The cellular level of organization is where the magic of... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Knowunity AI
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
97
•
Feb 12, 2026
•
Bri💟
@aestheticbri
The cellular level of organization is where the magic of... Show more
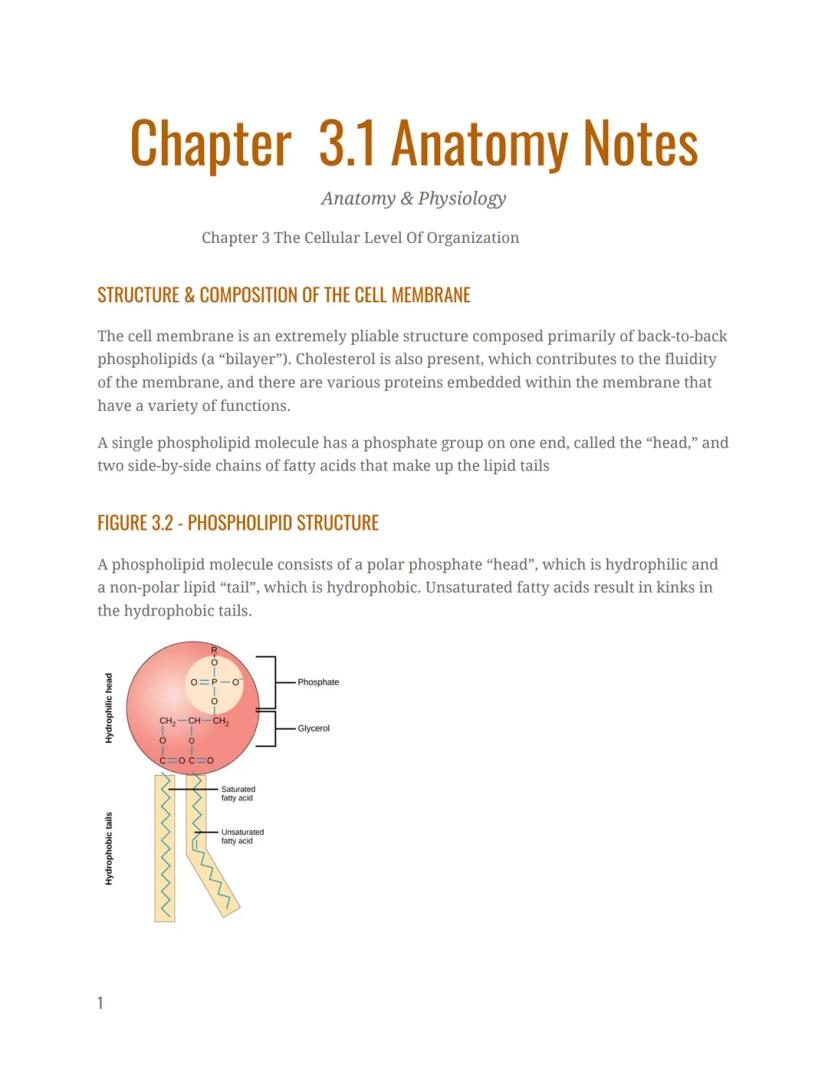







Ever wonder how cells keep their insides separate from the outside world? The answer is the cell membrane—a remarkable structure made primarily of phospholipids arranged in a bilayer . These phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails .
The phospholipid structure is perfectly designed for its job. Each molecule has a phosphate group on one end that forms the "head," while two fatty acid chains make up the lipid "tails." This design is crucial because it allows the membrane to form a protective barrier while still being flexible enough for cellular functions.
Cholesterol is also present in the membrane, contributing to its fluidity. Various proteins embedded within the membrane perform specialized functions that we'll explore further.
Quick Fact: The term "amphipathic" describes molecules like phospholipids that have both water-loving and water-fearing regions in the same molecule. This property is what allows cell membranes to form!

The cell membrane's structure is brilliantly simple yet effective. The phospholipids arrange themselves with their polar, hydrophilic heads facing outward toward watery environments both inside the cell (intracellular fluid or ICF) and outside the cell (extracellular fluid or ECF). Meanwhile, their hydrophobic tails huddle together in the middle, away from water.
