Ever wondered how your body actually works at the microscopic... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Subjects

83
0
person with this ability
12/9/2025
GenBio
GENBIO 1
1,610
•
Dec 9, 2025
•
person with this ability
@o0ootm3al.xahsn
Ever wondered how your body actually works at the microscopic... Show more











Your whole body - from your brain to your toenails - is made up of tiny building blocks called cells. The cell theory tells us three key things: all living things are made of cells, cells are life's basic units, and every cell comes from another existing cell.
Robert Hooke was the first person to actually see cells when he looked at cork (dead plant material) under a microscope. He called them "cells" because they looked like the small rooms monks lived in. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek took it further by making his own microscope and discovering living organisms in pond water and teeth scrapings - pretty gross but groundbreaking!
The theory really came together when three scientists made their discoveries. Matthias Schleiden (botanist) said all plants are made of cells, Theodore Schwann (zoologist) said all animals are made of cells, and Rudolph Virchow observed cells dividing and concluded that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
💡 Remember: The modern cell theory also includes that energy flows within cells, cells carry DNA, and all cells have similar chemical composition.

Think of organelles as tiny organs inside your cells - each one has a specific job that keeps the cell alive. The cell membrane acts like a security guard, deciding what gets in and out of your cell. It's made mainly of phospholipids and controls everything that passes through.
The nucleus is basically the cell's brain - it stores DNA and controls all cell activities. Ribosomes are the protein factories where amino acids get assembled into proteins your body needs. Mitochondria are called the "powerhouse of the cell" because they produce ATP, which is like cellular energy currency.
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: rough ER (has ribosomes attached for making proteins) and smooth ER (makes lipids and steroids). The Golgi complex works like a post office - it packages and ships proteins and lipids to where they need to go.
Lysosomes are the cleanup crew that digest waste and break down worn-out organelles. In plant cells, chloroplasts capture sunlight for photosynthesis, and vacuoles store water and maintain cell shape.
💡 Quick tip: Remember the mitochondria motto - "mighty mitochondria make my energy!"

Cells come in two main types that are pretty different from each other. Eukaryotic cells (like yours) have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles - they're more complex and can be part of multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) don't have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles and are always unicellular.
Both types share some basics though: DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and cell membranes. Prokaryotes get energy in different ways - some use sunlight (photosynthetic), some cause diseases by feeding on living things, and others decompose dead material.
When similar cells group together to do the same job, they form tissues. Animals have four main tissue types: epithelial tissue (covers body surfaces and lines cavities), connective tissue (binds organs together), muscle tissue (creates movement), and nervous tissue (sends signals).
Plants have three tissue types: ground tissue (does photosynthesis and storage), vascular tissue (transports water and food), and dermal tissue (protects the plant surface).
💡 Memory trick: Eukaryotes are "true nucleus" cells (more complex), prokaryotes are "before nucleus" cells (simpler).

Different cells in your body have evolved to do specific tasks really well. Red blood cells are disk-shaped and packed with hemoglobin to carry oxygen efficiently. White blood cells are your immune system's soldiers - they hunt down and destroy bacteria and other invaders.
Nerve cells have long extensions to send electrical signals throughout your body at lightning speed. Muscle cells are packed with mitochondria because moving your body requires tons of energy. Ciliated epithelial cells line your airways and sweep out dust and bacteria like tiny brooms.
Plant cells are specialized too. Root hair cells have no chloroplasts but lots of mitochondria to absorb water and minerals from soil. Palisade cells are stuffed with chloroplasts to capture sunlight for photosynthesis. Xylem cells lose their end walls and internal structures to become hollow tubes for transporting water.
Gametes (sex cells) are super specialized - sperm cells are built for swimming to eggs, while egg cells are large and nutrient-rich to support a developing embryo.
💡 Key insight: Cell structure always matches cell function - form follows function in biology!

Your body constantly makes new cells through cell division - when one "parent cell" splits into two "daughter cells." The cell cycle has two main phases: interphase (when cells grow and copy their DNA) and M phase (when actual division happens).
Interphase has three stages: G1 (cell grows and makes organelles), S (DNA gets copied), and G2 (final preparations for division). During this time, chromatin (loose DNA) condenses into visible chromosomes, and centrioles prepare the machinery needed for division.
Mitosis creates two identical body cells and has five stages. Prophase: chromosomes become visible and centrioles move apart. Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the cell's center. Anaphase: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends. Telophase: new nuclei form around each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis actually splits the cytoplasm - in animal cells, the membrane pinches inward, while plant cells build a new wall down the middle.
💡 Memory aid: PMAT helps you remember mitosis phases - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase!

