Physics is all about understanding how matter and energy interact... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Knowunity AI
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
63
•
Updated Mar 3, 2026
•
Julius Ceazar Monares
@juliusceazarmon
Physics is all about understanding how matter and energy interact... Show more


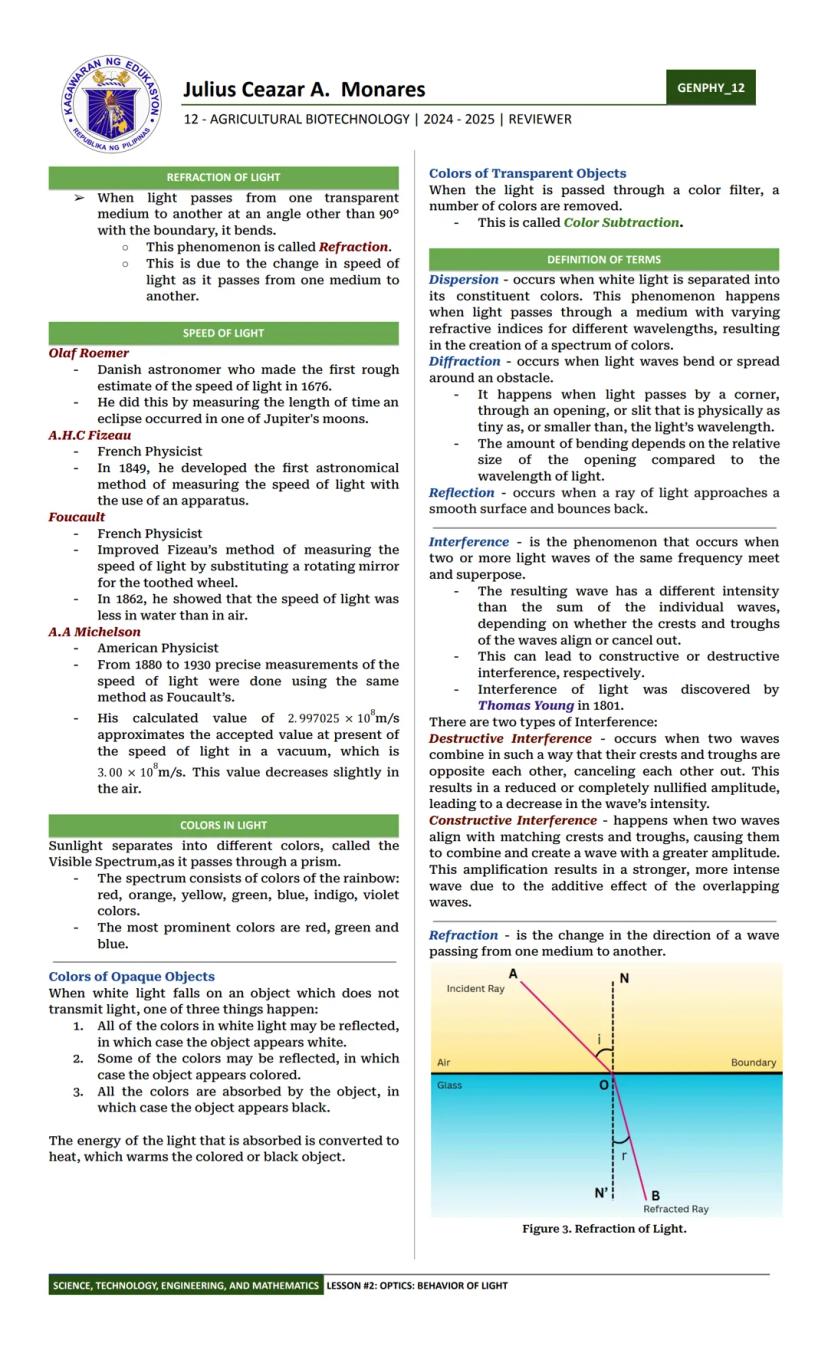
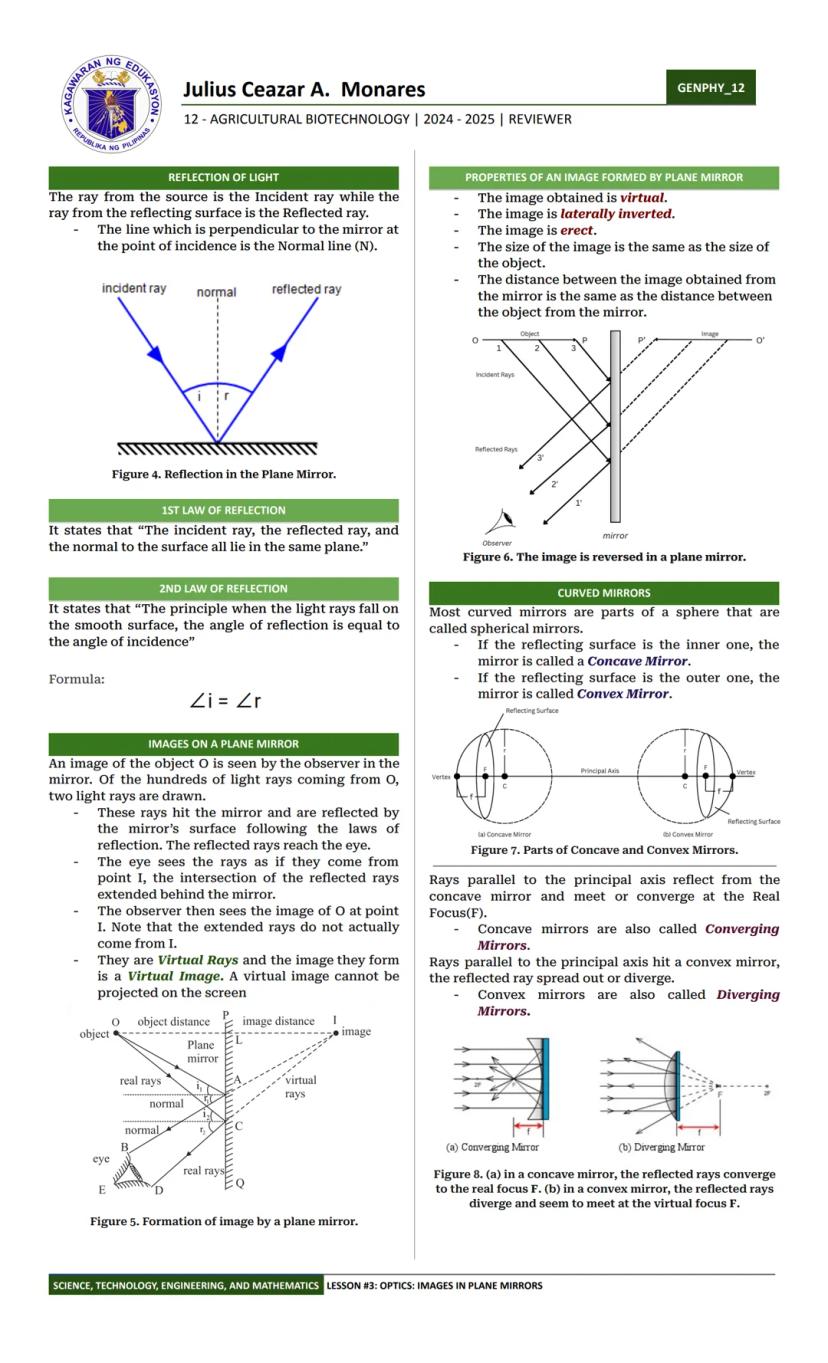
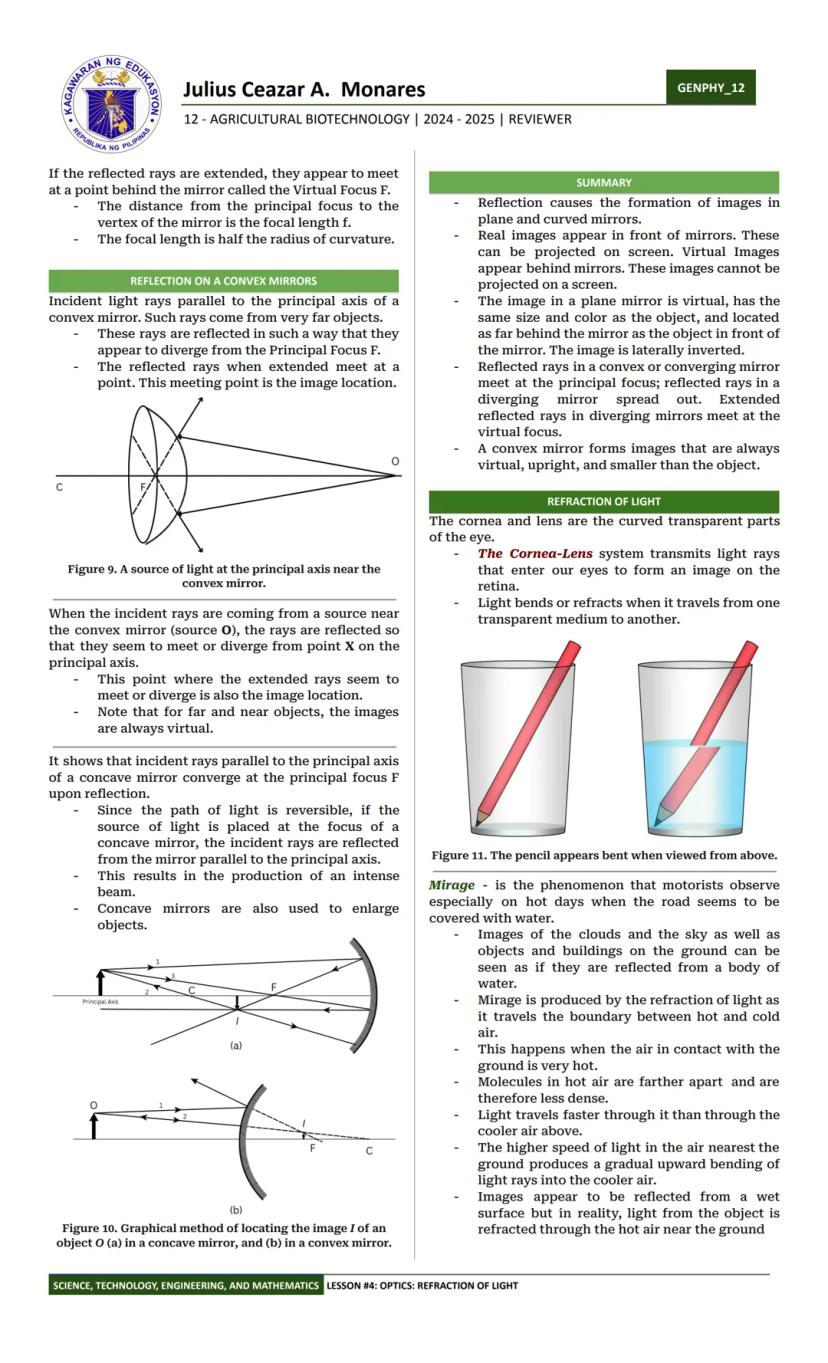
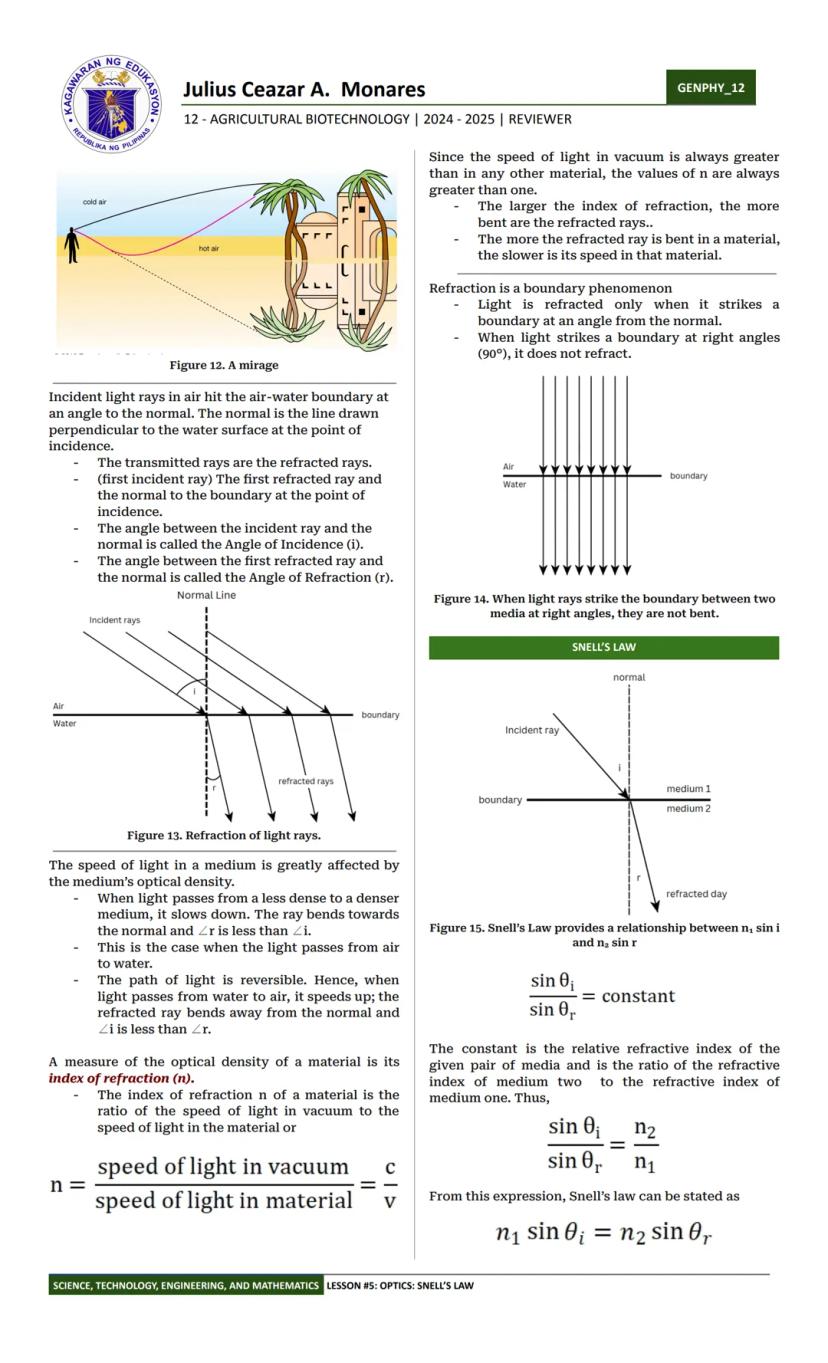
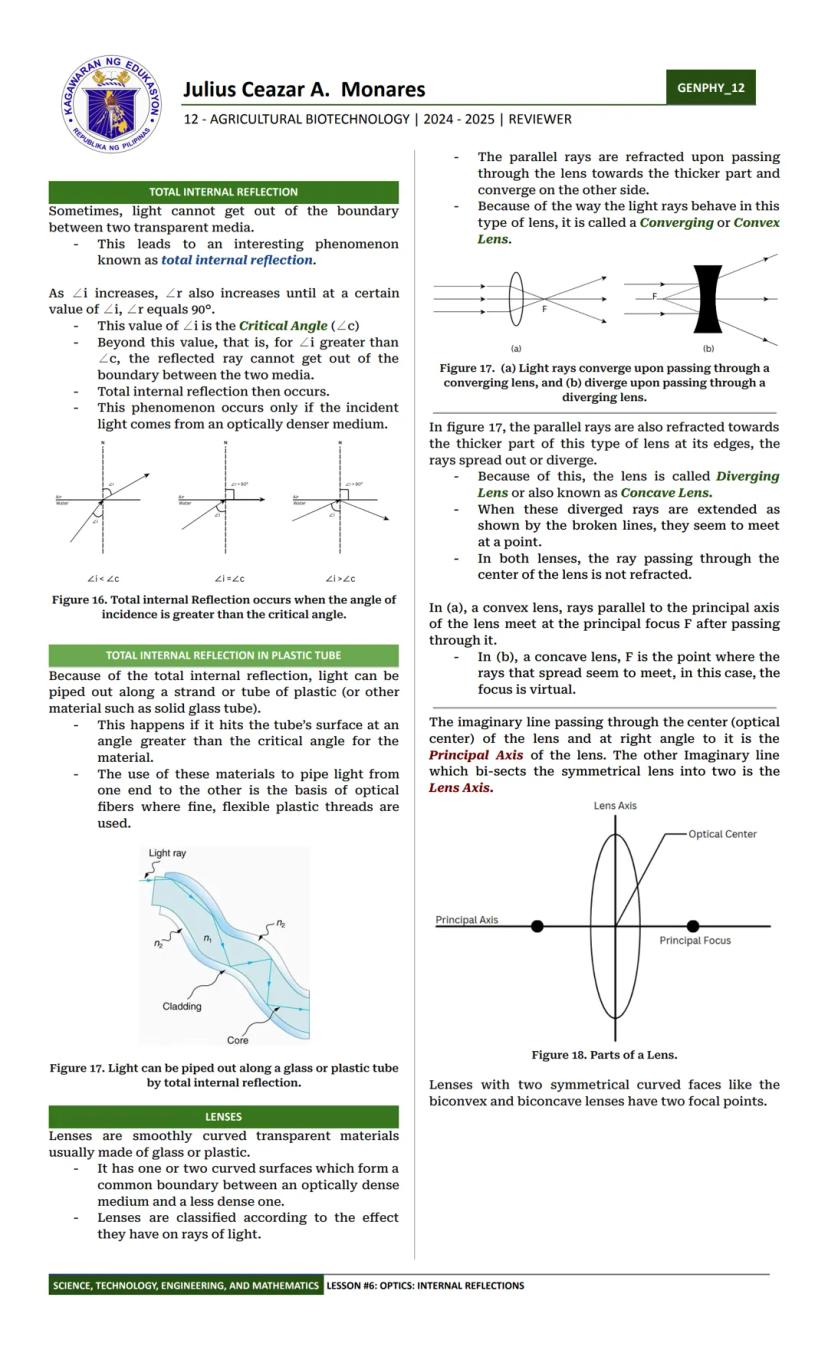


Ever wondered why things fall down or how light bends? Physics has the answers! Physics is the study of matter and its interactions with energy. It helps us understand everything from why apples fall to how smartphones work.