This arrangement creates a selective barrier that keeps the cell's contents from leaking out while preventing unwanted materials from getting in. The phosphate heads, with their negative charge, are attracted to the water molecules in both environments, while the uncharged lipid tails repel water.
Some of these lipid tails contain saturated fatty acids (straight tails) while others have unsaturated fatty acids (kinked tails). This combination gives the membrane its necessary fluidity—it's not rigid but more like a liquid mosaic that's constantly in motion.
Remember this: The fluid nature of the cell membrane is essential for cell function. If it were too rigid, cells couldn't grow, divide, or adapt to their environment!

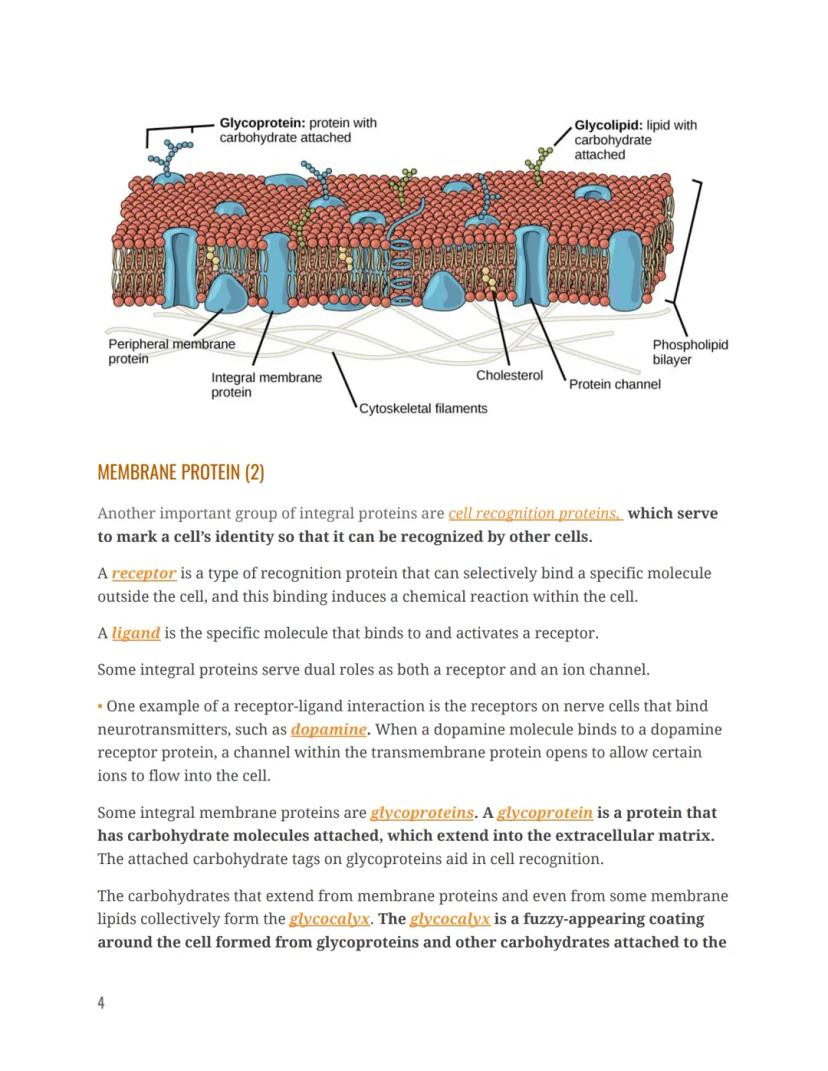
The cell membrane isn't just a lipid bilayer—it's packed with proteins that give it specific functions. Two main types of proteins exist in the membrane: integral proteins and peripheral proteins.
Integral proteins are embedded within the membrane itself. Some, called channel proteins, create passageways that allow specific substances to cross the membrane. Others serve as cell recognition proteins that help cells identify each other—kind of like cellular ID tags. Receptors are another type of integral protein that can bind to specific molecules (ligands) outside the cell, triggering reactions inside.