While mitosis makes identical body cells, meiosis creates sex cells (gametes) that are genetically unique. This process happens in two rounds of division and produces four haploid cells instead of two diploid ones.
Meiosis I is where the magic happens. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs - this swaps genetic material between chromosomes, creating new combinations. Metaphase I lines up chromosome pairs, then anaphase I separates the pairs (not individual chromatids yet).
Meiosis II is basically like mitosis but with half the chromosomes. The cells go through prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. This time, sister chromatids actually separate, giving you four genetically different haploid cells.
Crossing over and the random separation of chromosomes are why you don't look exactly like your siblings - meiosis creates genetic diversity that makes each person unique.
💡 Big picture: Meiosis reduces chromosome number by half and shuffles genes - that's how sexual reproduction creates genetic variety!

Your cell membrane isn't just a simple barrier - it's a complex structure that carefully controls what enters and exits your cells. The fluid mosaic model describes it as a double layer of phospholipids with various proteins floating in it like pieces in a mosaic.
Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. They arrange themselves in a bilayer with heads facing outward toward water and tails pointing inward away from water. This creates a semi-permeable barrier.
Cholesterol molecules scattered throughout make the membrane less fluid and more stable. Glycolipids on the outer surface help with cell recognition and stability. Various proteins embedded in the membrane serve as channels, transporters, and receptors.
Glycoproteins span the entire membrane and act as doorways for large molecules. Receptor proteins help cells communicate by binding to hormones and other signaling molecules. Globular proteins assist with moving specific substances across the membrane.
💡 Visual aid: Picture the membrane like a fluid sandwich with protein "chunks" - it's flexible but selective about what passes through!