Physics branches into several major fields that explore different aspects of our physical world. Classical mechanics studies the motion of objects according to Newton's laws - this is what we'll focus on first. Other important fields include electricity and magnetism (think lightning and compasses), quantum mechanics (the weird science of very tiny particles), and optics (how light behaves).
More specialized areas include thermodynamics (the study of heat), acoustics (sound waves), and relativity (Einstein's theories about space, time, and gravity). Physics also crosses into other sciences through fields like astrophysics, biophysics, and geophysics.
💡 When you understand physics, you're actually understanding the basic rules that control everything around you - from why your phone screen cracks when you drop it to how light creates rainbows!
If you're specifically interested in motion, you'll want to know about kinematics (describing motion without worrying about what causes it) and dynamics (studying the forces that cause motion). Statics focuses on objects that aren't moving but are being acted upon by balanced forces.

Light is everywhere around us, but have you ever thought about how we actually see it? Optics is the branch of physics that studies light and how it behaves. It splits into two main areas: geometrical optics, which treats light as rays traveling in straight lines, and wave optics, which studies phenomena like diffraction and interference where light acts as a wave.
Your eyes are amazing optical instruments! The cornea acts as the window of your eye, working with the lens to bend incoming light rays. While the cornea does most of the focusing, the lens fine-tunes it to create a clear image on your retina at the back of your eye. The iris (the colored part of your eye) controls how much light enters through the pupil, protecting your sensitive retina.
