The water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles are natural processes... Show more
Sign up to see the contentIt's free!
Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Knowunity AI
Subjects
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Theorems
Triangle Properties and Classification
Linear Equations and Graphs
Geometric Angle Relationships
Trigonometric Functions and Identities
Equation Solving Techniques
Circle Geometry Fundamentals
Division Operations and Methods
Basic Differentiation Rules
Exponent and Logarithm Properties
Show all topics
Human Organ Systems
Reproductive Cell Cycles
Biological Sciences Subdisciplines
Cellular Energy Metabolism
Autotrophic Energy Processes
Inheritance Patterns and Principles
Biomolecular Structure and Organization
Cell Cycle and Division Mechanics
Cellular Organization and Development
Biological Structural Organization
Show all topics
Chemical Sciences and Applications
Atomic Structure and Composition
Molecular Electron Structure Representation
Atomic Electron Behavior
Matter Properties and Water
Mole Concept and Calculations
Gas Laws and Behavior
Periodic Table Organization
Chemical Thermodynamics Fundamentals
Chemical Bond Types and Properties
Show all topics
European Renaissance and Enlightenment
European Cultural Movements 800-1920
American Revolution Era 1763-1797
American Civil War 1861-1865
Global Imperial Systems
Mongol and Chinese Dynasties
U.S. Presidents and World Leaders
Historical Sources and Documentation
World Wars Era and Impact
World Religious Systems
Show all topics
Classic and Contemporary Novels
Literary Character Analysis
Rhetorical Theory and Practice
Classic Literary Narratives
Reading Analysis and Interpretation
Narrative Structure and Techniques
English Language Components
Influential English-Language Authors
Basic Sentence Structure
Narrative Voice and Perspective
Show all topics
42
•
Updated Feb 19, 2026
•
Savannah Gurley
@savannahgurley_qvfi
The water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles are natural processes... Show more





Ever wonder where rain comes from? The water cycle is a continuous process driven by the sun that moves water through the Earth and atmosphere. Water never actually leaves Earth—it just changes form and location!
When the sun heats water in oceans, lakes, and ponds, it transforms into a gas through evaporation. Plants also release water vapor through a process called transpiration. This water vapor rises, cools, and forms clouds through condensation.
Eventually, water returns to Earth as precipitation (rain, snow, or hail). Some water is absorbed into the ground becoming groundwater, while other water flows across land as runoff into streams, rivers, and eventually back to the oceans.
Did you know? The water you drink today might have once been part of a dinosaur's body millions of years ago!

The water cycle follows a simple pattern: the sun causes evaporation and transpiration, increasing water vapor in the air. This warming triggers more evaporation and transpiration, creating a continuous cycle that keeps water moving through our environment.
The phosphorous cycle involves the movement of phosphorous between soil, water, and living organisms. Unlike other elements, phosphorous cannot be found in air—it's always in soil, rocks, or water. Plants absorb dissolved phosphorous through their roots.
Phosphorous is vital for life as a key component of cell membranes and molecules essential to all living things. However, too much phosphorous in water bodies causes eutrophication, leading to harmful algae overgrowth. This typically happens when rain and wind erode phosphorous-rich rocks.
Think about it: Phosphorous is in your DNA and the bones in your body—it's literally part of who you are!