Your cell membrane is semi-permeable, meaning it lets some things through but not others. Passive transport moves substances without using energy, while active transport requires energy in the form of ATP.
Simple diffusion lets small, nonpolar molecules move from high to low concentration - like oxygen entering your blood. Facilitated diffusion uses channel or carrier proteins to help larger or polar molecules cross. Osmosis is just diffusion of water through special channels called aquaporins.
Tonicity describes how solutions affect cell shape. Hypertonic solutions (more solutes) make cells shrink, hypotonic solutions (fewer solutes) make cells swell, and isotonic solutions keep cells normal-sized.
Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient using ATP. Endocytosis brings materials into cells by wrapping them in membrane vesicles - phagocytosis ("cell eating") and pinocytosis ("cell drinking"). Exocytosis does the opposite, shipping materials out of cells.
💡 Remember: Passive transport goes "downhill" (no energy needed), active transport goes "uphill" (energy required)!
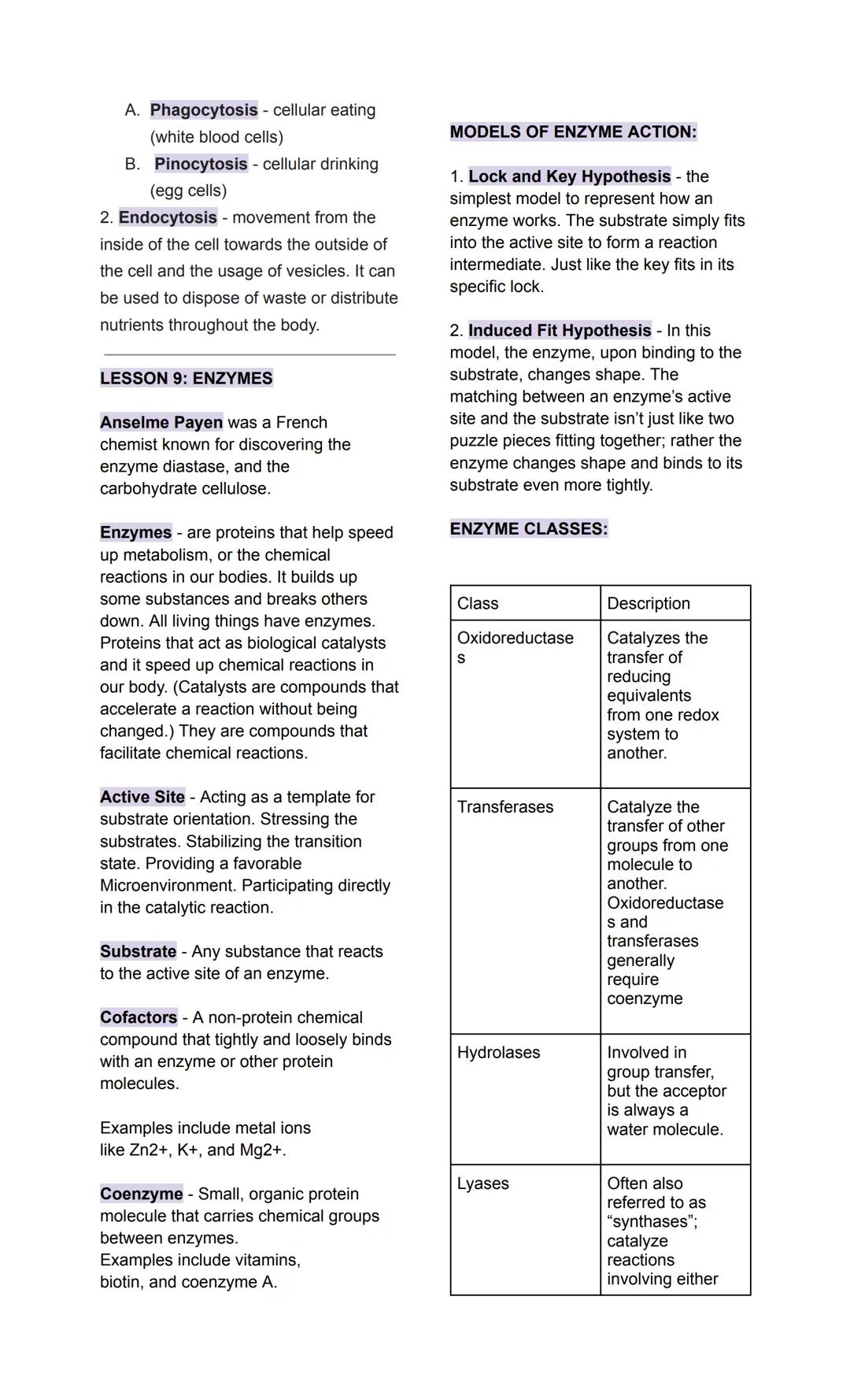
Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in your body without being used up themselves. Discovered by Anselme Payen, these molecular machines make life possible by accelerating reactions that would otherwise happen too slowly.
Every enzyme has an active site where substrates (the molecules being changed) bind and react. Cofactors (like metal ions) and coenzymes (like vitamins) often help enzymes work properly.
The lock and key model suggests substrates fit perfectly into enzyme active sites, like a key in a lock. The induced fit model is more accurate - enzymes actually change shape slightly when substrates bind, creating an even better fit.
Enzymes are classified into six main types: oxidoreductases (handle electron transfers), transferases (move chemical groups), hydrolases (break bonds using water), lyases (form or break double bonds), isomerases (rearrange molecules), and ligases (join molecules using ATP energy).