Inside your eye, millions of light-sensitive cells called rods and cones detect light hitting the retina. Cones work best in bright light and help you see colors, while rods function in dim conditions but don't distinguish colors well. That's why it's harder to see colors in the dark! The information from these cells travels through the optic nerve to your brain for processing.
🔍 Did you know? The center of your eye's sharpest vision is the fovea centralis, which is packed with cone cells for detailed color perception.
Light itself is a form of energy that can travel through some materials but not others. Transparent materials like glass allow light to pass through clearly, while opaque materials block light completely. When light hits opaque surfaces, it can reflect regularly (like from a mirror) or in all directions (diffuse reflection), depending on whether the surface is smooth or rough.

Ever noticed how a straw looks bent in a glass of water? That's refraction at work! When light travels from one transparent medium to another at an angle, it bends because its speed changes. This simple phenomenon explains everything from rainbows to how eyeglasses correct vision.
The speed of light has fascinated scientists for centuries. While light travels at an incredible 300,000,000 meters per second in a vacuum (that's about 186,000 miles per second!), its speed decreases slightly in air and even more in denser materials like water. Scientists like Olaf Roemer, Fizeau, Foucault, and Michelson progressively refined measurements of this fundamental constant through ingenious experiments.
White light is actually a mixture of all colors! When passed through a prism, it separates into the visible spectrum – the familiar rainbow colors of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This separation happens because different colors refract at slightly different angles due to their varying wavelengths.
🌈 Color isn't actually in objects themselves! An object appears red because it reflects red light while absorbing all other colors. Black objects absorb all colors, while white objects reflect them all.
Light can interact with objects in fascinating ways. Dispersion separates white light into its component colors, while diffraction causes light to bend around obstacles. Interference occurs when light waves meet and either reinforce each other (constructive interference) or cancel each other out (destructive interference). These phenomena explain everything from the colorful sheen on soap bubbles to why sunglasses reduce glare.
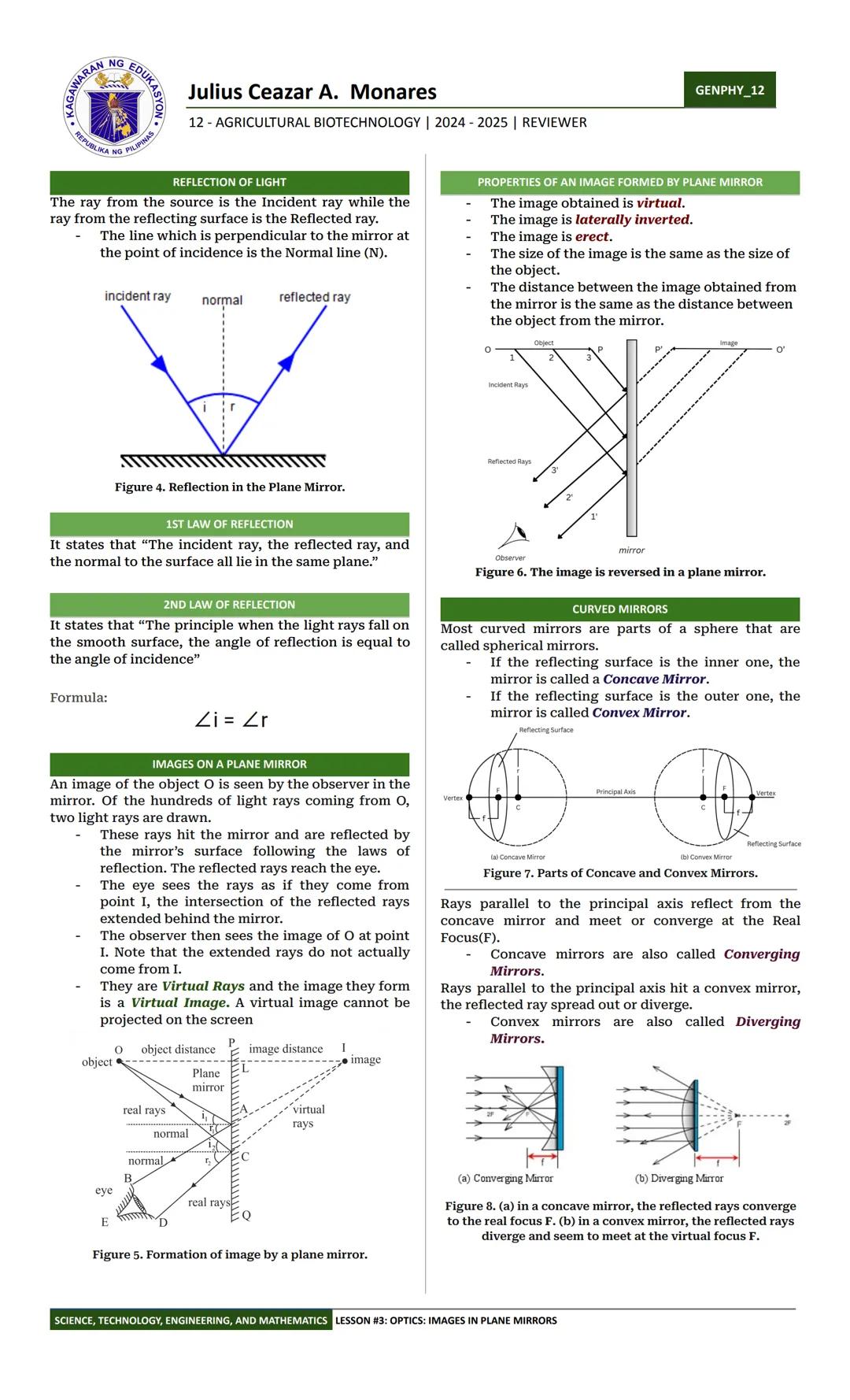
Have you ever wondered why your image in a mirror is flipped left to right but not up and down? The answer lies in the laws of reflection! When light hits a surface, the angle at which it bounces off equals the angle at which it hit - this is the second law of reflection. The first law states that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal line all lie in the same plane.
In a flat (plane) mirror, your image appears to be the same distance behind the mirror as you are in front of it. The image is virtual, meaning light rays don't actually come from there - they just appear to. Your mirror image is also laterally inverted (left and right are swapped), but it remains upright and the same size as you.
Curved mirrors create more interesting effects. A concave mirror (curved inward like the inside of a spoon) can focus parallel light rays to a point called the real focus. That's why they're also called converging mirrors - they're great for magnifying objects. Think of makeup mirrors or telescope reflectors!
🔍 Ever noticed how side-view mirrors on cars say "objects are closer than they appear"? Those are convex mirrors that diverge light rays, creating smaller images but providing a wider field of view.
Convex mirrors (curved outward like the back of a spoon) spread out or diverge light rays. The reflected rays appear to come from a point behind the mirror called the virtual focus. These mirrors always create images that are virtual, upright, and smaller than the object - perfect for seeing around corners or monitoring large areas in stores.