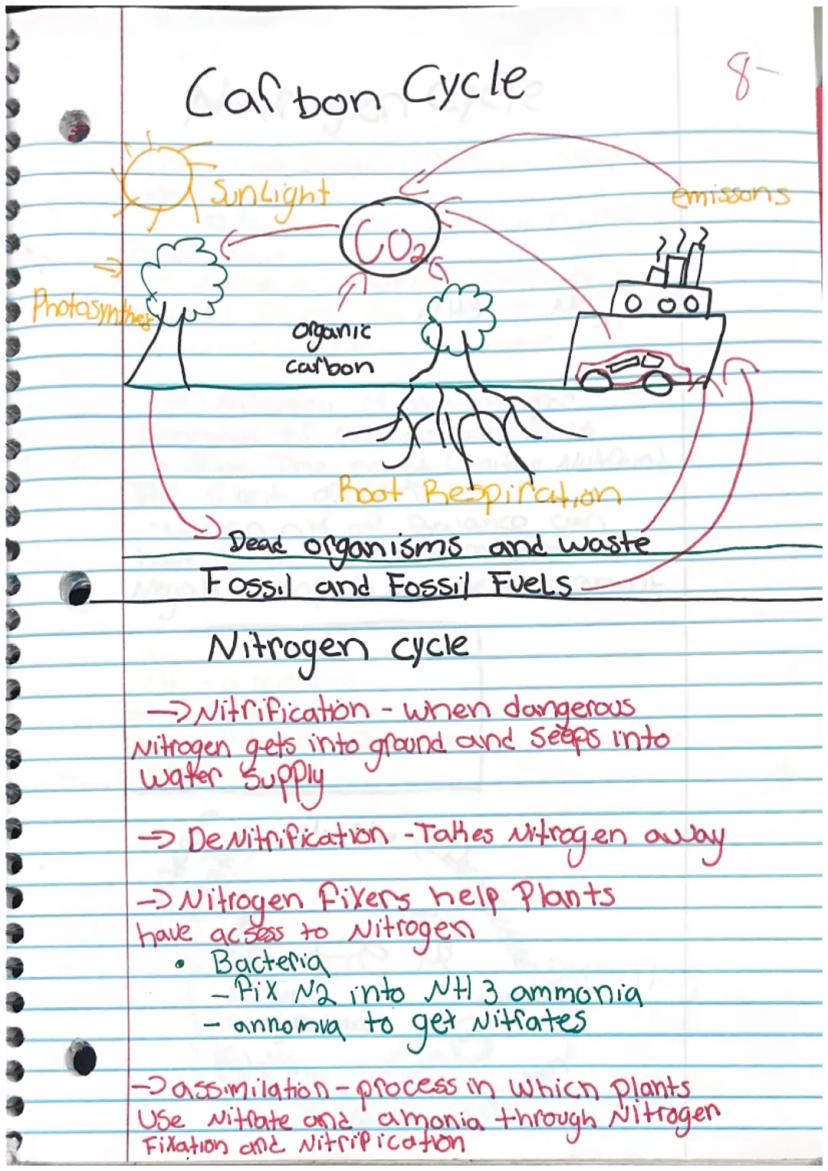
Carbon is everywhere—it makes up all living things including fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. The carbon cycle describes how carbon moves between living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and Earth.
Plants capture carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, combining CO₂ and water with sunlight energy to produce glucose and oxygen . The glucose stores energy for the plant, while oxygen is released into the air. Chlorophyll in plant cells helps capture the necessary sunlight.
When plants and animals die, they become detritus (waste and remains). As these materials decompose, carbon returns to the soil or atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that absorbs heat, affecting Earth's temperature.
Cool fact: Every time you exhale, you're releasing carbon dioxide that becomes part of the carbon cycle!
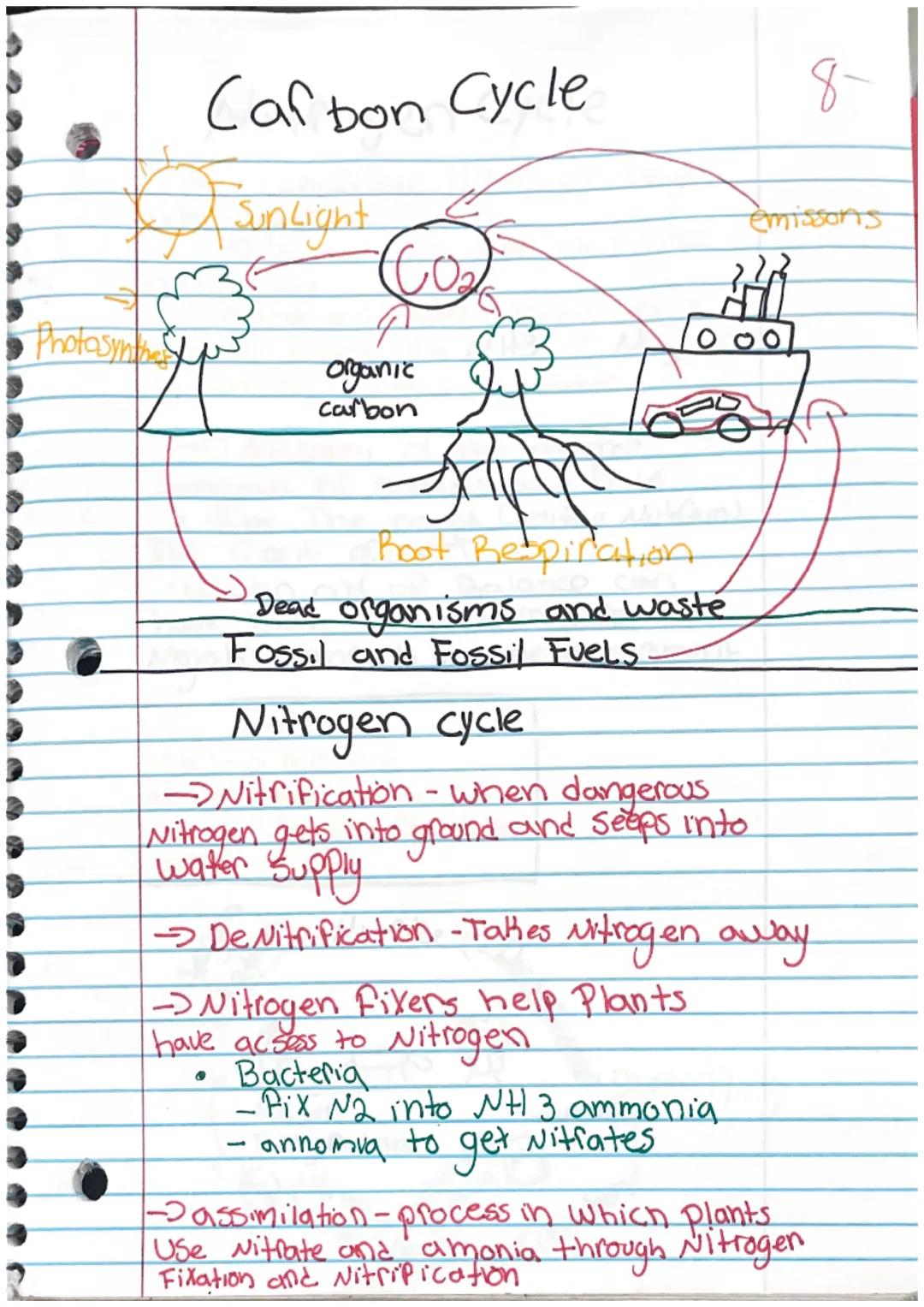
The carbon cycle continues as carbon moves through the environment. Carbon dioxide is absorbed during photosynthesis, transformed into organic carbon in plants, and eventually released back into the atmosphere through respiration, decomposition, and human activities like burning fossil fuels.
The nitrogen cycle is equally important, though more complex. Although nitrogen makes up 79% of our atmosphere, most organisms can't use it directly. Nitrogen must be converted to forms like ammonia (NH₃) or nitrates (NO₃) to be useful.
Nitrogen fixers (special bacteria) convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia through nitrogen fixation. Nitrification occurs when this ammonia is converted to nitrates. Plants absorb these compounds through assimilation. Denitrification returns nitrogen to the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
Warning: When nitrogen gets into groundwater through nitrification, it can create dangerous drinking water conditions.

Nitrogen may be abundant (making up 79% of our atmosphere), but it's tricky—most organisms can't use nitrogen in its atmospheric form (N₂). It only becomes useful when converted to reactive forms like ammonia (NH₃) or nitrates (NO₃).
Nitrogen is crucial as the major component of proteins and DNA. It's often the most limiting nutrient for plant growth, meaning plants can't grow without enough usable nitrogen. When nitrogen cycles get out of balance, they can harm the environment.
The full nitrogen cycle involves multiple steps: atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by nitrogen-fixing bacteria (nitrogen fixation), then to ammonium (NH₄⁺), then to nitrites (NO₂) and nitrates (NO₃) by nitrifying bacteria. Plants use these compounds, animals eat the plants, and when organisms die, decomposers release nitrogen back to the soil. Some bacteria convert nitrates back to atmospheric nitrogen (denitrification).