💡 Key concept: Enzymes lower activation energy - they're like removing speed bumps from chemical reactions!
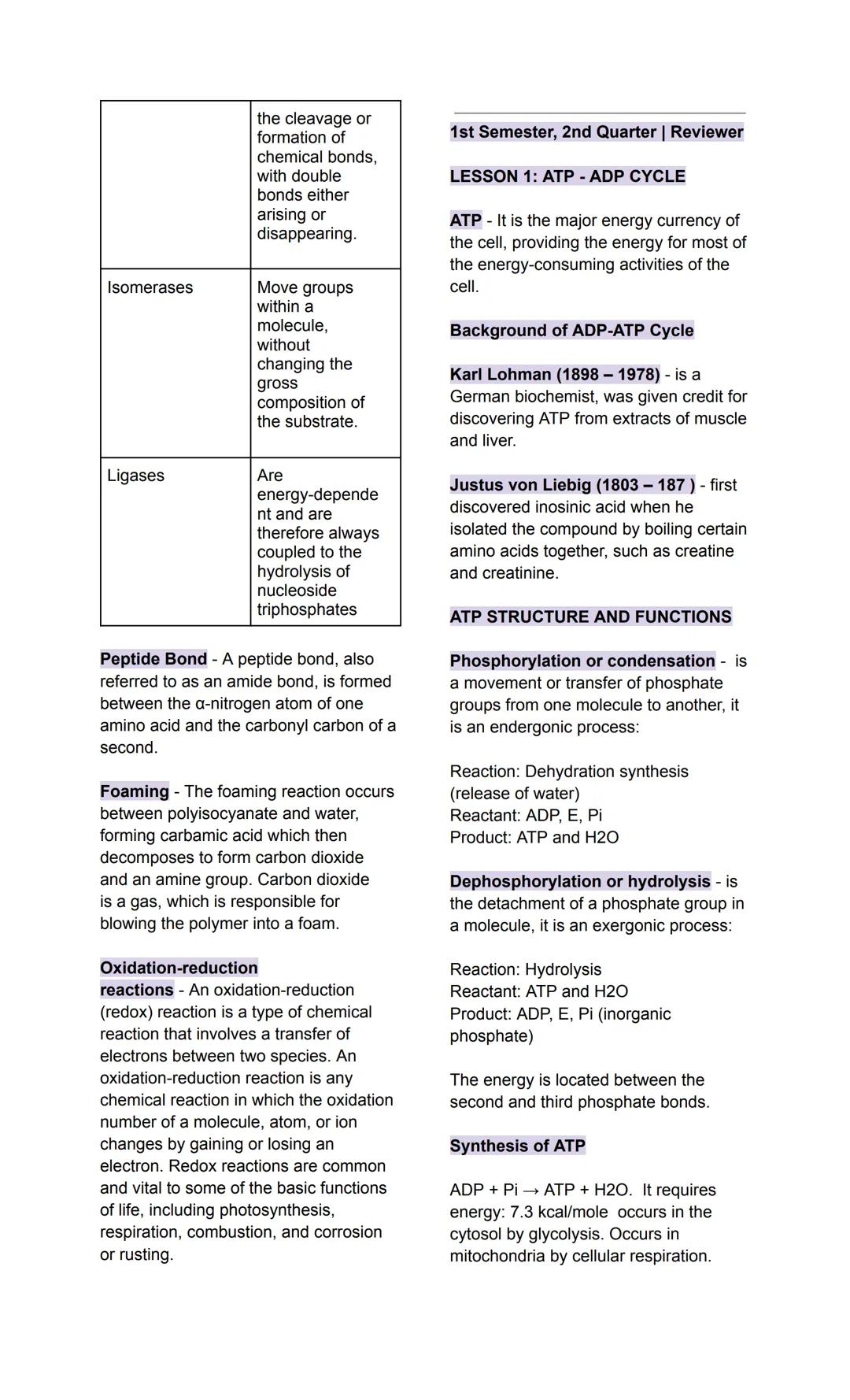
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is like your body's rechargeable battery - it stores and releases energy for almost everything your cells do. Discovered by Karl Lohman, this molecule powers muscle contractions, nerve signals, and countless other cellular processes.
ATP gets made through phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group) which requires energy input. The process combines ADP (adenosine diphosphate) with inorganic phosphate using energy from food. This is called dehydration synthesis because it releases water.
When your cells need energy, dephosphorylation (removing a phosphate) breaks down ATP back into ADP plus phosphate, releasing stored energy. This hydrolysis reaction provides about 7.3 kcal/mole of energy - enough to power cellular work.
The ATP-ADP cycle constantly recycles in your cells. ATP gets made in your cytoplasm through glycolysis and in your mitochondria through cellular respiration. The energy is stored in the bonds between phosphate groups, especially between the second and third phosphates.
💡 Think of it: ATP is like a rechargeable phone battery - it gets charged up (phosphorylation) then releases energy when needed (dephosphorylation)!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
person with this ability
@o0ootm3al.xahsn
Ever wondered how your body actually works at the microscopic level? This biology review covers everything from the basic building blocks of life (cells) to how your body creates energy to keep you alive and moving.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your whole body - from your brain to your toenails - is made up of tiny building blocks called cells. The cell theory tells us three key things: all living things are made of cells, cells are life's basic units, and every cell comes from another existing cell.
