The heart is a remarkable muscular organ that works tirelessly... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
244
•
Dec 9, 2025
•
Margaux
@margaux_eesu
The heart is a remarkable muscular organ that works tirelessly... Show more
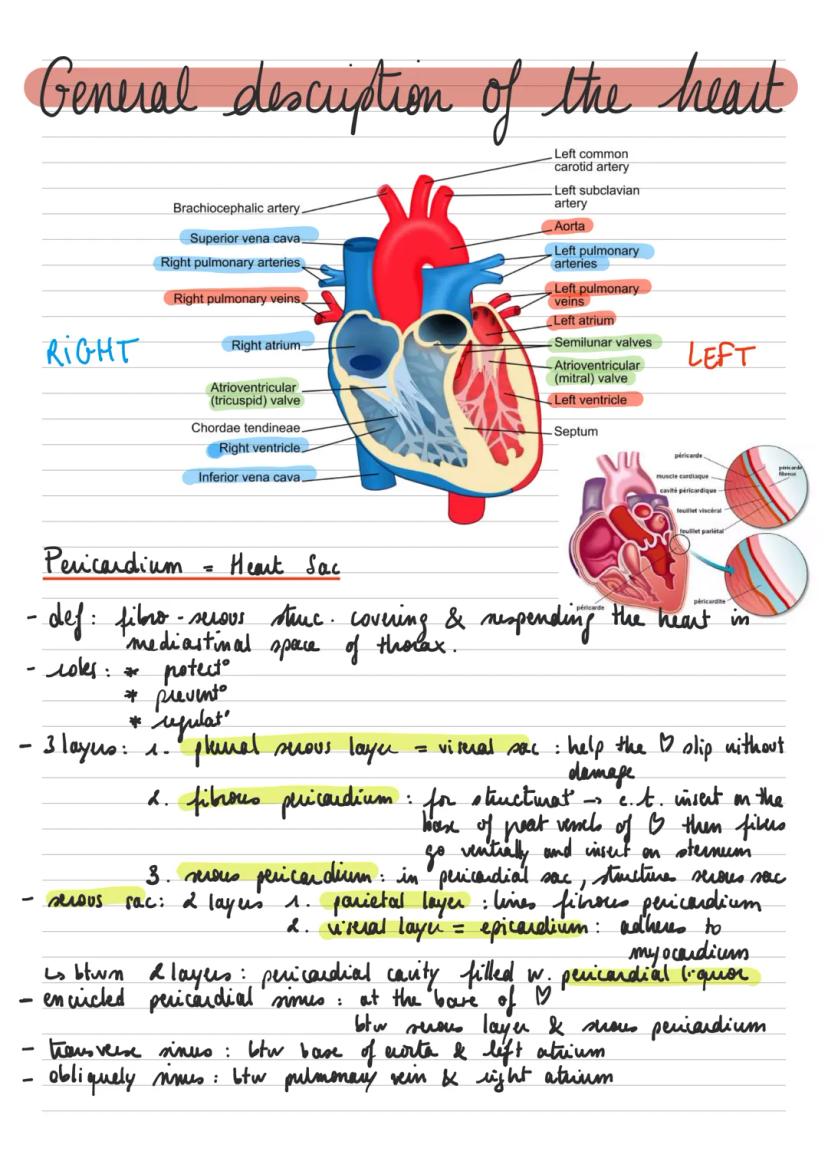








The heart is a remarkable muscular organ positioned within the thoracic cavity, serving as the body's primary pumping station. The anatomie du cœur et ses structures includes several key components working in harmony to maintain circulation.
The heart's location is precisely positioned between the third and sixth ribs, slightly offset to the left of the median plane. This positioning allows for optimal function while being protected by the ribcage. The organ is oriented with its base pointing cranially (toward the head) and its apex directed ventro-caudally (downward and forward).
Definition: The pericardium is a protective sac that completely envelops the heart, consisting of multiple specialized layers that allow for smooth cardiac movement while maintaining structural integrity.
The description de l'enveloppe péricardique et ses couches reveals three distinct layers: the fibrous pericardium (outermost), the parietal layer, and the visceral layer (innermost). These layers work together to provide protection and facilitate proper cardiac function. The space between the parietal and visceral layers contains pericardial fluid, which reduces friction during cardiac movements.

The heart consists of four main chambers - two atria and two ventricles. The fonction des valves cardiaques et leur rôle is crucial for maintaining unidirectional blood flow through these chambers. The right side handles deoxygenated blood while the left manages oxygenated blood.
Highlight: The atrioventricular valves (tricuspid on the right, mitral on the left) prevent backflow of blood from ventricles to atria during contraction.
The semilunar valves guard the exits of both ventricles - the pulmonary valve at the right ventricular outlet and the aortic valve at the left ventricular outlet. These valves ensure blood flows forward into the major vessels without regurgitation.
The heart's external surface features several important grooves and landmarks. The coronary groove (sulcus coronarius) marks the external boundary between atria and ventricles, while longitudinal grooves indicate the separation between right and left ventricles.