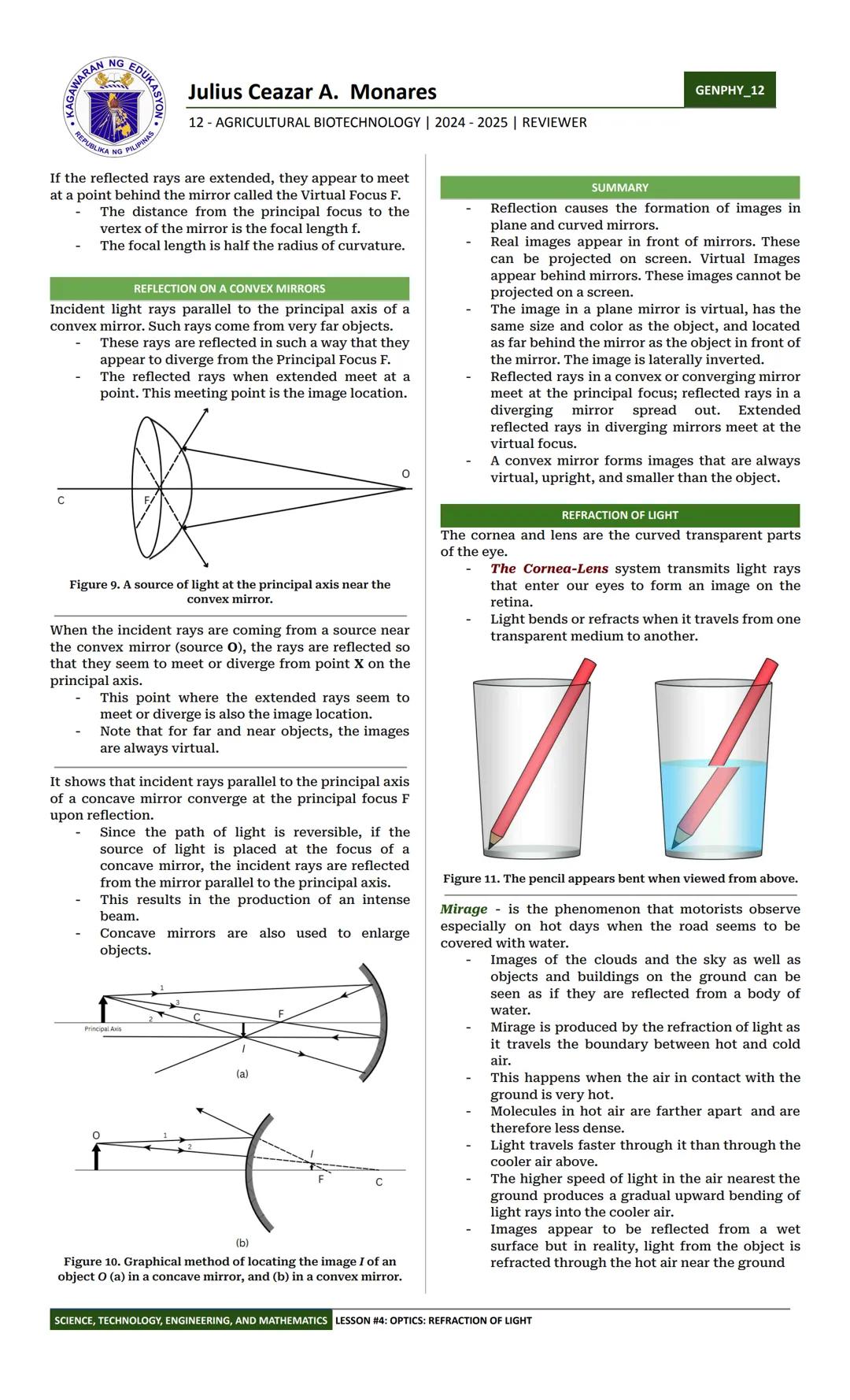
Have you ever seen a pencil appear bent in a glass of water? That's refraction in action! When light travels from one medium to another with different optical densities, it changes speed and direction. This bending of light rays explains many fascinating phenomena we see in everyday life.
The angle of incidence (the angle light hits a surface) and the angle of refraction (the angle light bends when entering a new medium) are related by an important rule: when light moves from a less dense to a denser medium, it slows down and bends toward the normal line (perpendicular to the surface). The opposite happens when light moves from dense to less dense media - it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
A mirage is one of nature's most fascinating optical illusions. On hot days, the road ahead sometimes appears wet, showing reflections of the sky or buildings. This happens because air near the hot ground is less dense than cooler air above, creating a gradual refraction of light that tricks our eyes into seeing reflections that aren't really there.
🔥 Mirages aren't hallucinations - they're real optical phenomena caused by light refraction through air of different temperatures! Your brain interprets these bent light rays as reflections from water.
Each transparent material has its own index of refraction (n), which tells us how much light slows down in that material compared to its speed in a vacuum. This relationship is described by Snell's Law: n₁sin θ₁ = n₂sin θ₂, which connects the angles and refractive indices of light traveling between two materials. Understanding this principle helps explain everything from how eyeglasses work to why diamonds sparkle.
