Your computer's inner workings might seem mysterious, but understanding the... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
153
•
Feb 14, 2026
•
Zyx Tempest
@zyxtempest_cusk
Your computer's inner workings might seem mysterious, but understanding the... Show more







Ever wonder what makes your computer tick? It all starts with the CPU (Central Processing Unit), which transforms raw data into useful information and controls the entire system. Think of it as your computer's brain!
Your computer has different types of storage. Primary storage temporarily holds data and instructions during processing, while secondary storage keeps information when the computer is off. Input devices like keyboards and output devices like screens help you interact with the computer.
Inside the system unit (the main box of your computer) sits the motherboard, which connects everything together. This main circuit board contains adapter cards, processor chips, and memory chips.
Fun Fact: Computers speak binary! Everything you see on screen—all text, images, and videos—is converted into binary code (just 0s and 1s). Each letter or character is represented by a specific pattern, like 01000001 for the letter "A".

When you press a key on your keyboard, a fascinating process begins! That keypress becomes an electronic signal, gets converted to binary code (using standards like ASCII or EBCDIC), and eventually appears on your screen.
The CPU has two main parts that work together. The Control Unit acts like a traffic director, coordinating operations and telling components what to do. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) handles all the math operations and comparisons—it adds, subtracts, and figures out when one value is greater than another.
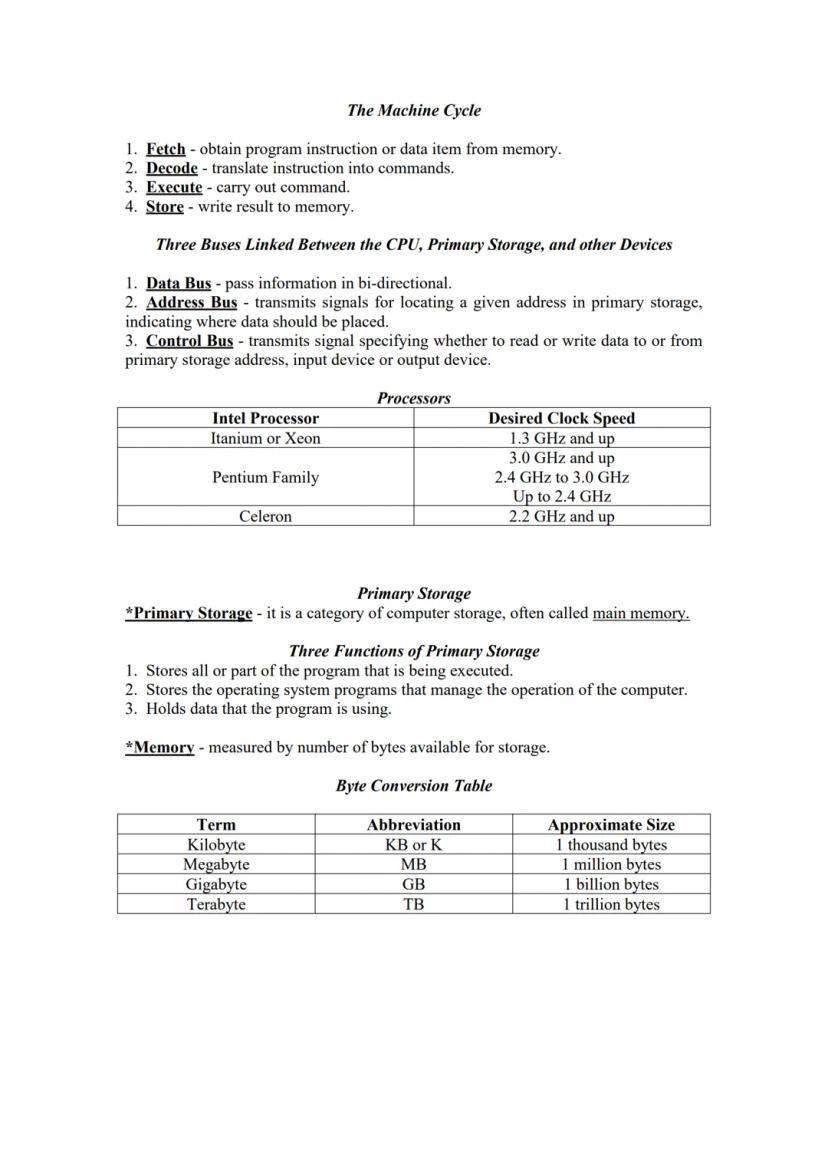
Your computer follows a specific cycle called the Machine Cycle: fetch an instruction, decode it, execute the command, and store the result. This happens millions of times per second!
Quick Tip: When you see computer speeds measured in GHz (gigahertz), that's telling you how many billions of machine cycles your processor can complete each second. Higher numbers usually mean faster performance!
The machine cycle happens incredibly fast! Your computer fetches instructions, decodes them, executes commands, and stores results—all through three types of "buses" (data pathways): the data bus, address bus, and control bus.
Different processors have different speeds. Intel processors range from basic Celeron models (up to 2.4 GHz) to powerful Itanium or Xeon processors (3.0 GHz and up). The faster the processor, the quicker your computer can complete tasks.
Primary storage (also called main memory) serves three key functions: it stores the program currently running, holds the operating system programs, and keeps the data being used. We measure memory in bytes, from kilobytes (KB) to terabytes (TB).
Memory Matters: Your computer's memory affects performance as much as processor speed! A terabyte (TB) is approximately one trillion bytes—enough to store about 250,000 songs or 500 hours of HD video.

