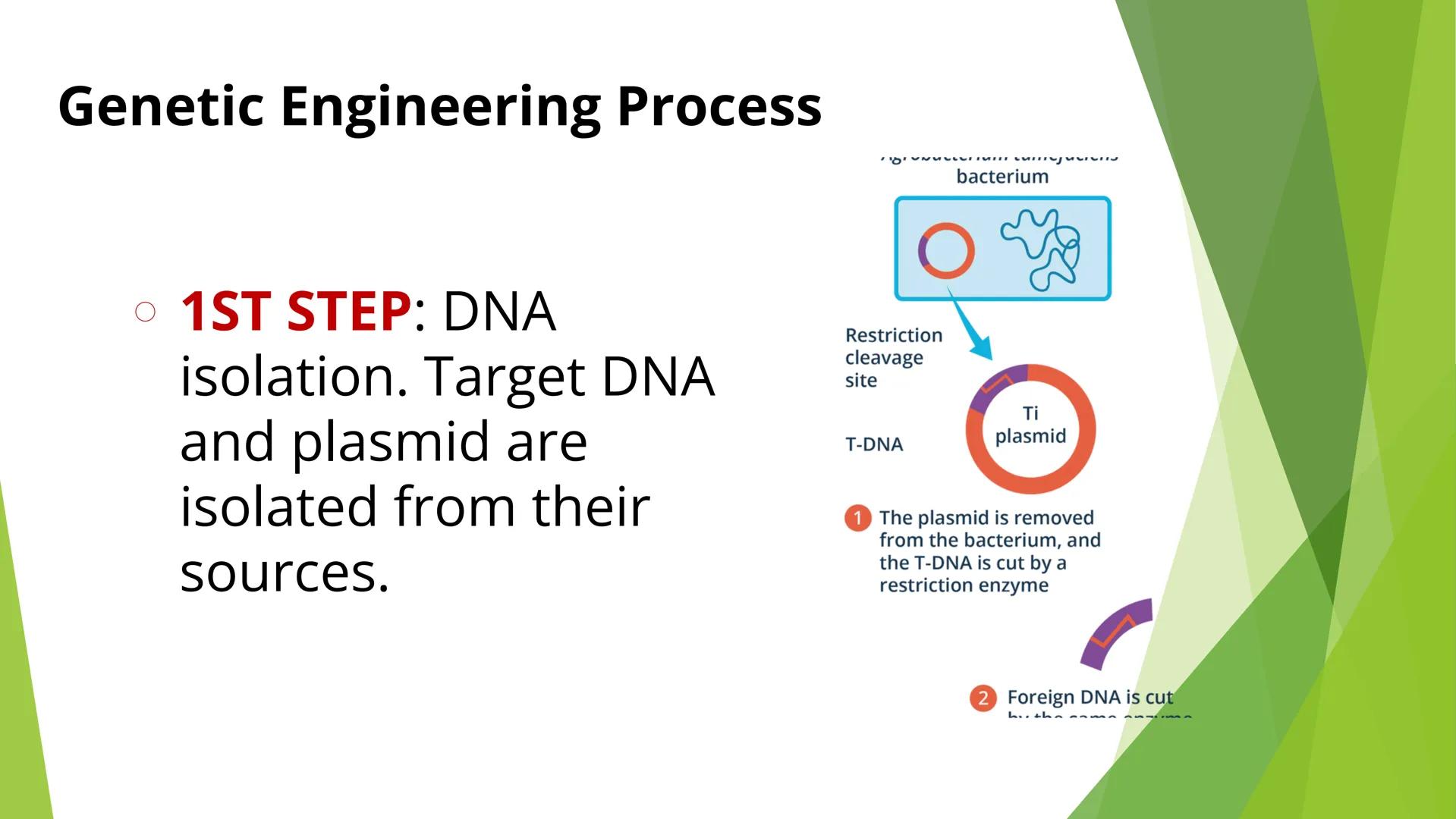
GMOs: The Products of Genetic Engineering
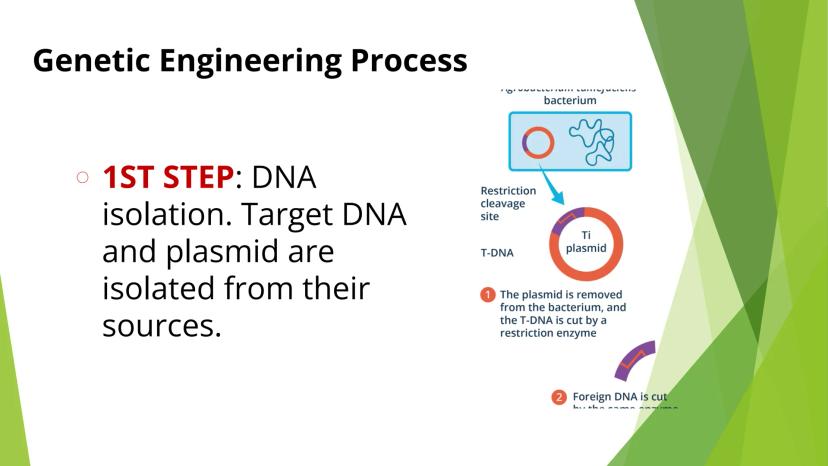
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are living things whose genetic material has been artificially manipulated through genetic engineering. Unlike traditional breeding methods, genetic engineering allows for precise changes to an organism's DNA.