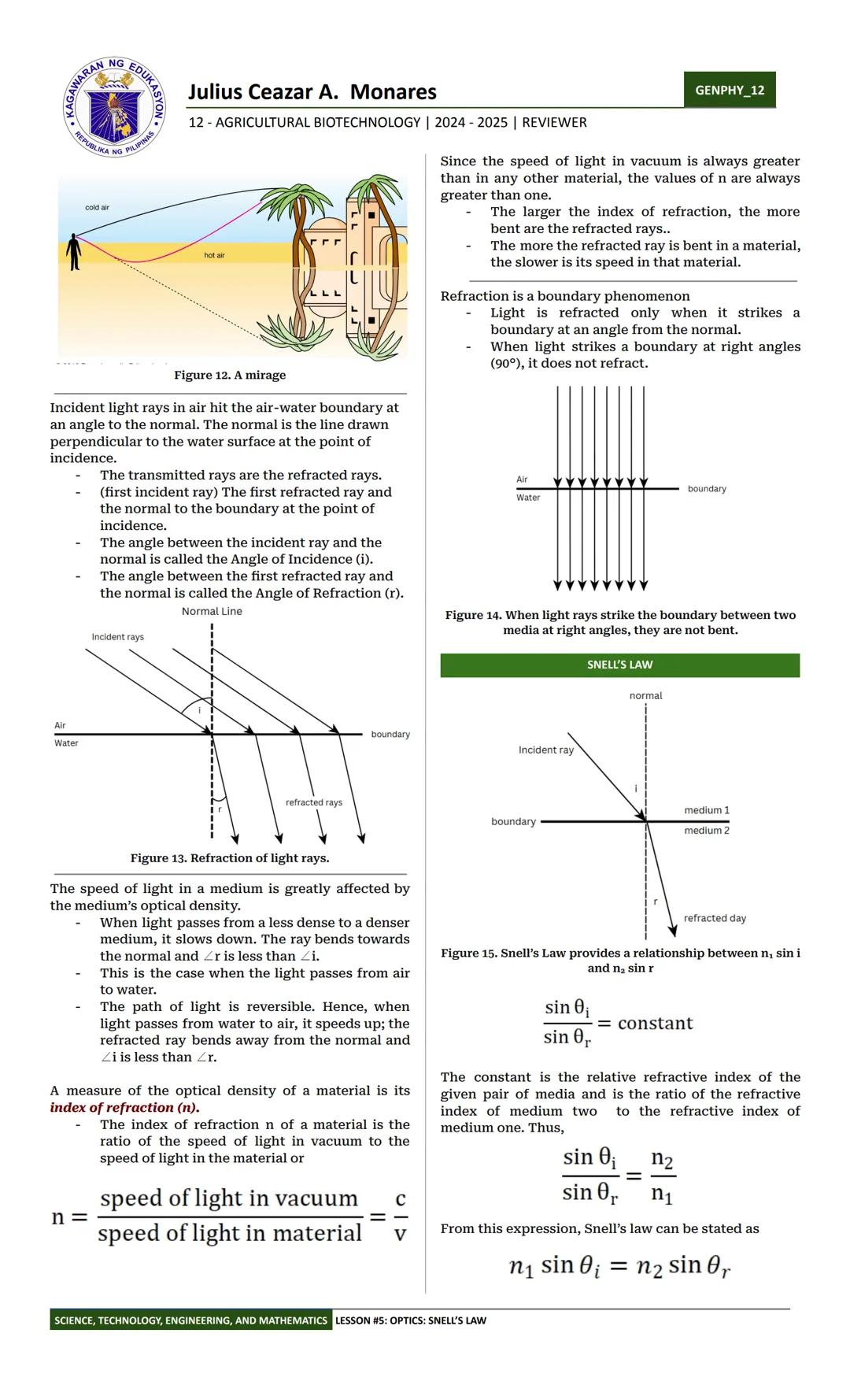
Have you ever wondered how fiber optic cables transmit internet data across oceans? The secret is total internal reflection! This fascinating phenomenon happens when light tries to pass from a denser medium to a less dense one at an angle greater than the critical angle.
When light hits the boundary between two media at an angle larger than the critical angle, it can't pass through and gets completely reflected back into the original medium. This principle enables fiber optic technology, where light signals bounce along the inside of thin glass or plastic fibers without escaping, carrying data over long distances with minimal loss.
The critical angle depends on the refractive indices of the two materials. You can calculate it using Snell's Law when the angle of refraction equals 90°. Beyond the critical angle, light can't escape the denser medium, making total internal reflection possible.
💡 Total internal reflection is why diamonds sparkle so brilliantly! Light entering a diamond gets trapped by internal reflection, bouncing around inside before exiting in a dazzling display.
Lenses work by refracting light to focus or spread it out. They come in various shapes - some curved on both sides (biconvex or biconcave) and others curved on just one side. Convex lenses bulge outward and converge light rays, while concave lenses curve inward and diverge light. The distance from the center of a lens to its focal point is called the focal length, which determines how strongly the lens bends light.
Opticians describe lens strength using diopters (D) rather than focal length. A lens with a focal length of 1 meter has a power of 1 diopter. Converging lenses have positive power, while diverging lenses have negative power. The stronger the lens, the greater its absolute power value.
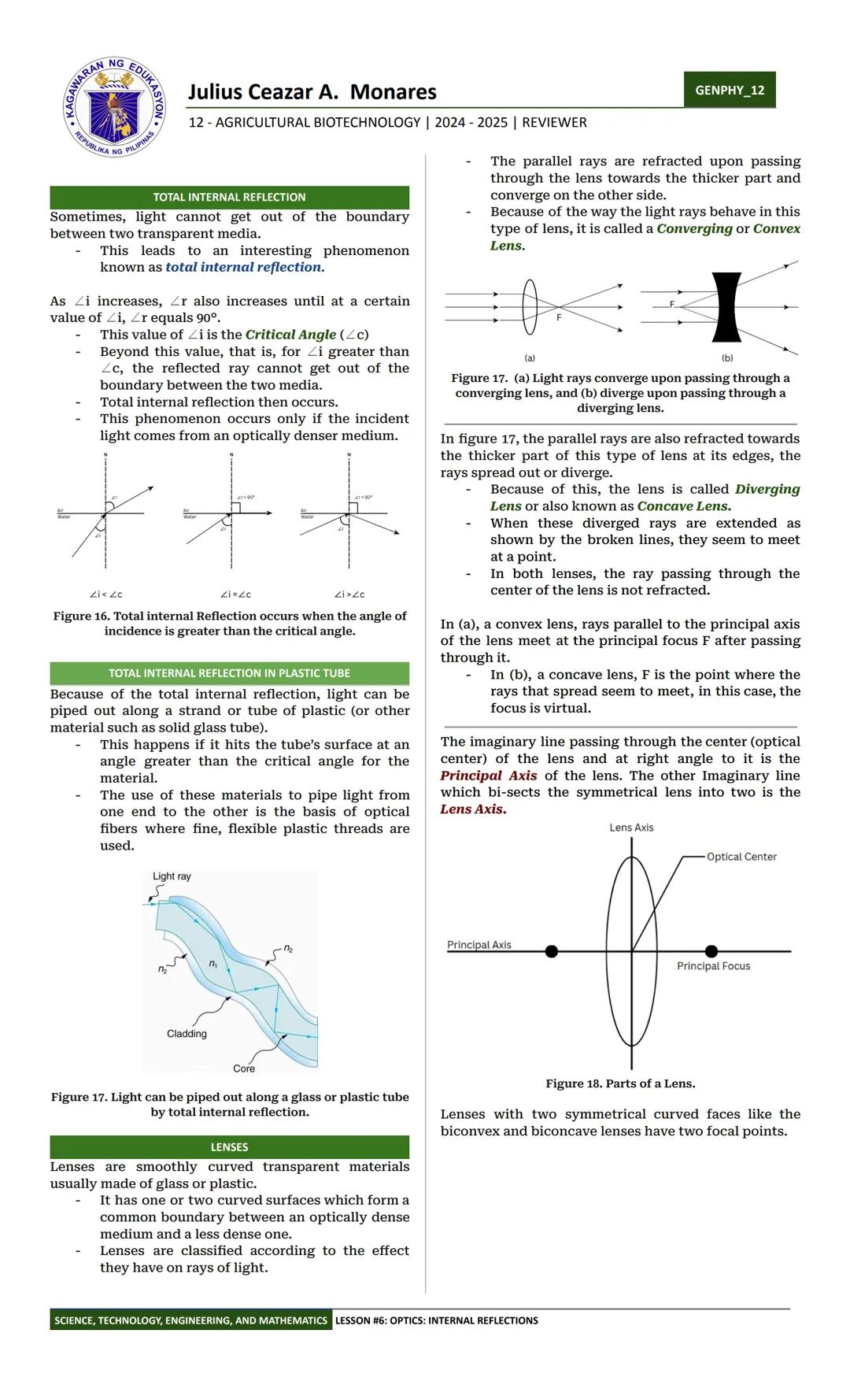
Ever seen those fiber optic lamps with strands of light that seem to glow? They work because of total internal reflection! This occurs when light hits the boundary between two transparent media at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing it to bounce completely back into the original medium rather than passing through.