Robert Hooke was the first person to actually see cells when he looked at cork (dead plant material) under a microscope. He called them "cells" because they looked like the small rooms monks lived in. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek took it further by making his own microscope and discovering living organisms in pond water and teeth scrapings - pretty gross but groundbreaking!
The theory really came together when three scientists made their discoveries. Matthias Schleiden (botanist) said all plants are made of cells, Theodore Schwann (zoologist) said all animals are made of cells, and Rudolph Virchow observed cells dividing and concluded that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
💡 Remember: The modern cell theory also includes that energy flows within cells, cells carry DNA, and all cells have similar chemical composition.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Think of organelles as tiny organs inside your cells - each one has a specific job that keeps the cell alive. The cell membrane acts like a security guard, deciding what gets in and out of your cell. It's made mainly of phospholipids and controls everything that passes through.
The nucleus is basically the cell's brain - it stores DNA and controls all cell activities. Ribosomes are the protein factories where amino acids get assembled into proteins your body needs. Mitochondria are called the "powerhouse of the cell" because they produce ATP, which is like cellular energy currency.
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: rough ER (has ribosomes attached for making proteins) and smooth ER (makes lipids and steroids). The Golgi complex works like a post office - it packages and ships proteins and lipids to where they need to go.
Lysosomes are the cleanup crew that digest waste and break down worn-out organelles. In plant cells, chloroplasts capture sunlight for photosynthesis, and vacuoles store water and maintain cell shape.
💡 Quick tip: Remember the mitochondria motto - "mighty mitochondria make my energy!"