Mind-blowing fact: The nitrogen in your body has been cycled countless times through other organisms, perhaps even through dinosaurs millions of years ago!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
Savannah Gurley
@savannahgurley_qvfi
The water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles are natural processes that keep Earth's essential elements moving through living organisms and the environment. These cycles are powered by the sun and are critical for all life on Earth. Understanding how these... Show more

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Ever wonder where rain comes from? The water cycle is a continuous process driven by the sun that moves water through the Earth and atmosphere. Water never actually leaves Earth—it just changes form and location!
When the sun heats water in oceans, lakes, and ponds, it transforms into a gas through evaporation. Plants also release water vapor through a process called transpiration. This water vapor rises, cools, and forms clouds through condensation.
Eventually, water returns to Earth as precipitation (rain, snow, or hail). Some water is absorbed into the ground becoming groundwater, while other water flows across land as runoff into streams, rivers, and eventually back to the oceans.
Did you know? The water you drink today might have once been part of a dinosaur's body millions of years ago!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The water cycle follows a simple pattern: the sun causes evaporation and transpiration, increasing water vapor in the air. This warming triggers more evaporation and transpiration, creating a continuous cycle that keeps water moving through our environment.
The phosphorous cycle involves the movement of phosphorous between soil, water, and living organisms. Unlike other elements, phosphorous cannot be found in air—it's always in soil, rocks, or water. Plants absorb dissolved phosphorous through their roots.
Phosphorous is vital for life as a key component of cell membranes and molecules essential to all living things. However, too much phosphorous in water bodies causes eutrophication, leading to harmful algae overgrowth. This typically happens when rain and wind erode phosphorous-rich rocks.
Think about it: Phosphorous is in your DNA and the bones in your body—it's literally part of who you are!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Carbon is everywhere—it makes up all living things including fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. The carbon cycle describes how carbon moves between living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and Earth.
Plants capture carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, combining CO₂ and water with sunlight energy to produce glucose and oxygen . The glucose stores energy for the plant, while oxygen is released into the air. Chlorophyll in plant cells helps capture the necessary sunlight.
When plants and animals die, they become detritus (waste and remains). As these materials decompose, carbon returns to the soil or atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that absorbs heat, affecting Earth's temperature.
Cool fact: Every time you exhale, you're releasing carbon dioxide that becomes part of the carbon cycle!

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
The carbon cycle continues as carbon moves through the environment. Carbon dioxide is absorbed during photosynthesis, transformed into organic carbon in plants, and eventually released back into the atmosphere through respiration, decomposition, and human activities like burning fossil fuels.
The nitrogen cycle is equally important, though more complex. Although nitrogen makes up 79% of our atmosphere, most organisms can't use it directly. Nitrogen must be converted to forms like ammonia (NH₃) or nitrates (NO₃) to be useful.
Nitrogen fixers (special bacteria) convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia through nitrogen fixation. Nitrification occurs when this ammonia is converted to nitrates. Plants absorb these compounds through assimilation. Denitrification returns nitrogen to the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
Warning: When nitrogen gets into groundwater through nitrification, it can create dangerous drinking water conditions.

Access to all documents
Improve your grades
Join milions of students
Nitrogen may be abundant (making up 79% of our atmosphere), but it's tricky—most organisms can't use nitrogen in its atmospheric form (N₂). It only becomes useful when converted to reactive forms like ammonia (NH₃) or nitrates (NO₃).
Nitrogen is crucial as the major component of proteins and DNA. It's often the most limiting nutrient for plant growth, meaning plants can't grow without enough usable nitrogen. When nitrogen cycles get out of balance, they can harm the environment.
The full nitrogen cycle involves multiple steps: atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by nitrogen-fixing bacteria (nitrogen fixation), then to ammonium (NH₄⁺), then to nitrites (NO₂) and nitrates (NO₃) by nitrifying bacteria. Plants use these compounds, animals eat the plants, and when organisms die, decomposers release nitrogen back to the soil. Some bacteria convert nitrates back to atmospheric nitrogen (denitrification).
Mind-blowing fact: The nitrogen in your body has been cycled countless times through other organisms, perhaps even through dinosaurs millions of years ago!