Many of these proteins have carbohydrate chains attached to them, making them glycoproteins. These carbohydrates extend from the cell surface and collectively form the glycocalyx—a fuzzy coating that surrounds the cell and helps with cell recognition, binding to other cells, and capturing important molecules like hormones.
Fun biology fact: The glycocalyx is unique to each person, almost like a cellular fingerprint! This is why our immune systems can recognize which cells belong in our bodies and which don't—crucial for fighting infections and why organ transplants sometimes get rejected.

Membrane proteins perform diverse functions that are essential for cell survival. Some integral proteins act as both receptors and ion channels simultaneously. For example, when a neurotransmitter like dopamine binds to its receptor on a nerve cell, it opens a channel that allows specific ions to flow into the cell.
Glycoproteins (proteins with attached carbohydrates) extend into the extracellular space and help cells recognize each other. Along with glycolipids (lipids with carbohydrates attached), they form the glycocalyx—a carbohydrate-rich coating around the cell that serves multiple functions:
The glycocalyx is genetically determined, giving each person's trillions of cells their unique identity. This cellular "ID system" helps immune cells recognize which cells belong in your body and which are foreign invaders.
Think about this: The glycocalyx is why organ transplants can be rejected! Your immune system recognizes the donor's cells as "not self" because their glycocalyx carries different molecular markers.

The cell membrane's most impressive feat is regulating what gets in and out of the cell. It controls the movement of ions (like calcium, sodium, and potassium), nutrients (sugars, fatty acids, amino acids), and waste products (especially carbon dioxide).
The membrane's structure creates selective permeability—only certain substances can pass through easily. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol can slip right through the lipid bilayer. However, water-soluble substances like glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes need assistance to cross because they're repelled by the hydrophobic interior of the membrane.
Peripheral proteins attach to the membrane's inner or outer surface and perform specific functions. Some act as digestive enzymes on intestinal cells, breaking down nutrients into smaller pieces that can pass through the membrane and enter the bloodstream.
Real-world application: Understanding membrane transport helps explain how medications enter cells, why certain toxins are dangerous, and how nutrients from the food you eat get absorbed into your bloodstream!

Substances move across the cell membrane using two general methods: passive transport (requiring no energy) and active transport (requiring cellular energy from ATP).
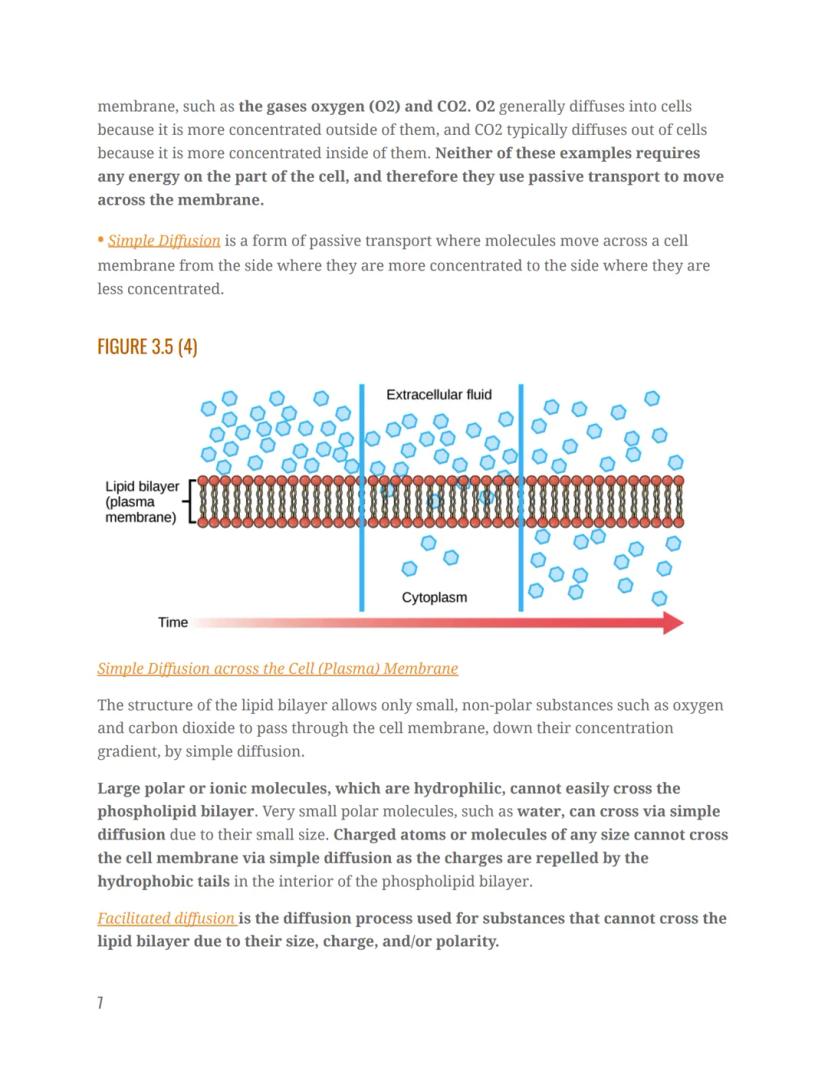
Passive transport relies on concentration gradients—the difference in concentration of a substance across a space. During diffusion, molecules naturally spread from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration until they're evenly distributed. Think about dropping food coloring in water—it spreads on its own without you doing anything!