For total internal reflection to happen, light must travel from an optically denser medium (like glass) toward a less dense medium (like air). As you increase the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases until it reaches 90° at the critical angle. Beyond this angle, light can't escape and reflects entirely back into the denser medium.
This principle has revolutionized communications through optical fibers - thin, flexible strands of pure glass or plastic that carry light signals. When light enters one end of the fiber, it bounces along inside due to total internal reflection, allowing data to travel long distances with minimal loss. This technology forms the backbone of high-speed internet and telecommunications networks worldwide.
🔌 Fiber optic cables transmit information much faster than traditional copper wires and are immune to electromagnetic interference. A single fiber optic cable can carry tens of thousands of phone calls simultaneously!
The critical angle depends on the refractive indices of the two materials involved. For example, the critical angle for the glass-air boundary is about 42°. Any light ray hitting this boundary at an angle greater than 42° will undergo total internal reflection. Diamonds have a much lower critical angle (about 24°), which is why they trap so much light inside, making them sparkle brilliantly.

How do lenses in your camera, glasses, or telescope actually work? It all comes down to how they bend light rays! Lenses are curved transparent materials (usually glass or plastic) that refract light to form images. Their shape determines whether they bring light rays together or spread them apart.
Convex lenses (thicker in the middle) focus parallel light rays to a point called the focal point. The distance from this point to the center of the lens is the focal length. These lenses create different types of images depending on where the object is placed. When an object is beyond twice the focal length, the image is real, inverted, and smaller. When it's between one and two focal lengths away, the image is real, inverted, but larger - this is how magnifying glasses work!
Concave lenses (thinner in the middle) cause light rays to spread out or diverge. When viewed through a concave lens, objects always appear smaller, upright, and virtual (meaning the image appears to be on the same side of the lens as the object). These lenses are often used to correct nearsightedness.
👁️ Your eye's lens is naturally convex, but its focal length can change! The ciliary muscles in your eye contract or relax to change the lens shape, allowing you to focus on objects at different distances.
Rather than using focal length, opticians describe lens strength with power, measured in diopters (D). Power is simply the reciprocal of the focal length in meters . A lens with a focal length of 0.5 meters has a power of +2 diopters, while one with a focal length of -0.25 meters has a power of -4 diopters. Convex lenses have positive power; concave lenses have negative power. The higher the absolute value, the stronger the lens effect.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
Summary of atomic structure, subatomic particles, isotopes, ions, and the most prominent names when talking about tye atomic model.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Julius Ceazar Monares
@juliusceazarmon
Physics is all about understanding how matter and energy interact in our world. From the motion of objects to the behavior of light, physics helps explain the fundamental principles that govern our universe. Let's break down some key concepts that... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wondered why things fall down or how light bends? Physics has the answers! Physics is the study of matter and its interactions with energy. It helps us understand everything from why apples fall to how smartphones work.
Physics branches into several major fields that explore different aspects of our physical world. Classical mechanics studies the motion of objects according to Newton's laws - this is what we'll focus on first. Other important fields include electricity and magnetism (think lightning and compasses), quantum mechanics (the weird science of very tiny particles), and optics (how light behaves).
More specialized areas include thermodynamics (the study of heat), acoustics (sound waves), and relativity (Einstein's theories about space, time, and gravity). Physics also crosses into other sciences through fields like astrophysics, biophysics, and geophysics.
💡 When you understand physics, you're actually understanding the basic rules that control everything around you - from why your phone screen cracks when you drop it to how light creates rainbows!
If you're specifically interested in motion, you'll want to know about kinematics (describing motion without worrying about what causes it) and dynamics (studying the forces that cause motion). Statics focuses on objects that aren't moving but are being acted upon by balanced forces.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Light is everywhere around us, but have you ever thought about how we actually see it? Optics is the branch of physics that studies light and how it behaves. It splits into two main areas: geometrical optics, which treats light as rays traveling in straight lines, and wave optics, which studies phenomena like diffraction and interference where light acts as a wave.
Your eyes are amazing optical instruments! The cornea acts as the window of your eye, working with the lens to bend incoming light rays. While the cornea does most of the focusing, the lens fine-tunes it to create a clear image on your retina at the back of your eye. The iris (the colored part of your eye) controls how much light enters through the pupil, protecting your sensitive retina.
Inside your eye, millions of light-sensitive cells called rods and cones detect light hitting the retina. Cones work best in bright light and help you see colors, while rods function in dim conditions but don't distinguish colors well. That's why it's harder to see colors in the dark! The information from these cells travels through the optic nerve to your brain for processing.
🔍 Did you know? The center of your eye's sharpest vision is the fovea centralis, which is packed with cone cells for detailed color perception.
Light itself is a form of energy that can travel through some materials but not others. Transparent materials like glass allow light to pass through clearly, while opaque materials block light completely. When light hits opaque surfaces, it can reflect regularly (like from a mirror) or in all directions (diffuse reflection), depending on whether the surface is smooth or rough.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever noticed how a straw looks bent in a glass of water? That's refraction at work! When light travels from one transparent medium to another at an angle, it bends because its speed changes. This simple phenomenon explains everything from rainbows to how eyeglasses correct vision.
The speed of light has fascinated scientists for centuries. While light travels at an incredible 300,000,000 meters per second in a vacuum (that's about 186,000 miles per second!), its speed decreases slightly in air and even more in denser materials like water. Scientists like Olaf Roemer, Fizeau, Foucault, and Michelson progressively refined measurements of this fundamental constant through ingenious experiments.
White light is actually a mixture of all colors! When passed through a prism, it separates into the visible spectrum – the familiar rainbow colors of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This separation happens because different colors refract at slightly different angles due to their varying wavelengths.
🌈 Color isn't actually in objects themselves! An object appears red because it reflects red light while absorbing all other colors. Black objects absorb all colors, while white objects reflect them all.