Our AI companion is specifically built for the needs of students. Based on the millions of content pieces we have on the platform we can provide truly meaningful and relevant answers to students. But its not only about answers, the companion is even more about guiding students through their daily learning challenges, with personalised study plans, quizzes or content pieces in the chat and 100% personalisation based on the students skills and developments.
You can download the app in the Google Play Store and in the Apple App Store.
That's right! Enjoy free access to study content, connect with fellow students, and get instant help – all at your fingertips.
1
Smart Tools NEW
Transform this note into: ✓ 50+ Practice Questions ✓ Interactive Flashcards ✓ Full Practice Test ✓ Essay Outlines
For Unit 3.5 of AP Environmental Science, discusses population growth and resource availability.
Notes of the high weighted units of APES. Watch Jordan Smedes' videos on youtube and use these notes to review for the AP test.
Learn about the differences between magma and lava, where volcanoes occur, types of volcanoes, and the reasons behind volcanic eruptions.
For Unit 3.3 of AP Environmental Science, discusses survivorship curves.
Very interesting and full of info presentation about human impact on our planet and the biodiversity among the animal species
For Unit 3.4 of AP Environmental Science, discusses carrying capacity.
App Store
Google Play
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user
The app is very easy to use and well designed. I have found everything I was looking for so far and have been able to learn a lot from the presentations! I will definitely use the app for a class assignment! And of course it also helps a lot as an inspiration.
Stefan S
iOS user
This app is really great. There are so many study notes and help [...]. My problem subject is French, for example, and the app has so many options for help. Thanks to this app, I have improved my French. I would recommend it to anyone.
Samantha Klich
Android user
Wow, I am really amazed. I just tried the app because I've seen it advertised many times and was absolutely stunned. This app is THE HELP you want for school and above all, it offers so many things, such as workouts and fact sheets, which have been VERY helpful to me personally.
Anna
iOS user
I think it’s very much worth it and you’ll end up using it a lot once you get the hang of it and even after looking at others notes you can still ask your Artificial intelligence buddy the question and ask to simplify it if you still don’t get it!!! In the end I think it’s worth it 😊👍 ⚠️Also DID I MENTION ITS FREEE YOU DON’T HAVE TO PAY FOR ANYTHING AND STILL GET YOUR GRADES IN PERFECTLY❗️❗️⚠️
Thomas R
iOS user
Knowunity is the BEST app I’ve used in a minute. This is not an ai review or anything this is genuinely coming from a 7th grade student (I know 2011 im young) but dude this app is a 10/10 i have maintained a 3.8 gpa and have plenty of time for gaming. I love it and my mom is just happy I got good grades
Brad T
Android user
Not only did it help me find the answer but it also showed me alternative ways to solve it. I was horrible in math and science but now I have an a in both subjects. Thanks for the help🤍🤍
David K
iOS user
The app's just great! All I have to do is enter the topic in the search bar and I get the response real fast. I don't have to watch 10 YouTube videos to understand something, so I'm saving my time. Highly recommended!
Sudenaz Ocak
Android user
In school I was really bad at maths but thanks to the app, I am doing better now. I am so grateful that you made the app.
Greenlight Bonnie
Android user
I found this app a couple years ago and it has only gotten better since then. I really love it because it can help with written questions and photo questions. Also, it can find study guides that other people have made as well as flashcard sets and practice tests. The free version is also amazing for students who might not be able to afford it. Would 100% recommend
Aubrey
iOS user
Best app if you're in Highschool or Junior high. I have been using this app for 2 school years and it's the best, it's good if you don't have anyone to help you with school work.😋🩷🎀
Marco B
iOS user
THE QUIZES AND FLASHCARDS ARE SO USEFUL AND I LOVE Knowunity AI. IT ALSO IS LITREALLY LIKE CHATGPT BUT SMARTER!! HELPED ME WITH MY MASCARA PROBLEMS TOO!! AS WELL AS MY REAL SUBJECTS ! DUHHH 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Elisha
iOS user
This app is phenomenal down to the correct info and the various topics you can study! I greatly recommend it for people who struggle with procrastination and those who need homework help. It has been perfectly accurate for world 1 history as far as I’ve seen! Geometry too!
Paul T
iOS user