Temperature affects diffusion speed—molecules move faster at higher temperatures, which is why your body's 98.6°F temperature helps substances move efficiently throughout your cells. Real-world examples include:
Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide use passive transport to move across cell membranes. Oxygen typically diffuses into cells (where it's less concentrated), while carbon dioxide diffuses out (where it's more concentrated).
Make the connection: Next time you're breathing, remember that oxygen is passively diffusing into your cells while carbon dioxide is diffusing out—no energy required! This efficient system happens billions of times every minute in your body.

Simple diffusion is the most basic form of passive transport—molecules move directly through the cell membrane from higher to lower concentration. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can easily pass through the lipid bilayer this way.
However, not all molecules can cross so easily. Large or charged molecules face a challenge: they're repelled by the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. Very small polar molecules like water can squeeze through because of their tiny size, but larger polar molecules and ions need help.
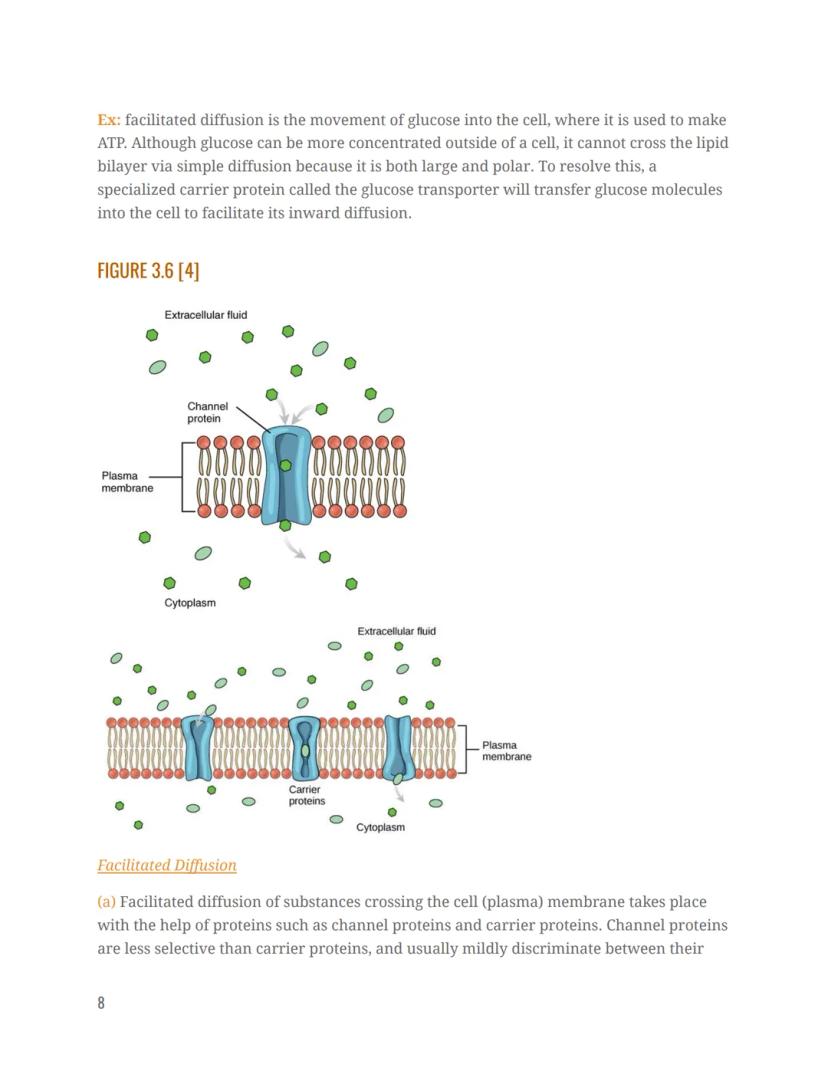
This is where facilitated diffusion comes in—special transport proteins help molecules cross the membrane without using energy. Take glucose for example: despite sometimes being more concentrated outside cells, this large, polar molecule can't cross the membrane on its own. Instead, a glucose transporter protein helps move glucose into the cell where it's needed to produce energy.