Light can interact with objects in fascinating ways. Dispersion separates white light into its component colors, while diffraction causes light to bend around obstacles. Interference occurs when light waves meet and either reinforce each other (constructive interference) or cancel each other out (destructive interference). These phenomena explain everything from the colorful sheen on soap bubbles to why sunglasses reduce glare.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Have you ever wondered why your image in a mirror is flipped left to right but not up and down? The answer lies in the laws of reflection! When light hits a surface, the angle at which it bounces off equals the angle at which it hit - this is the second law of reflection. The first law states that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal line all lie in the same plane.
In a flat (plane) mirror, your image appears to be the same distance behind the mirror as you are in front of it. The image is virtual, meaning light rays don't actually come from there - they just appear to. Your mirror image is also laterally inverted (left and right are swapped), but it remains upright and the same size as you.
Curved mirrors create more interesting effects. A concave mirror (curved inward like the inside of a spoon) can focus parallel light rays to a point called the real focus. That's why they're also called converging mirrors - they're great for magnifying objects. Think of makeup mirrors or telescope reflectors!
🔍 Ever noticed how side-view mirrors on cars say "objects are closer than they appear"? Those are convex mirrors that diverge light rays, creating smaller images but providing a wider field of view.
Convex mirrors (curved outward like the back of a spoon) spread out or diverge light rays. The reflected rays appear to come from a point behind the mirror called the virtual focus. These mirrors always create images that are virtual, upright, and smaller than the object - perfect for seeing around corners or monitoring large areas in stores.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Have you ever seen a pencil appear bent in a glass of water? That's refraction in action! When light travels from one medium to another with different optical densities, it changes speed and direction. This bending of light rays explains many fascinating phenomena we see in everyday life.
The angle of incidence (the angle light hits a surface) and the angle of refraction (the angle light bends when entering a new medium) are related by an important rule: when light moves from a less dense to a denser medium, it slows down and bends toward the normal line (perpendicular to the surface). The opposite happens when light moves from dense to less dense media - it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
A mirage is one of nature's most fascinating optical illusions. On hot days, the road ahead sometimes appears wet, showing reflections of the sky or buildings. This happens because air near the hot ground is less dense than cooler air above, creating a gradual refraction of light that tricks our eyes into seeing reflections that aren't really there.
🔥 Mirages aren't hallucinations - they're real optical phenomena caused by light refraction through air of different temperatures! Your brain interprets these bent light rays as reflections from water.
Each transparent material has its own index of refraction (n), which tells us how much light slows down in that material compared to its speed in a vacuum. This relationship is described by Snell's Law: n₁sin θ₁ = n₂sin θ₂, which connects the angles and refractive indices of light traveling between two materials. Understanding this principle helps explain everything from how eyeglasses work to why diamonds sparkle.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Have you ever wondered how fiber optic cables transmit internet data across oceans? The secret is total internal reflection! This fascinating phenomenon happens when light tries to pass from a denser medium to a less dense one at an angle greater than the critical angle.
When light hits the boundary between two media at an angle larger than the critical angle, it can't pass through and gets completely reflected back into the original medium. This principle enables fiber optic technology, where light signals bounce along the inside of thin glass or plastic fibers without escaping, carrying data over long distances with minimal loss.
The critical angle depends on the refractive indices of the two materials. You can calculate it using Snell's Law when the angle of refraction equals 90°. Beyond the critical angle, light can't escape the denser medium, making total internal reflection possible.
💡 Total internal reflection is why diamonds sparkle so brilliantly! Light entering a diamond gets trapped by internal reflection, bouncing around inside before exiting in a dazzling display.
Lenses work by refracting light to focus or spread it out. They come in various shapes - some curved on both sides (biconvex or biconcave) and others curved on just one side. Convex lenses bulge outward and converge light rays, while concave lenses curve inward and diverge light. The distance from the center of a lens to its focal point is called the focal length, which determines how strongly the lens bends light.
Opticians describe lens strength using diopters (D) rather than focal length. A lens with a focal length of 1 meter has a power of 1 diopter. Converging lenses have positive power, while diverging lenses have negative power. The stronger the lens, the greater its absolute power value.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever seen those fiber optic lamps with strands of light that seem to glow? They work because of total internal reflection! This occurs when light hits the boundary between two transparent media at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing it to bounce completely back into the original medium rather than passing through.
For total internal reflection to happen, light must travel from an optically denser medium (like glass) toward a less dense medium (like air). As you increase the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases until it reaches 90° at the critical angle. Beyond this angle, light can't escape and reflects entirely back into the denser medium.
This principle has revolutionized communications through optical fibers - thin, flexible strands of pure glass or plastic that carry light signals. When light enters one end of the fiber, it bounces along inside due to total internal reflection, allowing data to travel long distances with minimal loss. This technology forms the backbone of high-speed internet and telecommunications networks worldwide.
🔌 Fiber optic cables transmit information much faster than traditional copper wires and are immune to electromagnetic interference. A single fiber optic cable can carry tens of thousands of phone calls simultaneously!
The critical angle depends on the refractive indices of the two materials involved. For example, the critical angle for the glass-air boundary is about 42°. Any light ray hitting this boundary at an angle greater than 42° will undergo total internal reflection. Diamonds have a much lower critical angle (about 24°), which is why they trap so much light inside, making them sparkle brilliantly.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
How do lenses in your camera, glasses, or telescope actually work? It all comes down to how they bend light rays! Lenses are curved transparent materials (usually glass or plastic) that refract light to form images. Their shape determines whether they bring light rays together or spread them apart.
Convex lenses (thicker in the middle) focus parallel light rays to a point called the focal point. The distance from this point to the center of the lens is the focal length. These lenses create different types of images depending on where the object is placed. When an object is beyond twice the focal length, the image is real, inverted, and smaller. When it's between one and two focal lengths away, the image is real, inverted, but larger - this is how magnifying glasses work!
Concave lenses (thinner in the middle) cause light rays to spread out or diverge. When viewed through a concave lens, objects always appear smaller, upright, and virtual (meaning the image appears to be on the same side of the lens as the object). These lenses are often used to correct nearsightedness.
👁️ Your eye's lens is naturally convex, but its focal length can change! The ciliary muscles in your eye contract or relax to change the lens shape, allowing you to focus on objects at different distances.
Rather than using focal length, opticians describe lens strength with power, measured in diopters (D). Power is simply the reciprocal of the focal length in meters . A lens with a focal length of 0.5 meters has a power of +2 diopters, while one with a focal length of -0.25 meters has a power of -4 diopters. Convex lenses have positive power; concave lenses have negative power. The higher the absolute value, the stronger the lens effect.
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
0
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
Summary of atomic structure, subatomic particles, isotopes, ions, and the most prominent names when talking about tye atomic model.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user