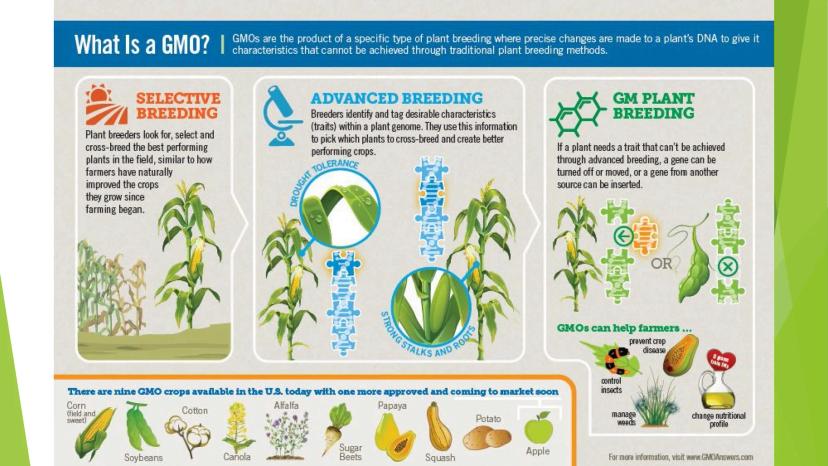
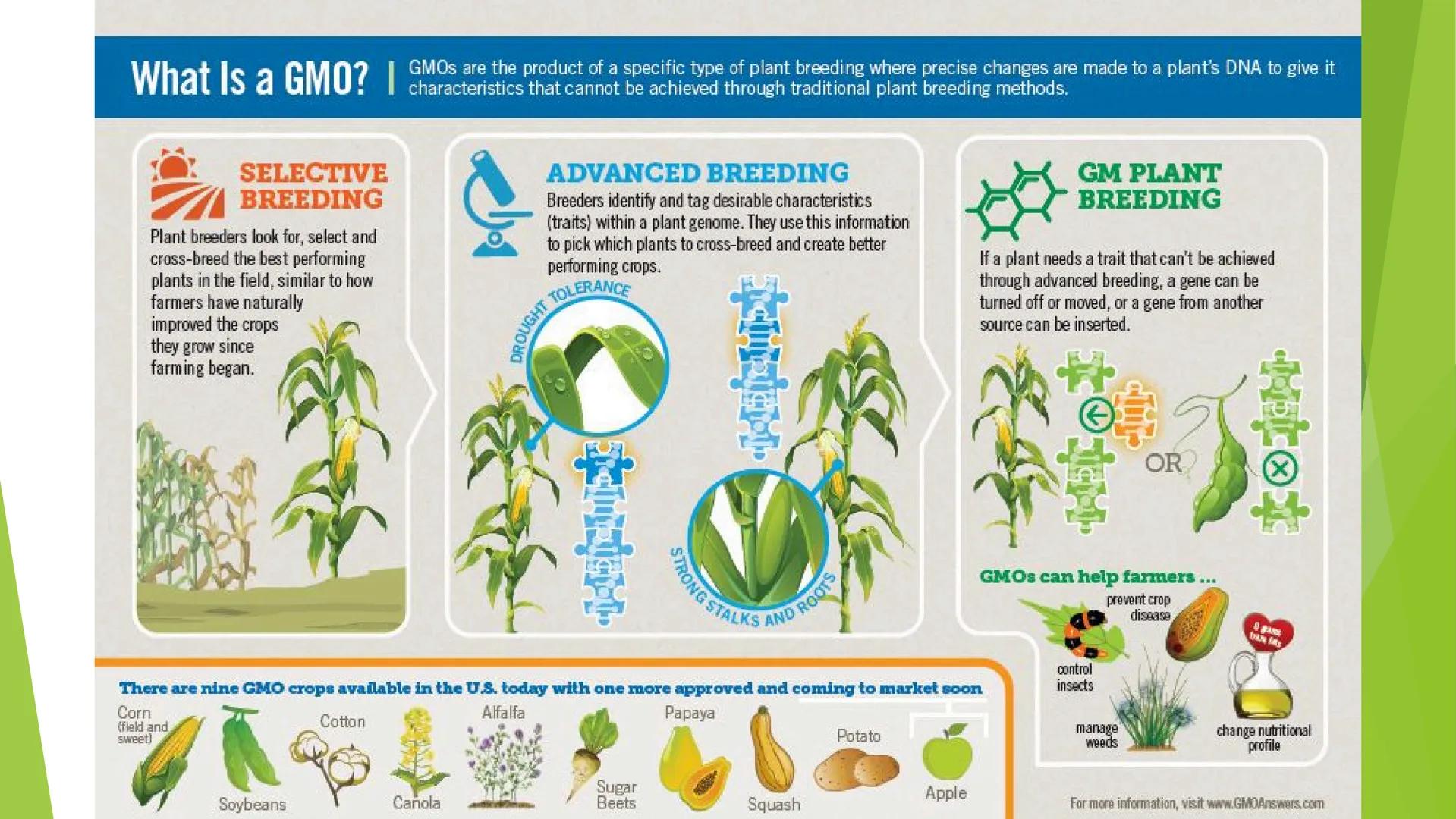
There are currently nine GMO crops available in the U.S. including corn, cotton, soybeans, alfalfa, sugar beets, canola, papaya, potato, and squash. Each has been modified for specific purposes like pest resistance, improved nutritional profiles, or extended shelf life.
Two famous examples demonstrate GMO potential: Golden Rice was engineered to contain higher vitamin A levels to address nutritional deficiencies in developing countries, while the Flavr Savr Tomato was designed to have a longer shelf life by delaying ripening.
Think about this: GMOs help farmers in multiple ways - controlling insects, managing weeds, preventing crop disease, and even adapting to drought conditions. How might these benefits affect food security globally?