The heart wall consists of three distinct layers, each serving specific functions in cardiac operation. The epicardium (outer layer) provides a protective covering and connects with the pericardial sac. The myocardium (middle layer) comprises the cardiac muscle tissue responsible for pumping action.
Vocabulary: The myocardium contains specialized cardiac muscle cells called cardiomyocytes, which enable rhythmic contractions through both intrinsic and unifying fiber systems.
The endocardium (inner layer) lines the heart chambers and is continuous with blood vessel endothelium. This smooth lining prevents blood clot formation and facilitates efficient blood flow through the chambers.
The cardiac muscle fibers are arranged in complex patterns that optimize pumping efficiency. These include deep proper fibers specific to each chamber and superficial unitive fibers that coordinate contractions across multiple chambers.

The circulation through the heart follows a precise sequence, with blood entering the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. The blood then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
Example: Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs via pulmonary veins to the left atrium, then passes through the mitral valve to the left ventricle before being ejected into the aorta for systemic circulation.
The interventricular septum completely separates the right and left ventricles, preventing mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This separation is crucial for maintaining efficient oxygen delivery to body tissues.
Special conducting tissues within the heart walls coordinate the timing of contractions. The sinoatrial node, located in the right atrial wall, serves as the heart's natural pacemaker, initiating each heartbeat through electrical impulses.




Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Margaux
@margaux_eesu
The heart is a remarkable muscular organ that works tirelessly to pump blood throughout our bodies.
The anatomie du cœur et ses structuresconsists of four main chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles. The right side handles... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The heart is a remarkable muscular organ positioned within the thoracic cavity, serving as the body's primary pumping station. The anatomie du cœur et ses structures includes several key components working in harmony to maintain circulation.
The heart's location is precisely positioned between the third and sixth ribs, slightly offset to the left of the median plane. This positioning allows for optimal function while being protected by the ribcage. The organ is oriented with its base pointing cranially (toward the head) and its apex directed ventro-caudally (downward and forward).
Definition: The pericardium is a protective sac that completely envelops the heart, consisting of multiple specialized layers that allow for smooth cardiac movement while maintaining structural integrity.
The description de l'enveloppe péricardique et ses couches reveals three distinct layers: the fibrous pericardium (outermost), the parietal layer, and the visceral layer (innermost). These layers work together to provide protection and facilitate proper cardiac function. The space between the parietal and visceral layers contains pericardial fluid, which reduces friction during cardiac movements.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The heart consists of four main chambers - two atria and two ventricles. The fonction des valves cardiaques et leur rôle is crucial for maintaining unidirectional blood flow through these chambers. The right side handles deoxygenated blood while the left manages oxygenated blood.
Highlight: The atrioventricular valves (tricuspid on the right, mitral on the left) prevent backflow of blood from ventricles to atria during contraction.
The semilunar valves guard the exits of both ventricles - the pulmonary valve at the right ventricular outlet and the aortic valve at the left ventricular outlet. These valves ensure blood flows forward into the major vessels without regurgitation.
The heart's external surface features several important grooves and landmarks. The coronary groove (sulcus coronarius) marks the external boundary between atria and ventricles, while longitudinal grooves indicate the separation between right and left ventricles.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The heart wall consists of three distinct layers, each serving specific functions in cardiac operation. The epicardium (outer layer) provides a protective covering and connects with the pericardial sac. The myocardium (middle layer) comprises the cardiac muscle tissue responsible for pumping action.
Vocabulary: The myocardium contains specialized cardiac muscle cells called cardiomyocytes, which enable rhythmic contractions through both intrinsic and unifying fiber systems.
The endocardium (inner layer) lines the heart chambers and is continuous with blood vessel endothelium. This smooth lining prevents blood clot formation and facilitates efficient blood flow through the chambers.
The cardiac muscle fibers are arranged in complex patterns that optimize pumping efficiency. These include deep proper fibers specific to each chamber and superficial unitive fibers that coordinate contractions across multiple chambers.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
The circulation through the heart follows a precise sequence, with blood entering the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. The blood then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
Example: Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs via pulmonary veins to the left atrium, then passes through the mitral valve to the left ventricle before being ejected into the aorta for systemic circulation.
The interventricular septum completely separates the right and left ventricles, preventing mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This separation is crucial for maintaining efficient oxygen delivery to body tissues.
Special conducting tissues within the heart walls coordinate the timing of contractions. The sinoatrial node, located in the right atrial wall, serves as the heart's natural pacemaker, initiating each heartbeat through electrical impulses.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
9
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
Notes on different homeostatic disorders of the stomach (like GERD, appendicitis, etc.) for anatomy and physiology classes. My tummy hurts too, man.
Uncover the secrets of life with this comprehensive Biology flashcard set. Perfect for grade 10 students studying Living Environment.
Short Intro of GMO
A brief topic about genetically modified organisms (GMO) in Biology
flashcards for cell membrane
Explore the fundamentals of genetics, including the roles of DNA, mRNA, and tRNA in protein synthesis. Understand key concepts such as alleles, genotypes, phenotypes, and the processes of transcription and translation. This summary provides essential insights into genetic inheritance and the expression of traits.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user