Random Access Memory (RAM) is where your computer keeps programs and data it's actively using. When you start your web browser, its instructions load from the hard disk into RAM. RAM is volatile—everything disappears when you turn off your computer!
The RAM process is something you experience every day: When you turn on your computer, operating system files load into RAM. When you open programs, they load into RAM too. Close a program, and it's removed from RAM.
There are different types of RAM: Dynamic RAM (DRAM) needs constant refreshing and is most common, while Static RAM (SRAM) is faster but doesn't need refreshing as often. A newer type called Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) is being developed.
Know the Difference: Unlike RAM, Read-Only Memory (ROM) doesn't forget! ROM is non-volatile memory that keeps its data even when powered off. It stores critical programs that rarely change, like the instructions that help your computer start up.

While RAM disappears when you shut down, secondary storage keeps your data safe long-term. These peripheral devices (sitting outside the main system unit) are non-volatile, meaning they retain information even when powered off.
Magnetic disks let you access data directly without having to search through everything sequentially. Hard disks have multiple rigid platters sealed in an airtight case, while floppy disks (now obsolete) used flexible film in a plastic shell.
Hard disks work through fascinating mechanics: A motor spins the platters while a head actuator positions read/write heads over the correct tracks (circular recording bands) and sectors (storage areas). Before use, disks must go through formatting to prepare them for storing data.
Behind the Scenes: When you save a file, your computer doesn't just dump data anywhere on the disk. It carefully organizes information into tracks and sectors—like a librarian shelving books in specific locations so they can be found later!

Optical disks like CDs and DVDs use laser technology to store data at much higher densities than magnetic disks. When a laser reads an optical disk, it shines light on the surface—if light hits a pit, it scatters; if it hits a land, it reflects back. These different reflections create the 1s and 0s of digital data.
CD-ROMs can typically hold 650 MB to 1 GB but can't be modified once created. For writable options, CD-R (write once) and CD-RW (rewritable) discs let you save your own data. These were common for distributing software and multimedia.
DVDs took optical storage further with capacities from 4.7 GB to 17 GB! DVDs achieve this by using multiple layers and sides. The most advanced version—double-sided, dual-layer DVDs—can hold 17 GB. Modern Blu-ray discs push capacity even higher, storing up to 27 GB.
Storage Evolution: If you had to store 17 GB of data using floppy disks from the 1990s, you'd need over 12,000 disks! Technology has made storage dramatically more efficient over time.

Magnetic tape might seem outdated, but it's still used for storing massive amounts of data. This technology uses magnetically coated plastic ribbons that can hold incredible amounts of information at low cost.
The main advantages of tape are its affordability, stability, and enormous storage capacity. However, it has significant drawbacks too. Data is stored sequentially , and it's much slower than modern storage options.
PC Cards add capabilities to computers—especially notebooks and laptops. These credit card-sized devices plug into special slots, allowing you to expand your computer's functionality without opening up the case.
Backup Basics: Large companies often still use magnetic tape for backups because it's inexpensive and reliable for long-term storage. One tape can last 30+ years when properly stored, making it perfect for archiving data that isn't accessed frequently!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Zyx Tempest
@zyxtempest_cusk
Your computer's inner workings might seem mysterious, but understanding the basic components helps you make sense of this technology. This summary breaks down how computer systems function, from the CPU that processes information to the various storage types that keep... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wonder what makes your computer tick? It all starts with the CPU (Central Processing Unit), which transforms raw data into useful information and controls the entire system. Think of it as your computer's brain!
Your computer has different types of storage. Primary storage temporarily holds data and instructions during processing, while secondary storage keeps information when the computer is off. Input devices like keyboards and output devices like screens help you interact with the computer.
Inside the system unit (the main box of your computer) sits the motherboard, which connects everything together. This main circuit board contains adapter cards, processor chips, and memory chips.
Fun Fact: Computers speak binary! Everything you see on screen—all text, images, and videos—is converted into binary code (just 0s and 1s). Each letter or character is represented by a specific pattern, like 01000001 for the letter "A".