Biology hack: Understanding facilitated diffusion helps explain why some medications work better than others. Drug designers often modify molecules to better interact with membrane transporters, improving how well medicines enter your cells!

There are two main types of proteins that assist with facilitated diffusion across cell membranes: channel proteins and carrier proteins.
Channel proteins form pores or tunnels through the membrane that allow specific substances to pass through. They're somewhat selective, typically discriminating between molecules based on size and charge. For example, sodium ions are highly concentrated outside cells but can't pass through the nonpolar lipid bilayer alone. Sodium channels allow these ions to move through the membrane down their concentration gradient.
Carrier proteins are more selective than channel proteins. They often transport only one specific molecule—like the glucose transporter that moves only glucose molecules. These proteins work by binding to their target molecule, changing shape, and then releasing the molecule on the other side of the membrane.
Despite the assistance of proteins, facilitated diffusion still qualifies as passive transport because it doesn't require energy from the cell. The concentration gradient provides the necessary force for movement.
Connect the dots: Many diseases involve problems with membrane transport proteins. Cystic fibrosis, for example, results from a defective chloride channel protein that disrupts normal fluid balance in the lungs.

Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Water can move freely through most cell membranes, either through special water channels or by slipping between the lipid molecules.
For cells to maintain their normal shape and function, they need to be in balance with their environment. This balance relates to tonicity—the relative concentration of solutes (dissolved substances) on either side of the membrane:
Your body works hard to maintain an isotonic environment for your cells. The kidneys play a crucial role in this process, regulating water and solute balance in your bloodstream.
Real-life application: This is why drinking seawater is dangerous! The high salt content creates a hypertonic environment that causes cells to lose water, leading to dehydration despite drinking liquid.

Besides diffusion and osmosis, filtration is another important passive transport mechanism. Unlike diffusion (which relies on concentration differences), filtration uses hydrostatic pressure to push fluids and dissolved substances from areas of higher pressure to areas of lower pressure.
Think of squeezing water through a coffee filter—pressure forces the water through while larger particles stay behind. Your body uses this principle extensively:
Filtration doesn't require cellular energy—just the pressure difference—making it another form of passive transport. This process is crucial for maintaining homeostasis throughout your body.
Make the connection: Next time you get a cut and see fluid leaking from tissues, you're witnessing filtration in action! Blood pressure forces plasma through capillary walls into surrounding tissues, creating the clear fluid that appears around wounds.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Bri💟
@aestheticbri
The cellular level of organization is where the magic of life begins. This chapter explores how cells maintain their structure and function through the cell membrane, which acts as a gatekeeper controlling what enters and exits the cell. Understanding how... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wonder how cells keep their insides separate from the outside world? The answer is the cell membrane—a remarkable structure made primarily of phospholipids arranged in a bilayer . These phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails .
The phospholipid structure is perfectly designed for its job. Each molecule has a phosphate group on one end that forms the "head," while two fatty acid chains make up the lipid "tails." This design is crucial because it allows the membrane to form a protective barrier while still being flexible enough for cellular functions.