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Cells come in two main types that are pretty different from each other. Eukaryotic cells (like yours) have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles - they're more complex and can be part of multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) don't have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles and are always unicellular.
Both types share some basics though: DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and cell membranes. Prokaryotes get energy in different ways - some use sunlight (photosynthetic), some cause diseases by feeding on living things, and others decompose dead material.
When similar cells group together to do the same job, they form tissues. Animals have four main tissue types: epithelial tissue (covers body surfaces and lines cavities), connective tissue (binds organs together), muscle tissue (creates movement), and nervous tissue (sends signals).
Plants have three tissue types: ground tissue (does photosynthesis and storage), vascular tissue (transports water and food), and dermal tissue (protects the plant surface).
💡 Memory trick: Eukaryotes are "true nucleus" cells (more complex), prokaryotes are "before nucleus" cells (simpler).

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Different cells in your body have evolved to do specific tasks really well. Red blood cells are disk-shaped and packed with hemoglobin to carry oxygen efficiently. White blood cells are your immune system's soldiers - they hunt down and destroy bacteria and other invaders.
Nerve cells have long extensions to send electrical signals throughout your body at lightning speed. Muscle cells are packed with mitochondria because moving your body requires tons of energy. Ciliated epithelial cells line your airways and sweep out dust and bacteria like tiny brooms.
Plant cells are specialized too. Root hair cells have no chloroplasts but lots of mitochondria to absorb water and minerals from soil. Palisade cells are stuffed with chloroplasts to capture sunlight for photosynthesis. Xylem cells lose their end walls and internal structures to become hollow tubes for transporting water.
Gametes (sex cells) are super specialized - sperm cells are built for swimming to eggs, while egg cells are large and nutrient-rich to support a developing embryo.
💡 Key insight: Cell structure always matches cell function - form follows function in biology!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your body constantly makes new cells through cell division - when one "parent cell" splits into two "daughter cells." The cell cycle has two main phases: interphase (when cells grow and copy their DNA) and M phase (when actual division happens).
Interphase has three stages: G1 (cell grows and makes organelles), S (DNA gets copied), and G2 (final preparations for division). During this time, chromatin (loose DNA) condenses into visible chromosomes, and centrioles prepare the machinery needed for division.
Mitosis creates two identical body cells and has five stages. Prophase: chromosomes become visible and centrioles move apart. Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the cell's center. Anaphase: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends. Telophase: new nuclei form around each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis actually splits the cytoplasm - in animal cells, the membrane pinches inward, while plant cells build a new wall down the middle.
💡 Memory aid: PMAT helps you remember mitosis phases - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
While mitosis makes identical body cells, meiosis creates sex cells (gametes) that are genetically unique. This process happens in two rounds of division and produces four haploid cells instead of two diploid ones.
Meiosis I is where the magic happens. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs - this swaps genetic material between chromosomes, creating new combinations. Metaphase I lines up chromosome pairs, then anaphase I separates the pairs (not individual chromatids yet).
Meiosis II is basically like mitosis but with half the chromosomes. The cells go through prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. This time, sister chromatids actually separate, giving you four genetically different haploid cells.
Crossing over and the random separation of chromosomes are why you don't look exactly like your siblings - meiosis creates genetic diversity that makes each person unique.
💡 Big picture: Meiosis reduces chromosome number by half and shuffles genes - that's how sexual reproduction creates genetic variety!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your cell membrane isn't just a simple barrier - it's a complex structure that carefully controls what enters and exits your cells. The fluid mosaic model describes it as a double layer of phospholipids with various proteins floating in it like pieces in a mosaic.
Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. They arrange themselves in a bilayer with heads facing outward toward water and tails pointing inward away from water. This creates a semi-permeable barrier.
Cholesterol molecules scattered throughout make the membrane less fluid and more stable. Glycolipids on the outer surface help with cell recognition and stability. Various proteins embedded in the membrane serve as channels, transporters, and receptors.
Glycoproteins span the entire membrane and act as doorways for large molecules. Receptor proteins help cells communicate by binding to hormones and other signaling molecules. Globular proteins assist with moving specific substances across the membrane.
💡 Visual aid: Picture the membrane like a fluid sandwich with protein "chunks" - it's flexible but selective about what passes through!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Your cell membrane is semi-permeable, meaning it lets some things through but not others. Passive transport moves substances without using energy, while active transport requires energy in the form of ATP.
Simple diffusion lets small, nonpolar molecules move from high to low concentration - like oxygen entering your blood. Facilitated diffusion uses channel or carrier proteins to help larger or polar molecules cross. Osmosis is just diffusion of water through special channels called aquaporins.
Tonicity describes how solutions affect cell shape. Hypertonic solutions (more solutes) make cells shrink, hypotonic solutions (fewer solutes) make cells swell, and isotonic solutions keep cells normal-sized.
Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient using ATP. Endocytosis brings materials into cells by wrapping them in membrane vesicles - phagocytosis ("cell eating") and pinocytosis ("cell drinking"). Exocytosis does the opposite, shipping materials out of cells.
💡 Remember: Passive transport goes "downhill" (no energy needed), active transport goes "uphill" (energy required)!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in your body without being used up themselves. Discovered by Anselme Payen, these molecular machines make life possible by accelerating reactions that would otherwise happen too slowly.
Every enzyme has an active site where substrates (the molecules being changed) bind and react. Cofactors (like metal ions) and coenzymes (like vitamins) often help enzymes work properly.
The lock and key model suggests substrates fit perfectly into enzyme active sites, like a key in a lock. The induced fit model is more accurate - enzymes actually change shape slightly when substrates bind, creating an even better fit.
Enzymes are classified into six main types: oxidoreductases (handle electron transfers), transferases (move chemical groups), hydrolases (break bonds using water), lyases (form or break double bonds), isomerases (rearrange molecules), and ligases (join molecules using ATP energy).
💡 Key concept: Enzymes lower activation energy - they're like removing speed bumps from chemical reactions!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
By signing up you accept Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is like your body's rechargeable battery - it stores and releases energy for almost everything your cells do. Discovered by Karl Lohman, this molecule powers muscle contractions, nerve signals, and countless other cellular processes.
ATP gets made through phosphorylation (adding a phosphate group) which requires energy input. The process combines ADP (adenosine diphosphate) with inorganic phosphate using energy from food. This is called dehydration synthesis because it releases water.
When your cells need energy, dephosphorylation (removing a phosphate) breaks down ATP back into ADP plus phosphate, releasing stored energy. This hydrolysis reaction provides about 7.3 kcal/mole of energy - enough to power cellular work.
The ATP-ADP cycle constantly recycles in your cells. ATP gets made in your cytoplasm through glycolysis and in your mitochondria through cellular respiration. The energy is stored in the bonds between phosphate groups, especially between the second and third phosphates.
💡 Think of it: ATP is like a rechargeable phone battery - it gets charged up (phosphorylation) then releases energy when needed (dephosphorylation)!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
83
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Mock Exam ✓ Essay Outlines
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE THE SCHOOLGPT. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user