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
When you press a key on your keyboard, a fascinating process begins! That keypress becomes an electronic signal, gets converted to binary code (using standards like ASCII or EBCDIC), and eventually appears on your screen.
The CPU has two main parts that work together. The Control Unit acts like a traffic director, coordinating operations and telling components what to do. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) handles all the math operations and comparisons—it adds, subtracts, and figures out when one value is greater than another.
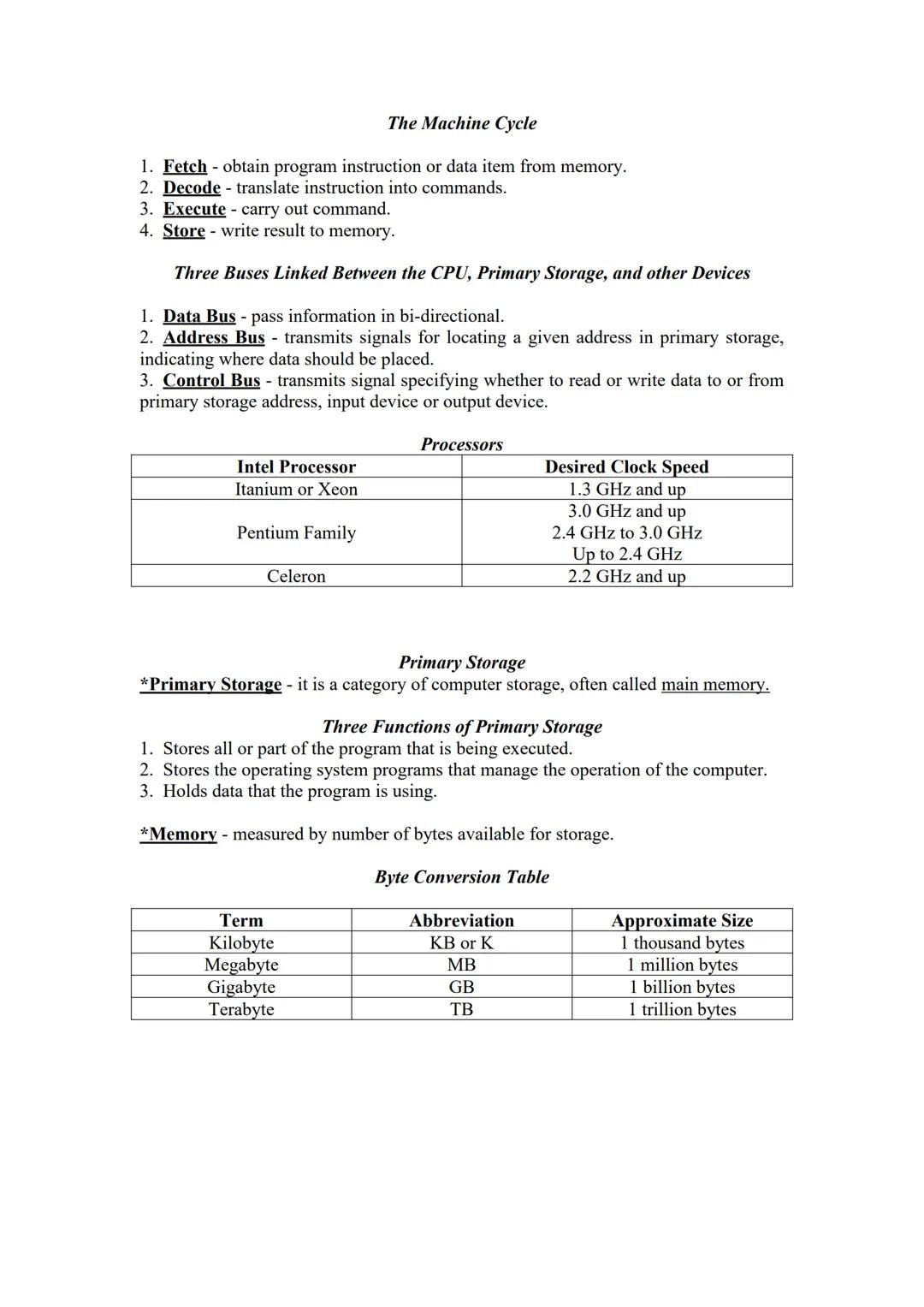
Your computer follows a specific cycle called the Machine Cycle: fetch an instruction, decode it, execute the command, and store the result. This happens millions of times per second!
Quick Tip: When you see computer speeds measured in GHz (gigahertz), that's telling you how many billions of machine cycles your processor can complete each second. Higher numbers usually mean faster performance!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The machine cycle happens incredibly fast! Your computer fetches instructions, decodes them, executes commands, and stores results—all through three types of "buses" (data pathways): the data bus, address bus, and control bus.
Different processors have different speeds. Intel processors range from basic Celeron models (up to 2.4 GHz) to powerful Itanium or Xeon processors (3.0 GHz and up). The faster the processor, the quicker your computer can complete tasks.
Primary storage (also called main memory) serves three key functions: it stores the program currently running, holds the operating system programs, and keeps the data being used. We measure memory in bytes, from kilobytes (KB) to terabytes (TB).
Memory Matters: Your computer's memory affects performance as much as processor speed! A terabyte (TB) is approximately one trillion bytes—enough to store about 250,000 songs or 500 hours of HD video.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Random Access Memory (RAM) is where your computer keeps programs and data it's actively using. When you start your web browser, its instructions load from the hard disk into RAM. RAM is volatile—everything disappears when you turn off your computer!
The RAM process is something you experience every day: When you turn on your computer, operating system files load into RAM. When you open programs, they load into RAM too. Close a program, and it's removed from RAM.
There are different types of RAM: Dynamic RAM (DRAM) needs constant refreshing and is most common, while Static RAM (SRAM) is faster but doesn't need refreshing as often. A newer type called Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) is being developed.
Know the Difference: Unlike RAM, Read-Only Memory (ROM) doesn't forget! ROM is non-volatile memory that keeps its data even when powered off. It stores critical programs that rarely change, like the instructions that help your computer start up.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
While RAM disappears when you shut down, secondary storage keeps your data safe long-term. These peripheral devices (sitting outside the main system unit) are non-volatile, meaning they retain information even when powered off.