Cholesterol is also present in the membrane, contributing to its fluidity. Various proteins embedded within the membrane perform specialized functions that we'll explore further.
Quick Fact: The term "amphipathic" describes molecules like phospholipids that have both water-loving and water-fearing regions in the same molecule. This property is what allows cell membranes to form!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The cell membrane's structure is brilliantly simple yet effective. The phospholipids arrange themselves with their polar, hydrophilic heads facing outward toward watery environments both inside the cell (intracellular fluid or ICF) and outside the cell (extracellular fluid or ECF). Meanwhile, their hydrophobic tails huddle together in the middle, away from water.
This arrangement creates a selective barrier that keeps the cell's contents from leaking out while preventing unwanted materials from getting in. The phosphate heads, with their negative charge, are attracted to the water molecules in both environments, while the uncharged lipid tails repel water.
Some of these lipid tails contain saturated fatty acids (straight tails) while others have unsaturated fatty acids (kinked tails). This combination gives the membrane its necessary fluidity—it's not rigid but more like a liquid mosaic that's constantly in motion.
Remember this: The fluid nature of the cell membrane is essential for cell function. If it were too rigid, cells couldn't grow, divide, or adapt to their environment!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The cell membrane isn't just a lipid bilayer—it's packed with proteins that give it specific functions. Two main types of proteins exist in the membrane: integral proteins and peripheral proteins.
Integral proteins are embedded within the membrane itself. Some, called channel proteins, create passageways that allow specific substances to cross the membrane. Others serve as cell recognition proteins that help cells identify each other—kind of like cellular ID tags. Receptors are another type of integral protein that can bind to specific molecules (ligands) outside the cell, triggering reactions inside.
Many of these proteins have carbohydrate chains attached to them, making them glycoproteins. These carbohydrates extend from the cell surface and collectively form the glycocalyx—a fuzzy coating that surrounds the cell and helps with cell recognition, binding to other cells, and capturing important molecules like hormones.
Fun biology fact: The glycocalyx is unique to each person, almost like a cellular fingerprint! This is why our immune systems can recognize which cells belong in our bodies and which don't—crucial for fighting infections and why organ transplants sometimes get rejected.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Membrane proteins perform diverse functions that are essential for cell survival. Some integral proteins act as both receptors and ion channels simultaneously. For example, when a neurotransmitter like dopamine binds to its receptor on a nerve cell, it opens a channel that allows specific ions to flow into the cell.
Glycoproteins (proteins with attached carbohydrates) extend into the extracellular space and help cells recognize each other. Along with glycolipids (lipids with carbohydrates attached), they form the glycocalyx—a carbohydrate-rich coating around the cell that serves multiple functions:
The glycocalyx is genetically determined, giving each person's trillions of cells their unique identity. This cellular "ID system" helps immune cells recognize which cells belong in your body and which are foreign invaders.
Think about this: The glycocalyx is why organ transplants can be rejected! Your immune system recognizes the donor's cells as "not self" because their glycocalyx carries different molecular markers.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The cell membrane's most impressive feat is regulating what gets in and out of the cell. It controls the movement of ions (like calcium, sodium, and potassium), nutrients (sugars, fatty acids, amino acids), and waste products (especially carbon dioxide).
The membrane's structure creates selective permeability—only certain substances can pass through easily. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol can slip right through the lipid bilayer. However, water-soluble substances like glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes need assistance to cross because they're repelled by the hydrophobic interior of the membrane.
Peripheral proteins attach to the membrane's inner or outer surface and perform specific functions. Some act as digestive enzymes on intestinal cells, breaking down nutrients into smaller pieces that can pass through the membrane and enter the bloodstream.
Real-world application: Understanding membrane transport helps explain how medications enter cells, why certain toxins are dangerous, and how nutrients from the food you eat get absorbed into your bloodstream!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Substances move across the cell membrane using two general methods: passive transport (requiring no energy) and active transport (requiring cellular energy from ATP).
Passive transport relies on concentration gradients—the difference in concentration of a substance across a space. During diffusion, molecules naturally spread from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration until they're evenly distributed. Think about dropping food coloring in water—it spreads on its own without you doing anything!