Magnetic disks let you access data directly without having to search through everything sequentially. Hard disks have multiple rigid platters sealed in an airtight case, while floppy disks (now obsolete) used flexible film in a plastic shell.
Hard disks work through fascinating mechanics: A motor spins the platters while a head actuator positions read/write heads over the correct tracks (circular recording bands) and sectors (storage areas). Before use, disks must go through formatting to prepare them for storing data.
Behind the Scenes: When you save a file, your computer doesn't just dump data anywhere on the disk. It carefully organizes information into tracks and sectors—like a librarian shelving books in specific locations so they can be found later!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Optical disks like CDs and DVDs use laser technology to store data at much higher densities than magnetic disks. When a laser reads an optical disk, it shines light on the surface—if light hits a pit, it scatters; if it hits a land, it reflects back. These different reflections create the 1s and 0s of digital data.
CD-ROMs can typically hold 650 MB to 1 GB but can't be modified once created. For writable options, CD-R (write once) and CD-RW (rewritable) discs let you save your own data. These were common for distributing software and multimedia.
DVDs took optical storage further with capacities from 4.7 GB to 17 GB! DVDs achieve this by using multiple layers and sides. The most advanced version—double-sided, dual-layer DVDs—can hold 17 GB. Modern Blu-ray discs push capacity even higher, storing up to 27 GB.
Storage Evolution: If you had to store 17 GB of data using floppy disks from the 1990s, you'd need over 12,000 disks! Technology has made storage dramatically more efficient over time.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Magnetic tape might seem outdated, but it's still used for storing massive amounts of data. This technology uses magnetically coated plastic ribbons that can hold incredible amounts of information at low cost.
The main advantages of tape are its affordability, stability, and enormous storage capacity. However, it has significant drawbacks too. Data is stored sequentially , and it's much slower than modern storage options.
PC Cards add capabilities to computers—especially notebooks and laptops. These credit card-sized devices plug into special slots, allowing you to expand your computer's functionality without opening up the case.
Backup Basics: Large companies often still use magnetic tape for backups because it's inexpensive and reliable for long-term storage. One tape can last 30+ years when properly stored, making it perfect for archiving data that isn't accessed frequently!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
6
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
Computer Science (9718)
This is a lecture note that is all about using Microsoft Word. This includes detailed step by step process as well as the important parts in Microsoft Word.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user