Temperature affects diffusion speed—molecules move faster at higher temperatures, which is why your body's 98.6°F temperature helps substances move efficiently throughout your cells. Real-world examples include:
Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide use passive transport to move across cell membranes. Oxygen typically diffuses into cells (where it's less concentrated), while carbon dioxide diffuses out (where it's more concentrated).
Make the connection: Next time you're breathing, remember that oxygen is passively diffusing into your cells while carbon dioxide is diffusing out—no energy required! This efficient system happens billions of times every minute in your body.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Simple diffusion is the most basic form of passive transport—molecules move directly through the cell membrane from higher to lower concentration. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can easily pass through the lipid bilayer this way.
However, not all molecules can cross so easily. Large or charged molecules face a challenge: they're repelled by the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. Very small polar molecules like water can squeeze through because of their tiny size, but larger polar molecules and ions need help.
This is where facilitated diffusion comes in—special transport proteins help molecules cross the membrane without using energy. Take glucose for example: despite sometimes being more concentrated outside cells, this large, polar molecule can't cross the membrane on its own. Instead, a glucose transporter protein helps move glucose into the cell where it's needed to produce energy.
Biology hack: Understanding facilitated diffusion helps explain why some medications work better than others. Drug designers often modify molecules to better interact with membrane transporters, improving how well medicines enter your cells!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
There are two main types of proteins that assist with facilitated diffusion across cell membranes: channel proteins and carrier proteins.
Channel proteins form pores or tunnels through the membrane that allow specific substances to pass through. They're somewhat selective, typically discriminating between molecules based on size and charge. For example, sodium ions are highly concentrated outside cells but can't pass through the nonpolar lipid bilayer alone. Sodium channels allow these ions to move through the membrane down their concentration gradient.
Carrier proteins are more selective than channel proteins. They often transport only one specific molecule—like the glucose transporter that moves only glucose molecules. These proteins work by binding to their target molecule, changing shape, and then releasing the molecule on the other side of the membrane.
Despite the assistance of proteins, facilitated diffusion still qualifies as passive transport because it doesn't require energy from the cell. The concentration gradient provides the necessary force for movement.
Connect the dots: Many diseases involve problems with membrane transport proteins. Cystic fibrosis, for example, results from a defective chloride channel protein that disrupts normal fluid balance in the lungs.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Water can move freely through most cell membranes, either through special water channels or by slipping between the lipid molecules.
For cells to maintain their normal shape and function, they need to be in balance with their environment. This balance relates to tonicity—the relative concentration of solutes (dissolved substances) on either side of the membrane:
Your body works hard to maintain an isotonic environment for your cells. The kidneys play a crucial role in this process, regulating water and solute balance in your bloodstream.
Real-life application: This is why drinking seawater is dangerous! The high salt content creates a hypertonic environment that causes cells to lose water, leading to dehydration despite drinking liquid.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Besides diffusion and osmosis, filtration is another important passive transport mechanism. Unlike diffusion (which relies on concentration differences), filtration uses hydrostatic pressure to push fluids and dissolved substances from areas of higher pressure to areas of lower pressure.
Think of squeezing water through a coffee filter—pressure forces the water through while larger particles stay behind. Your body uses this principle extensively:
Filtration doesn't require cellular energy—just the pressure difference—making it another form of passive transport. This process is crucial for maintaining homeostasis throughout your body.
Make the connection: Next time you get a cut and see fluid leaking from tissues, you're witnessing filtration in action! Blood pressure forces plasma through capillary walls into surrounding tissues, creating the clear fluid that appears around wounds.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
4
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
Intro to Healthcare
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of Multidisciplinary Teams (MDTs) in addressing the holistic needs of service users. This summary covers the collaborative methods used by healthcare professionals, the importance of a person-centred approach, and the challenges faced in delivering comprehensive care. Ideal for students studying case management and the biopsychosocial approach in healthcare.
Medical health 2 nervous system study notes
This has medical terms that students can utilize
What it is, History, Applied Fields, etc.
COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on societies, health, and the economy around the world. It has highlighted existing inequalities and the importance of effective leadership and governance in times of crisis.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user